| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Cetus |
| HD 11171 | |
| Right ascension | 01h 49m 35.10316s[2] |
| Declination | −10° 41′ 11.0674″[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 4.66[3] |
| HD 11131 | |
| Right ascension | 01h 49m 23.35579s[2] |
| Declination | −10° 42′ 12.8594″[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 6.75[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| HD 11171 | |
| Spectral type | F3 III[4] or F0 V[5] |
| U−B color index | +0.04[3] |
| B−V color index | +0.33[3] |
| HD 11131 | |
| Spectral type | G3 V[5] |
| U−B color index | +0.12[3] |
| B−V color index | +0.61[3] |
| Variable type | BY Dra[6] |
| Astrometry | |
| HD 11171 | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −1.8[4] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −148.11[2] mas/yr Dec.: −93.43[2] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 43.13 ± 0.26 mas[2] |
| Distance | 75.6 ± 0.5 ly (23.2 ± 0.1 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | +2.83±0.01[7] |
| HD 11131 | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −3.89±0.12[8] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −124.54[2] mas/yr Dec.: −105.82[2] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 44.32 ± 3.02 mas[2] |
| Distance | 74 ± 5 ly (23 ± 2 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | 4.98[9] |
| Details | |
| HD 11171 | |
| Mass | 1.36[4] M☉ |
| Luminosity | 5.6[4] L☉ |
| Temperature | 6,746±258[4] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | 0.14[7] dex |
| Age | 1.2[4] Gyr |
| HD 11131 | |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 4.53[10] cgs |
| Temperature | 5,804[10] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | −0.09[10] dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 3.34[11] km/s |
| Other designations | |
| χ Ceti A: 53 Cet, HD 11171, BD−11° 352, FK5 1051, HIP 8497, HR 531, SAO 148036.[12] | |
| χ Ceti B: EZ Cet, HD 11131, BD−11°351, HIP 8486, SAO 148033.[13] | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | χ Ceti |
| χ Ceti A | |
| χ Ceti B | |
Chi Ceti (χ Ceti), is the Bayer designation for a double star in the equatorial constellation of Cetus. They appear to be common proper motion companions, sharing a similar motion through space.[14] The brighter component, HD 11171, is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.66, while the fainter companion, HD 11131, is magnitude 6.75.[3] Both lie at roughly the same distance, with the brighter component lying at an estimated distance of 75.6 light years from the Sun based upon an annual parallax shift of 43.13 mass.[2]
The primary, component A, is an evolved K-type giant star with a stellar classification of F3 III.[4] However, Houk and Swift (1999) listed a classification of F0 V,[5] which would match an F-type main sequence star. It displays an infrared excess at a wavelength of 70 μm and thus is a candidate host of an orbiting debris disk.[15]
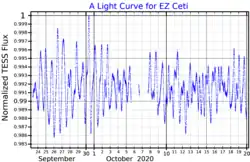
The common proper motion companion, component B, is a G-type main sequence star with a classification of G3 V.[5] It is a BY Draconis variable with a periodicity of 8.92 days and a variable star designation of EZ Cet.[6]
References
- ↑ "MAST: Barbara A. Mikulski Archive for Space Telescopes". Space Telescope Science Institute. Retrieved 8 December 2021.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 van Leeuwen, F. (2007), "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 474 (2): 653–664, arXiv:0708.1752, Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357, S2CID 18759600.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Mermilliod, J.-C. (1986), "Compilation of Eggen's UBV data, transformed to UBV (unpublished)", Catalogue of Eggen's UBV Data: 0, Bibcode:1986EgUBV........0M.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Luck, R. Earle (September 2015), "Abundances in the Local Region. I. G and K Giants", The Astronomical Journal, 150 (3): 23, arXiv:1507.01466, Bibcode:2015AJ....150...88L, doi:10.1088/0004-6256/150/3/88, S2CID 118505114, 88.
- 1 2 3 4 Houk, N.; Swift, C. (1999), "Michigan catalogue of two-dimensional spectral types for the HD Stars", Michigan Spectral Survey, 5: 0, Bibcode:1999MSS...C05....0H.
- 1 2 Kazarovets, E. V.; et al. (2006), "The 78th Name-List of Variable Stars", Information Bulletin on Variable Stars, 5721: 1, Bibcode:2006IBVS.5721....1K.
- 1 2 Holmberg, J.; et al. (July 2009), "The Geneva-Copenhagen survey of the solar neighbourhood. III. Improved distances, ages, and kinematics", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 501 (3): 941–947, arXiv:0811.3982, Bibcode:2009A&A...501..941H, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200811191, S2CID 118577511.
- ↑ de Bruijne, J. H. J.; Eilers, A.-C. (October 2012), "Radial velocities for the HIPPARCOS-Gaia Hundred-Thousand-Proper-Motion project", Astronomy & Astrophysics, 546: 14, arXiv:1208.3048, Bibcode:2012A&A...546A..61D, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201219219, S2CID 59451347, A61.
- ↑ Porto de Mello, G. F.; et al. (March 2014), "A photometric and spectroscopic survey of solar twin stars within 50 parsecs of the Sun; I. Atmospheric parameters and color similarity to the Sun", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 563: A52, arXiv:1312.7571, Bibcode:2014A&A...563A..52P, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201322277, S2CID 119111150.
- 1 2 3 Datson, Juliet; et al. (February 2015), "Spectroscopic study of solar twins and analogues", Astronomy & Astrophysics, 574: 12, arXiv:1412.8168, Bibcode:2015A&A...574A.124D, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201425000, S2CID 53708062, A124.
- ↑ Martínez-Arnáiz, R.; et al. (September 2010), "Chromospheric activity and rotation of FGK stars in the solar vicinity. An estimation of the radial velocity jitter", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 520: A79, arXiv:1002.4391, Bibcode:2010A&A...520A..79M, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200913725, S2CID 43455849.
- ↑ "chi Cet". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 2017-02-12.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link) - ↑ V* EZ Cet.
- ↑ Soderblom, David R.; Mayor, Michel (January 1993), "Stellar kinematic groups. I - The Ursa Major group", Astronomical Journal, 105 (1): 226–249, Bibcode:1993AJ....105..226S, doi:10.1086/116422.
- ↑ Koerner, D. W.; et al. (February 2010), "New Debris Disk Candidates Around 49 Nearby Stars" (PDF), The Astrophysical Journal Letters, 710 (1): L26–L29, Bibcode:2010ApJ...710L..26K, doi:10.1088/2041-8205/710/1/L26, S2CID 122844702.
External links
- Kaler, James B., "Chi Ceti, plus HD 11131", Stars, University of Illinois, retrieved 2017-02-13.
- http://www.alcyone.de/cgi-bin/search.pl?object=HR0531 Archived 2016-03-03 at the Wayback Machine
- http://server3.wikisky.org/starview?object_type=1&object_id=1287