 | |
| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
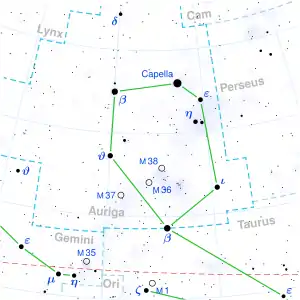
| Constellation | Auriga |
| Right ascension | 06h 24m 53.90155s[1] |
| Declination | +49° 17′ 16.4112″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 4.91[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | K5-M1Iab-Ib[3] |
| U−B color index | +2.29[2] |
| B−V color index | +1.97[2] |
| R−I color index | 1.07 |
| Variable type | LC[4] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | +4.7[5] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: –0.155[1] mas/yr Dec.: –2.131[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 0.4426 ± 0.1103 mas[1] |
| Distance | approx. 7,000 ly (approx. 2,300 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −5.53[6] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 14.4 ± 0.8[7] M☉ |
| Radius | 726[8] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 63,579[9] L☉ |
| Temperature | 3,750[10] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | +0.08[11] dex |
| Age | 12.3 ± 0.4[7] Myr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
Psi1 Aurigae (ψ1 Aur, ψ1 Aurigae) is a star in the northern constellation of Auriga. It is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.91.[2] Based upon a measured annual parallax shift of 0.44 mas,[1] it is approximately 7,500 light-years (2,300 parsecs) distant from the Earth. It is receding from the Sun with a radial velocity of +4.7 km/s.[5]
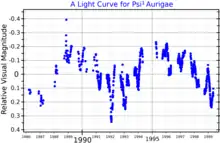
This is a massive supergiant star with a stellar classification of K5-M1Iab-Ib.[3] It is a slow irregular variable of the LC type, with its brightness varying in magnitude by 0.44.[4] The star is more than 14[7] times as massive as the Sun and is blazing with 63,579[9] times the Sun's luminosity. This energy is being radiated into outer space from its outer atmosphere at an effective temperature of 3,750 K,[10] giving it the orange-red hue of a cool M-type star.
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Vallenari, A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (2023). "Gaia Data Release 3. Summary of the content and survey properties". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 674: A1. arXiv:2208.00211. Bibcode:2023A&A...674A...1G. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202243940. S2CID 244398875. Gaia DR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- 1 2 3 4 Nicolet, B. (1978), "Photoelectric photometric Catalogue of homogeneous measurements in the UBV System", Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series, 34: 1–49, Bibcode:1978A&AS...34....1N.
- 1 2 Keenan, Philip C.; McNeil, Raymond C. (1989), "The Perkins Catalog of Revised MK Types for the Cooler Stars", The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, 71: 245, Bibcode:1989ApJS...71..245K, doi:10.1086/191373.
- 1 2 Adelman, Saul J. (2001), "Stars with the Largest Hipparcos Photometric Amplitudes", Baltic Astronomy, 10 (4): 589–593, Bibcode:2001BaltA..10..589A, doi:10.1515/astro-2001-0403, S2CID 116386247.
- 1 2 Wielen, R.; et al. (1999), "Sixth Catalogue of Fundamental Stars (FK6). Part I. Basic fundamental stars with direct solutions", Veroeffentlichungen des Astronomischen Rechen-Instituts Heidelberg, Astronomisches Rechen-Institut Heidelberg, 35 (35): 1, Bibcode:1999VeARI..35....1W.
- ↑ Schiavon, Ricardo P. (July 2007), "Population Synthesis in the Blue. IV. Accurate Model Predictions for Lick Indices and UBV Colors in Single Stellar Populations", The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, 171 (1): 146–205, arXiv:astro-ph/0611464, Bibcode:2007ApJS..171..146S, doi:10.1086/511753, S2CID 13946698.
- 1 2 3 Tetzlaff, N.; Neuhäuser, R.; Hohle, M. M. (January 2011), "A catalogue of young runaway Hipparcos stars within 3 kpc from the Sun", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 410 (1): 190–200, arXiv:1007.4883, Bibcode:2011MNRAS.410..190T, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.17434.x, S2CID 118629873.
- ↑ Stassun K.G.; et al. (October 2019), "The revised TESS Input Catalog and Candidate Target List", The Astronomical Journal, 158 (4): 138, arXiv:1905.10694, Bibcode:2019AJ....158..138S, doi:10.3847/1538-3881/ab3467, S2CID 166227927.
- 1 2 Hohle, M. M.; Neuhäuser, R.; Schutz, B. F. (April 2010), "Masses and luminosities of O- and B-type stars and red supergiants", Astronomische Nachrichten, 331 (4): 349, arXiv:1003.2335, Bibcode:2010AN....331..349H, doi:10.1002/asna.200911355, S2CID 111387483.
- 1 2 Levesque, Emily M.; et al. (August 2005), "The Effective Temperature Scale of Galactic Red Supergiants: Cool, but Not As Cool As We Thought", The Astrophysical Journal, 628 (2): 973–985, arXiv:astro-ph/0504337, Bibcode:2005ApJ...628..973L, doi:10.1086/430901, S2CID 15109583.
- ↑ Bakos, Gustav A. (October 1971), "Abundances of Heavy Elements in Late-Type Stars", Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society of Canada, 65: 222, Bibcode:1971JRASC..65..222B.
- ↑ "psi01 Aur", SIMBAD, Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg, retrieved 2012-08-23.
- ↑ Percy, John R.; Wilson, Joseph B.; Henry, Gregory W. (August 2001), "Long-Term VRI Photometry of Small-Amplitude Red Variables. I. Light Curves and Periods", Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific, 113 (786): 983–996, Bibcode:2001PASP..113..983P, doi:10.1086/322153, S2CID 14609175.