 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
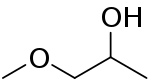
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-Methoxypropan-2-ol | |
| Other names
PGME 1-Methoxy-2-propanol Methoxypropanol α-Propylene glycol monomethyl ether Dowanol PM | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.218 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H10O2 | |
| Molar mass | 90.122 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid[1] |
| Odor | Ethereal[1] |
| Density | 0.92 g/cm3 (20 °C)[1] |
| Melting point | −97 °C (−143 °F; 176 K) |
| Boiling point | 120 °C (248 °F; 393 K)[1] |
| Miscible[1] | |
| log P | -0.45 [2] |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 32 °C (90 °F; 305 K)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Propylene glycol methyl ether (PGME or 1-methoxy-2-propanol) is an organic solvent with a wide variety of industrial and commercial uses.[3] Similar to other glycol ethers, it is used as a carrier/solvent in printing/writing inks and paints/coatings. It also finds use as an industrial and commercial paint stripper. It is used as an antifreeze in diesel engines.[4]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Record in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
- ↑ "1-Methoxy-2-propanol_msds".
- ↑ "Dowanol PM : Propylene glycol methyl ether; 1-Methoxy-2-propanol" (PDF). Msdssearch.dow.com. Retrieved 2015-05-22.
- ↑ Bosen, Sidney F.; Bowles, William A.; Ford, Emory A.; Perlson, Bruce D. (2000). "Antifreezes". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a03_023. ISBN 978-3527306732.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.