 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
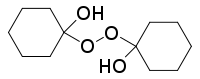
| IUPAC name
1-(1-hydroxycyclohexyl)peroxycyclohexan-1-ol | |
| Other names
Bis(1-hydroxycyclohexyl) peroxide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 3106 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H22O4 | |
| Molar mass | 230.304 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Melting point | 66–68 °C (151–154 °F; 339–341 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
   | |
| Danger | |
| H240, H302, H314 | |
| P210, P220, P234, P260, P264, P270, P280, P301+P312, P301+P330+P331, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P321, P330, P363, P370+P378, P370+P380+P375, P403+P235, P405, P411, P420, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
1,1′-Dihydroxydicyclohexyl peroxide is an organic compound with the formula (C6H10OH)2O2. It is one of the peroxides derived from the reaction of cyclohexanone and hydrogen peroxide. Upon treatment with acid and additional peroxide, it converts to the cyclic diperoxide, bis(cyclohexylidene peroxide), (C6H10)2(O2)2.[1][2]
1,1′-Dihydroxydicyclohexyl peroxide is a catalyst for radical-initiated vulcanization.
References
- ↑ Story, Paul R.; Lee, Bunge; Bishop, Clyde E.; Denson, Donald D.; Busch, Peter (1970). "Macrocyclic Synthesis. II. Cyclohexanone Peroxides". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 35 (9): 3059–3062. doi:10.1021/jo00834a042.
- ↑ McCullough, Kevin J.; Morgan, Alistair R.; Nonhebel, Derek C.; Pauson, Peter L.; White, Graham J. (1980). "Ketone-Derived Peroxides. Part 1. Synthetic Methods". Journal of Chemical Research, Synopses: 34.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.