| Dark nebula | |
|---|---|
.jpg.webp) | |
| Observation data: J2000.0 epoch | |
| Right ascension | 16h 28m 06s[3] |
| Declination | –24° 32.5′[3] |
| Distance | 460 ly (140 pc)[4] ly |
| Apparent dimensions (V) | 4.5° × 6.5°[5] |
| Constellation | Ophiuchus |
| Designations | Ophiuchus molecular cloud, Integral 691, XSS J16271-2423 |
The Rho Ophiuchi cloud complex is a complex of interstellar clouds with different nebulae, particularly dark nebulae which is centered 1° south of the star ρ Ophiuchi, which it among others extends to, of the constellation Ophiuchus. At an estimated distance of about 140 parsecs, or 460 light years, it is one of the closest star-forming regions to the Solar System.[1][6][7]
Cloud complex
This cloud covers an angular area of 4.5° × 6.5° on the celestial sphere. It consists of two major regions of dense gas and dust. The first contains a star-forming cloud (L1688) and two filaments (L1709 and L1755), while the second has a star-forming region (L1689) and a filament (L1712–L1729). These filaments extend up to 10–17.5 parsecs in length and can be as narrow as 0.24 parsecs in width. The large extensions of the complex are also called Dark River clouds[8] (or Rho Ophiuchi Streamers) and are identified as Barnard 44 and 45. Some of the structures within the complex appear to be the result of a shock front passing through the clouds from the direction of the neighboring Sco OB2 association.[5]
Temperatures of the clouds range from 13–22 K, and there is a total of about 3,000 times the mass of the Sun in the material. Over half of the mass of the complex is concentrated around the L1688 cloud, and this is the most active star-forming region.[5] There are embedded infrared sources within the complex.[9] A total of 425 infrared sources have been detected near the L1688 cloud. These are presumed to be young stellar objects, including 16 classified as protostars, 123 T Tauri stars with dense circumstellar disks, and 77 weaker T Tauri stars with thinner disks.[4] The last 2 categories of stars have estimated ages ranging from 100,000 to a million years.[10]
The first brown dwarf to be identified in a star-forming region was Rho Oph J162349.8-242601, located in the Rho Ophiuchi cloud.[11] One of the older objects at the edge of the primary star-forming region was found to be a circumstellar disk seen nearly edge-on. It spans a diameter of 300 AU and contains at least twice the mass of Jupiter. The million-year-old star at the center of the disk has a temperature of 3,000 K and is emitting 0.4 times the luminosity of the Sun.[12]
The 2023 NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope image—released on the telescope's first anniversary—shows young stars, roughly the size of the Sun, at the center of circumstellar discs. These represent planetary systems of the future being formed in a "stellar nursery".[1][7] Since the field of view of the photo is very small, at 6.4 arc-minutes, it displays just a tiny region of what appears in most other photographs of the Rho Ophiuchi cloud complex. [13]
Gallery
 Rho Ophiuchi Region, with the main dark nebula Lynds 1688 (and further L1689) to the left, ρ Ophiuchi at the center of the large blue area (IC 4604), Antares in the large yellow area and Sigma Scorpii in the redish Sh2-9 area, with Messier 4 inbetween the latter two stars. North is up. July 2, 2019 photo by Adam Block.
Rho Ophiuchi Region, with the main dark nebula Lynds 1688 (and further L1689) to the left, ρ Ophiuchi at the center of the large blue area (IC 4604), Antares in the large yellow area and Sigma Scorpii in the redish Sh2-9 area, with Messier 4 inbetween the latter two stars. North is up. July 2, 2019 photo by Adam Block. The Rho Ophiuchi cloud complex with its main dark nebula Lynds 1688, speckled with its pinkish young stellar objects, just left to HD 147889 surrounded by IC 4603 as the bright area at the center. The red area called Sh2-9 has Sigma Scorpii at its center, and Antares is just outside the picture at the bottom.
The Rho Ophiuchi cloud complex with its main dark nebula Lynds 1688, speckled with its pinkish young stellar objects, just left to HD 147889 surrounded by IC 4603 as the bright area at the center. The red area called Sh2-9 has Sigma Scorpii at its center, and Antares is just outside the picture at the bottom. The large multicoloured Rho Ophiuchi cloud complex with the Dark River clouds (or Rho Ophiuchi Streamers) as Barnard 44 and 45 on the right, seemingly radiating towards the distant Pipe Nebula and the Galactic Center, extending from the core L1688 as well as L1689 dark nebulae.[8] In the lower part of this wide field image the distinct blue eyed (Nu Scorpii) Blue Horsehead Nebula can be seen. The blue area at the back of the head is IC 4601. The cloud in the top left corner is LBN 1093 and Sh2-1 with the bright star being Pi Scorpii and the yellowish cloud in the middle on the left being Sh2-7 with Dschubba at its center.
The large multicoloured Rho Ophiuchi cloud complex with the Dark River clouds (or Rho Ophiuchi Streamers) as Barnard 44 and 45 on the right, seemingly radiating towards the distant Pipe Nebula and the Galactic Center, extending from the core L1688 as well as L1689 dark nebulae.[8] In the lower part of this wide field image the distinct blue eyed (Nu Scorpii) Blue Horsehead Nebula can be seen. The blue area at the back of the head is IC 4601. The cloud in the top left corner is LBN 1093 and Sh2-1 with the bright star being Pi Scorpii and the yellowish cloud in the middle on the left being Sh2-7 with Dschubba at its center. A starchart of the Galactic Center area, with the Rho Ophiuchi cloud complex marked as large green area in the middle of the right half of the chart.
A starchart of the Galactic Center area, with the Rho Ophiuchi cloud complex marked as large green area in the middle of the right half of the chart..png.webp) Map of the molecular clouds within 1000 parsecs, the Sun is at the center.
Map of the molecular clouds within 1000 parsecs, the Sun is at the center.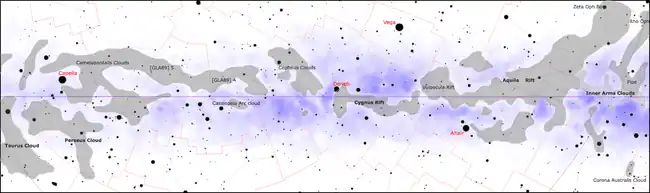 Main dark nebulae of the Solar apex half of the galactic plane, with the Rho Opiuchi cloud complex at the right edge
Main dark nebulae of the Solar apex half of the galactic plane, with the Rho Opiuchi cloud complex at the right edge The Milky Way as seen by Gaia, with prominent dark features labeled in white, as well as prominent star clouds labeled in black. Rho Ophiuchi is on the left top center.
The Milky Way as seen by Gaia, with prominent dark features labeled in white, as well as prominent star clouds labeled in black. Rho Ophiuchi is on the left top center.
See also
References
- 1 2 3 K. Pontoppidan; A. Pagan (July 12, 2023). "Rho Ophiuchi cloud complex". NASA/ESA/CSA STScI. Retrieved July 12, 2023.
- ↑ "Rho Ophiuchi (NIRCam Image)". Webb Space Telescope. Space Telescope Science Institute. 12 July 2023. Retrieved 14 July 2023.
- 1 2 "RHO OPH REGION -- Molecular Cloud". SIMBAD. Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 2009-10-24.
- 1 2 Bontemps, S.; et al. (June 2001). "ISOCAM observations of the rho Ophiuchi cloud: Luminosity and mass functions of the pre-main sequence embedded cluster". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 372: 173–194. arXiv:astro-ph/0103373. Bibcode:2001A&A...372..173B. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20010474. S2CID 17270972.
- 1 2 3 Loren, Robert B. (March 15, 1989). "The cobwebs of Ophiuchus. I - Strands of (C-13)O - The mass distribution". Astrophysical Journal, Part 1. 338: 902–924. Bibcode:1989ApJ...338..902L. doi:10.1086/167244.
- ↑ "Young Stars in Their Baby Blanket of Dust". Spitzer Multimedia Features. NASA. 2008-11-02. Retrieved 2009-10-24.
- 1 2 Miller, Katrina (12 July 2023). "A Year of Cosmic Wonder With the James Webb Space Telescope - With a new image, NASA commemorates the first anniversary of doing science with the most powerful observatory ever sent to space". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 12 July 2023. Retrieved 13 July 2023.
- 1 2 "APOD: 2010 July 19 - Dark River Wide Field". Astronomy Picture of the Day. 2010-06-06. Retrieved 2021-08-06.
- ↑ Wilking, B. A.; Lada, C. J. (November 15, 1983). "The discovery of new embedded sources in the centrally condensed core of the Rho Ophiuchi dark cloud - The formation of a bound cluster". Astrophysical Journal, Part 1. 274: 698–716. Bibcode:1983ApJ...274..698W. doi:10.1086/161482.
- ↑ Luhman, K. L.; Rieke, G. H. (November 1999). "Low-Mass Star Formation and the Initial Mass Function in the ρ Ophiuchi Cloud Core". The Astrophysical Journal. 525 (1): 440–465. arXiv:astro-ph/9905286. Bibcode:1999ApJ...525..440L. doi:10.1086/307891. S2CID 119393698.
- ↑ Martín, Eduardo L. (2001). "Spectroscopy of Young Brown Dwarfs and Isolated Planetary Mass Objects". In Jones, Hugh R. A.; Steele, Iain A. (eds.). Ultracool Dwarfs: New Spectral Types L and T. Springer. pp. 153–167. ISBN 3-540-42353-2.
- ↑ Grosso, Nicolas (May 7, 2002). "Infrared Images of an Infant Solar System". Press Releases. European Southern Observatory. Retrieved 2009-10-25.
- ↑ "Rho Ophiuchi (NIRCam Image)". STScI. 2023-07-12. Retrieved 2023-11-05.
External links
- Astronomy Picture of the Day
- The Colorful Clouds of Rho Ophiuchi 2007 September 3
- Young Stars in the Rho Ophiuchi Cloud 2009 November 13
- Rho Ophiucus Wide Field 2010 May 24
- Colorful Clouds Near Rho Ophiuchi 2012 August 28