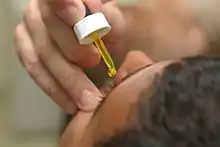
 Fluorescein drops being put in the eye before examination | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˈflʊərəsiːn/[1] |
| Trade names | Fluorescite, AK-Fluor, BioGlo, others |
| License data |
|
| Routes of administration | Eye drops, intravenous, by mouth |
| Drug class | Diagnostic agent |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII |
|
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H12O5 |
| Molar mass | 332.311 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Fluorescein is used to help in the diagnosis of a number of eye problems.[3] When applied as a drop or within a strip of paper to the surface of the eye it is used to help detect eye injuries such as foreign bodies and corneal abrasions.[4][5] When given by mouth or injection into a vein it is used to help evaluate the blood vessels in the back of the eye during fluorescein angiography.[3][6]
When applied to the surface of the eye, side effects may include a brief period of blurry vision and discoloration of contact lenses of the soft type.[7][3] When used by mouth or injection, side effects may include headache, nausea, and a change to the color of the skin for a brief period of time.[3] Allergic reactions may rarely occur.[3] Fluorescein is a dye which is taken up by damaged cornea such that the area appears green under cobalt blue light.[3] There is also a version that comes premixed with lidocaine.[4][8]
Fluorescein was first made in 1871.[9] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[10]
Brand names
It is also sold as a combination drug with oxybuprocaine under the brand name Altafluor Benox.[11][12]
Other animals
It is also sometimes administered to pets in multi-pet environments to determine which pet needs behavioral modification.
References
- ↑ "Fluorescein | Definition of Fluorescein by Oxford Dictionary on Lexico.com also meaning of Fluorescein". Lexico Dictionaries | English. Archived from the original on 14 January 2021.
- ↑ "Fluorescein sodium 100 mg/ml, solution for injection - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". (emc). 16 January 2018. Retrieved 11 March 2020.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Duvall B, Kershner RM (2006). "Ophthalmic medications and pharmacology". Journal of Ophthalmic Nursing & Technology. SLACK Incorporated. 17 (4): 151–158. ISBN 9781556427503. PMID 9883136. Archived from the original on 18 January 2017.
- 1 2 British national formulary : BNF 69 (69 ed.). British Medical Association. 2015. pp. 769, 772. ISBN 9780857111562.
- ↑ Hamilton R (2015). Tarascon Pocket Pharmacopoeia 2015 Deluxe Lab-Coat Edition. Jones & Bartlett Learning. p. 416. ISBN 9781284057560.
- ↑ "Anatera 100mg/ml solution for injection - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". (emc). 10 February 2020. Retrieved 11 March 2020.
- ↑ World Health Organization (2009). Stuart MC, Kouimtzi M, Hill SR (eds.). WHO Model Formulary 2008. World Health Organization. p. 314. hdl:10665/44053. ISBN 9789241547659.
- ↑ "Minims Lidocaine & Fluorescein Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC) - (emc)". (emc). 23 October 2017. Retrieved 11 March 2020.
- ↑ Bartlett JD, Jaanus SD (2008). Clinical Ocular Pharmacology. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 283. ISBN 978-0750675765. Archived from the original on 18 January 2017.
- ↑ World Health Organization (2019). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/325771. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
- ↑ "Drug Approval Package: Altafluor Benox (fluorescein sodium and benoxinate hydrochloride ophthalmic solution)". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 9 April 2018. Retrieved 11 March 2020.
- ↑ "Altafluor- fluorescein sodium and benoxinate hydrochloride solution". DailyMed. U.S. National Library of Medicine. 4 December 2017. Retrieved 10 March 2020.
External links
- "Fluorescein". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Fluorescein sodium". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.