 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
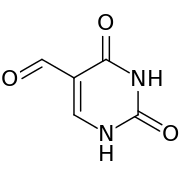
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,4-Dioxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.153.693 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H4N2O3 | |
| Molar mass | 140.098 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 | |
| Warning | |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
5-Formyluracil is a heterocyclic organic base. It is produced from the oxidation of the methyl group of thymine. It is found in bacteriophages, prokaryotes, as well as mammalian cells. Being mutagenic, it is of particular interest in the field of epigenetics.[1] It has been implicated in the formation of cancer causing cells.[2]
References
- ↑ Klungland, A; Paulsen, R; Rolseth, V; Yamada, Y; Ueno, Y; Wiik, P; Matsuda, A; Seeberg, E; Bjelland, S (2001). "5-Formyluracil and its nucleoside derivatives confer toxicity and mutagenicity to mammalian cells by interfering with normal RNA and DNA metabolism". Toxicol Lett. 119 (1): 71–8. doi:10.1016/s0378-4274(00)00308-8. PMID 11275423.
- ↑ Wang, Yafen; Zhang, Xiong; Zou, Guangrong; Peng, Shuang; Liu, Chaoxing; Zhou, Xiang (2019-04-16). "Detection and Application of 5-Formylcytosine and 5-Formyluracil in DNA". Accounts of Chemical Research. 52 (4): 1016–1024. doi:10.1021/acs.accounts.8b00543. ISSN 0001-4842. PMID 30666870. S2CID 58623597.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.