 | |
| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Perseus |
| A | |
| Right ascension | 03h 44m 19.13377s[1] |
| Declination | 32° 17′ 17.6874″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 3.83[2] |
| B | |
| Right ascension | 03h 44m 19.17122s[3] |
| Declination | 32° 17′ 18.5103″[3] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 6.68[4] |
| Characteristics | |
| A | |
| Spectral type | B1III / B2V[5] |
| U−B color index | -0.75[2] |
| B−V color index | +0.05[2] |
| Variable type | ellipsoidal[6] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | +12.20[7] km/s |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −4.4[5] |
| A | |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: +6.091[1] mas/yr Dec.: −9.732[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 3.0224 ± 0.3827 mas[1] |
| Distance | approx. 1,100 ly (approx. 330 pc) |
| Orbit[5] | |
| Primary | Aa |
| Companion | Ab |
| Period (P) | 4.4191447 days |
| Semi-major axis (a) | 33 R☉ |
| Eccentricity (e) | 0.0 |
| Inclination (i) | 39±15° |
| Semi-amplitude (K1) (primary) | 111.8 km/s |
| Semi-amplitude (K2) (secondary) | 155.0 km/s |
| Details | |
| Aa | |
| Mass | 14[8] M☉ |
| Radius | 9.6[5] R☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 3.4[8] cgs |
| Temperature | 22,700[8] K |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 70±5[5] km/s |
| Ab | |
| Mass | 10[8] M☉ |
| Radius | 8.9[5] R☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 4.0[8] cgs |
| Temperature | 21,000[8] K |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 65±15[5] km/s |
| Age | 15[5] Myr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
Omicron Persei (ο Persei, abbreviated Omicron Per, ο Per) is a triple star system in the constellation of Perseus. From parallax measurements taken during the Hipparcos mission it is approximately 1,100 light-years (330 parsecs) from the Sun.
The system consists of a spectroscopic binary pair designated Omicron Persei A and a third companion Omicron Persei B.[9] A's two components are themselves designated Omicron Persei Aa (officially named Atik /ˈeɪtɪk/, the traditional name of the system)[10][11] and Ab.
Etymology

ο Persei (Latinised to Omicron Persei) is the system's Bayer designation. The designations of the two constituents as Omicron Persei A and B, and those of A's components - Omicron Persei Aa and Ab - derive from the convention used by the Washington Multiplicity Catalog (WMC) for multiple star systems, and adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU).[12]
It bore the traditional name Atik (also Ati, Al Atik), Arabic for "the shoulder". Some sources attribute the name Atik to the nearby, brighter star Zeta Persei.[13][14] In 2016, the International Astronomical Union organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN)[15] to catalogue and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN decided to attribute proper names to individual stars rather than entire multiple systems.[16] It approved the name Atik for the component Omicron Persei A on 12 September 2016 and it is now so included in the List of IAU-approved Star Names.[11]
In Chinese, 卷舌 (Juǎn Shé), meaning Rolled Tongue, refers to an asterism consisting of Omicron Persei, Nu Persei, Epsilon Persei, Xi Persei, Zeta Persei and 40 Persei.[17] Consequently, the Chinese name for Omicron Persei itself is 卷舌五 (Juǎn Shé wu), "the Fifth Star of Rolled Tongue".[18]
Properties
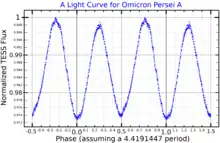
Omicron Persei A is a spectroscopic binary consisting of a spectral type B1 giant and a type B2 dwarf orbiting each other every 4.4 days. The orbit is near-circular although its inclination is not precisely known. The two stars are separated by approximately 33 R☉, the exact value depending on the inclination. The primary is approximately one magnitude brighter than the secondary at visual wavelengths.[5] The binary pair forms a rotating ellipsoidal variable star, which varies in brightness from visual magnitude 3.79 to 3.88 during the orbital period.[20]
Omicron Persei lies just north of the open cluster IC 348, but is not catalogued as a member. Both IC 348 and Omicron Persei belong to the Perseus OB2 association.[21]
Culture
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Brown, A. G. A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (2021). "Gaia Early Data Release 3: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 649: A1. arXiv:2012.01533. Bibcode:2021A&A...649A...1G. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202039657. S2CID 227254300. (Erratum: doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202039657e). Gaia EDR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- 1 2 3 Ducati, J. R. (2002). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: Catalogue of Stellar Photometry in Johnson's 11-color system". CDS/ADC Collection of Electronic Catalogues. 2237. Bibcode:2002yCat.2237....0D.
- 1 2 Brown, A. G. A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (2021). "Gaia Early Data Release 3: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 649: A1. arXiv:2012.01533. Bibcode:2021A&A...649A...1G. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202039657. S2CID 227254300. (Erratum: doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202039657e). Gaia EDR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ Fabricius, C.; Høg, E.; Makarov, V. V.; Mason, B. D.; Wycoff, G. L.; Urban, S. E. (2002). "The Tycho double star catalogue". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 384: 180–189. Bibcode:2002A&A...384..180F. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20011822.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Stickland, D. J.; Lloyd, C. (1998). "Spectroscopic binary orbits from ultraviolet radial velocities. Paper 28: Omicron Persei". The Observatory. 118: 138. Bibcode:1998Obs...118..138S.
- ↑ Samus, N. N.; Durlevich, O. V.; et al. (2009). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: General Catalogue of Variable Stars (Samus+ 2007-2013)". VizieR On-line Data Catalog: B/GCVS. Originally Published in: 2009yCat....102025S. 1. Bibcode:2009yCat....102025S.
- ↑ Pourbaix, D.; Tokovinin, A. A.; Batten, A. H.; Fekel, F. C.; Hartkopf, W. I.; Levato, H.; Morrell, N. I.; Torres, G.; Udry, S. (2004). "SB9: The ninth catalogue of spectroscopic binary orbits". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 424 (2): 727–732. arXiv:astro-ph/0406573. Bibcode:2004A&A...424..727P. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20041213. S2CID 119387088.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Lyubimkov, L. S.; Rachkovskaya, T. M.; Rostopchin, S. I.; Tarasov, A. E. (1997). "The binary system o per: Orbital elements, component parameters, and helium abundance". Astronomy Reports. 41 (5): 630. Bibcode:1997ARep...41..630L.
- ↑ "Displaying next number in catalog HIP => 17448". Multiple Star Catalog. Retrieved 2018-02-19.
- ↑ Kunitzsch, Paul; Smart, Tim (2006). A Dictionary of Modern star Names: A Short Guide to 254 Star Names and Their Derivations (2nd rev. ed.). Cambridge, Massachusetts: Sky Pub. ISBN 978-1-931559-44-7.
- 1 2 "Naming Stars". IAU.org. Retrieved 16 December 2017.
- ↑ Hessman, F. V.; Dhillon, V. S.; Winget, D. E.; Schreiber, M. R.; Horne, K.; Marsh, T. R.; Guenther, E.; Schwope, A.; Heber, U. (2010). "On the naming convention used for multiple star systems and extrasolar planets". arXiv:1012.0707 [astro-ph.SR].
- ↑ Mullaney, James, and Tirion, Wil (2009). The Cambridge Double Star Atlas, Chart 7. University Press, Cambridge. ISBN 978-0-521-49343-7.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Your Sky Object Catalogue: Named Stars
- ↑ IAU Working Group on Star Names (WGSN), International Astronomical Union, retrieved 22 May 2016.
- ↑ "WG Triennial Report (2015-2018) - Star Names" (PDF). p. 5. Retrieved 2018-07-14.
- ↑ (in Chinese) 中國星座神話, written by 陳久金. Published by 台灣書房出版有限公司, 2005, ISBN 978-986-7332-25-7.
- ↑ (in Chinese) 香港太空館 - 研究資源 - 亮星中英對照表 Archived 2008-10-25 at the Wayback Machine, Hong Kong Space Museum. Accessed on line November 23, 2010.
- ↑ "MAST: Barbara A. Mikulski Archive for Space Telescopes". Space Telescope Science Institute. Retrieved 8 December 2021.
- ↑ "omi Per". The International Variable Star Index. AAVSO. Retrieved 18 December 2022.
- ↑ Stelzer, B.; Preibisch, T.; Alexander, F.; Mucciarelli, P.; Flaccomio, E.; Micela, G.; Sciortino, S. (2012). "X-ray view of IC 348 in the light of an updated cluster census". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 537: A135. arXiv:1111.4420. Bibcode:2012A&A...537A.135S. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201118118.
- ↑ "Omicron Persei 8 meaning explored as hilarious Futurama memes spread". The Focus. 30 November 2021. Retrieved 9 October 2022.
- ↑ "How Futurama is related to the new Omicron COVID variant". MARCA. 28 November 2021. Retrieved 9 October 2022.