| Counties of New York | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Location | State of New York |
| Number | 62 |
| Populations | 5,118 (Hamilton) – 2,590,516 (Kings) |
| Areas | 33.77 square miles (87.5 km2) (New York) – 2,821 square miles (7,310 km2) (St. Lawrence) |
| Government | |
| Subdivisions | |
| Part of a series on |
| Regions of New York |
|---|
 |
There are 62 counties in the U.S. state of New York.
The first 12 were created immediately after the British took over the Dutch colony of New Amsterdam; two of these counties were later abolished, their land going to Massachusetts.[1] The newest is Bronx County, created in 1914 from the portions of New York City that had been annexed from Westchester County in the late 19th century and added to New York County.[2] New York's counties are named for various Native American words; British provinces, counties, cities, and royalty; early American statesmen and military personnel; and New York State politicians.[3]
The county boundaries in New York state were last changed in 1964, when the Bronx gained South Brother Island from Queens.[4]
Authority
Excepting the five boroughs of New York City, New York counties are governed by New York County Law and have governments run by either a Board of Supervisors or a County Legislature, and either an elected County Executive or appointed county manager. Counties without charters are run by a Board of Supervisors, in which Town Supervisors from towns within the county also sit on the county Board of Supervisors. For counties with a charter, the executives generally have powers to veto acts of the county legislature. The legislatures have powers of setting policies, levying taxes and distributing funds.
Five boroughs of New York City
Five of New York's counties are each coextensive with New York City's five boroughs. They are New York County (Manhattan), Kings County (Brooklyn), Bronx County (The Bronx), Richmond County (Staten Island), and Queens County (Queens).
In contrast to other counties of New York, the powers of the five boroughs of New York City are very limited and in nearly all respects are governed by the city government.[5] Only a few officials are elected on a borough-wide basis, such as the five borough presidents, district attorneys, and all county and state supreme court judges. There are no official county seats, but the locations of borough halls and courthouses bestow certain neighborhoods an informal designation as county seats within their boroughs:
- The Bronx County Courthouse and the borough's main post office are located in the Concourse section of the Bronx. The separate Bronx Borough Hall burned down in 1969.
- Brooklyn Borough Hall, the Federal Building and Post Office, and county Supreme Court are in Downtown Brooklyn.
- The Municipal Building, where the Manhattan Borough President's office is located, and most courthouses are in the downtown Civic Center. The General Post Office is in Midtown Manhattan.
- Queens Borough Hall and a courthouse are in Kew Gardens. Another major courthouse, post office, and the Long Island Railroad hub are in Jamaica. Queens also has general post offices in Flushing, Long Island City and Far Rockaway.
- Staten Island Borough Hall, three courthouses, and the St. George Terminal transportation hub are in the St. George neighborhood.
List of counties
| County |
FIPS Code [6] |
County seat [7] |
Est. [7][8] |
Formed from [2] |
Named for [3] |
Density (Pop./mi2) |
Pop. (2022) [9] |
Area [7] |
Map |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Albany County | 001 | Albany | November 1, 1683 | One of 12 original counties created in the New York colony | James II of England (James VII of Scotland) (1633–1701), who was Duke of York (English title) and Duke of Albany (Scottish title) before becoming King of England, Ireland, and Scotland. | 592.52 | 315,811 | 533 sq mi (1,380 km2) |  |
| Allegany County | 003 | Belmont | April 7, 1806 | Genesee County | A variant spelling of the Allegheny River | 45.16 | 46,694 | 1,034 sq mi (2,678 km2) |  |
| Bronx County | 005 | none (sui generis) | January 1, 1914[10] | New York County | Jonas Bronck (1600?–1643), an early settler of the Dutch colony of New Netherland | 24,028.31 | 1,379,946 | 57.43 sq mi (149 km2) |  |
| Broome County | 007 | Binghamton | March 28, 1806 | Tioga County | John Broome (1738–1810), fourth Lieutenant Governor of New York | 275.69 | 197,117 | 715 sq mi (1,852 km2) |  |
| Cattaraugus County | 009 | Little Valley | March 11, 1808 | Genesee County | A word from an uncertain Iroquoian language meaning "bad smelling banks", referring to the odor of natural gas which leaked from Cattaraugus Creek | 58.35 | 76,439 | 1,310 sq mi (3,393 km2) |  |
| Cayuga County | 011 | Auburn | March 8, 1799 | Onondaga County | The Cayuga tribe of Native Americans | 86.80 | 74,998 | 864 sq mi (2,238 km2) |  |
| Chautauqua County | 013 | Mayville | March 11, 1808 | Genesee County | Loanword from the Erie language describing Chautauqua Lake; language now lost and cannot be translated | 84.02 | 126,027 | 1,500 sq mi (3,885 km2) |  |
| Chemung County | 015 | Elmira | March 20, 1836 | Tioga County | A Lenape word meaning "big horn", which was the name of a local Native American village | 198.21 | 81,426 | 410.81 sq mi (1,064 km2) |  |
| Chenango County | 017 | Norwich | March 15, 1798 | Tioga County and Herkimer County | An Onondaga word meaning "large bull-thistle" | 51.69 | 46,458 | 898.85 sq mi (2,328 km2) |  |
| Clinton County | 019 | Plattsburgh | March 4, 1788 | Washington County | George Clinton (1739–1812), fourth Vice President of the United States and first and third Governor of New York | 70.44 | 78,753 | 1,118 sq mi (2,896 km2) |  |
| Columbia County | 021 | Hudson | April 1, 1786 | Albany County | Christopher Columbus (1451–1506), the European explorer | 94.58 | 61,286 | 648 sq mi (1,678 km2) |  |
| Cortland County | 023 | Cortland | April 8, 1808 | Onondaga County | Pierre Van Cortlandt (1721–1814), first Lieutenant Governor of New York | 91.88 | 46,126 | 502 sq mi (1,300 km2) |  |
| Delaware County | 025 | Delhi | March 10, 1797 | Otsego County and Ulster County | Thomas West, 3rd Baron De La Warr (1577–1618), an early colonial leader in Virginia. Name applied to the bay, river, and Lenape Native Americans | 30.48 | 44,740 | 1,468 sq mi (3,802 km2) |  |
| Dutchess County | 027 | Poughkeepsie | November 1, 1683 | One of 12 original counties created in the New York colony | Mary of Modena (1658–1718), Duchess of York and wife of King James II of England | 360.66 | 297,545 | 825 sq mi (2,137 km2) |  |
| Erie County | 029 | Buffalo | April 2, 1821 | Niagara County | The Erie tribe of Native Americans | 774.50 | 950,312 | 1,227 sq mi (3,178 km2) |  |
| Essex County | 031 | Elizabethtown | March 1, 1799 | Clinton County | The county of Essex in England | 19.26 | 36,910 | 1,916 sq mi (4,962 km2) |  |
| Franklin County | 033 | Malone | March 11, 1808 | Clinton County | Benjamin Franklin (1706–1790), the early American printer, scientist, and statesman | 27.33 | 46,373 | 1,697 sq mi (4,395 km2) |  |
| Fulton County | 035 | Johnstown | April 18, 1838 | Montgomery County | Robert Fulton (1765–1815), inventor of the steamship | 98.82 | 52,669 | 533 sq mi (1,380 km2) |  |
| Genesee County | 037 | Batavia | March 30, 1802 | Ontario County and land acquired in the Holland Purchase | A Seneca phrase meaning "good valley" | 116.23 | 57,535 | 495 sq mi (1,282 km2) |  |
| Greene County | 039 | Catskill | March 25, 1800 | Albany County and Ulster County | Nathanael Greene (1742–1786), the American Revolutionary War general | 73.04 | 48,061 | 658 sq mi (1,704 km2) |  |
| Hamilton County | 041 | Lake Pleasant | April 12, 1816 | Montgomery County | Alexander Hamilton (1755–1804), the early American political theorist and first Secretary of the Treasury | 2.83 | 5,118 | 1,808 sq mi (4,683 km2) |  |
| Herkimer County | 043 | Herkimer | February 16, 1791 | Montgomery County | Nicholas Herkimer (1728–1777), the American Revolutionary War general | 41.03 | 59,822 | 1,458 sq mi (3,776 km2) |  |
| Jefferson County | 045 | Watertown | March 28, 1805 | Oneida County | Thomas Jefferson (1743–1826), the early American statesman, author of the Declaration of Independence, and third President of the United States | 62.81 | 116,637 | 1,857 sq mi (4,810 km2) |  |
| Kings County | 047 | none (sui generis) | November 1, 1683 | One of 12 original counties created in the New York colony | King Charles II of England (1630–1685) | 26,733.91 | 2,590,516 | 96.9 sq mi (251 km2) | 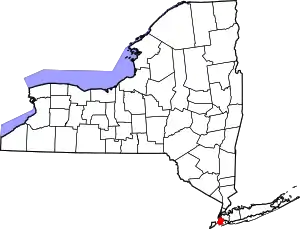 |
| Lewis County | 049 | Lowville | March 28, 1805 | Oneida County | Morgan Lewis (1754–1844), the fourth Governor of New York | 20.70 | 26,699 | 1,290 sq mi (3,341 km2) |  |
| Livingston County | 051 | Geneseo | February 23, 1821 | Genesee County and Ontario County | Robert Livingston (1746–1813), the early American statesman and New York delegate to the Continental Congress | 96.12 | 61,516 | 640 sq mi (1,658 km2) |  |
| Madison County | 053 | Wampsville | March 21, 1806 | Chenango County | James Madison (1751–1836), the early American statesman, principal author of the Constitution of the United States, and fourth President of the United States | 101.35 | 67,097 | 662 sq mi (1,715 km2) |  |
| Monroe County | 055 | Rochester | February 23, 1821 | Genesee County and Ontario County | James Monroe (1758–1831), the early American statesman and fifth President of the United States | 550.54 | 752,035 | 1,366 sq mi (3,538 km2) |  |
| Montgomery County | 057 | Fonda | March 12, 1772 | Albany County | Originally Tryon County after colonial governor William Tryon (1729–1788), renamed after the American Revolutionary War general Richard Montgomery (1738–1775) in 1784 | 121.03 | 49,623 | 410 sq mi (1,062 km2) |  |
| Nassau County | 059 | Mineola | January 1, 1899 | Queens County | The Princes of Orange-Nassau ruled the Netherlands when Long Island was a Dutch colony | 3,054.58 | 1,383,726 | 453 sq mi (1,173 km2) |  |
| New York County | 061 | none (sui generis) | November 1, 1683 | One of 12 original counties created in the New York colony | King James II of England (1633–1701), who was Duke of York and Albany before he ascended the throne of England, Duke of York being his English title | 47,268.97 | 1,596,273 | 33.77 sq mi (87 km2) |  |
| Niagara County | 063 | Lockport | March 11, 1808 | Genesee County | The Iroquoian name of a tribe within the Neutral Nation, the exact translation of which remains disputed | 184.98 | 210,880 | 1,140 sq mi (2,953 km2) |  |
| Oneida County | 065 | Utica | March 15, 1798 | Herkimer County | The Oneida tribe of Native Americans | 188.66 | 228,846 | 1,213 sq mi (3,142 km2) |  |
| Onondaga County | 067 | Syracuse | March 5, 1794 | Herkimer County | The Onondaga tribe of Native Americans | 580.95 | 468,249 | 806 sq mi (2,088 km2) |  |
| Ontario County | 069 | Canandaigua | January 27, 1789 | Land acquired in the Phelps and Gorham Purchase | An Iroquoian word meaning "beautiful lake" | 170.25 | 112,707 | 662 sq mi (1,715 km2) |  |
| Orange County | 071 | Goshen | November 1, 1683 | One of 12 original counties created in the New York colony | William of Orange-Nassau (1650–1702), who became King William III of England | 483.84 | 405,941 | 839 sq mi (2,173 km2) |  |
| Orleans County | 073 | Albion | November 12, 1824 | Genesee County | The French Royal House of Orléans | 48.12 | 39,318 | 817 sq mi (2,116 km2) |  |
| Oswego County | 075 | Oswego | March 1, 1816 | Oneida County and Onondaga County | The Oswego River, from an Iroquoian word meaning "the outpouring", referring to the mouth of the river | 90.16 | 118,287 | 1,312 sq mi (3,398 km2) |  |
| Otsego County | 077 | Cooperstown | February 16, 1791 | Montgomery County | A Native American word meaning "place of the rock" | 60.45 | 60,636 | 1,003 sq mi (2,598 km2) |  |
| Putnam County | 079 | Carmel Hamlet | June 12, 1812 | Dutchess County | Israel Putnam (1718–1790), an American Revolutionary War general | 398.56 | 98,045 | 246 sq mi (637 km2) |  |
| Queens County | 081 | none (sui generis) | November 1, 1683 | One of 12 original counties created in the New York colony | Catherine of Braganza (1638–1705), Queen of England and wife of King Charles II of England | 12,777.82 | 2,278,029 | 178.28 sq mi (462 km2) |  |
| Rensselaer County | 083 | Troy | February 7, 1791 | Albany County | In honor of the family of Kiliaen van Rensselaer (before 1596 – after 1643), the early landholder in the Dutch New Netherland colony | 240.38 | 159,853 | 665 sq mi (1,722 km2) |  |
| Richmond County | 085 | none (sui generis) | November 1, 1683 | One of 12 original counties created in the New York colony | Charles Lennox, 1st Duke of Richmond (1672–1723), the illegitimate son of King Charles II of England | 4,791.54 | 491,133 | 102.5 sq mi (265 km2) |  |
| Rockland County | 087 | New City | February 23, 1798 | Orange County | Early settlers' description of terrain as "rocky land" | 1,703.63 | 339,022 | 199 sq mi (515 km2) |  |
| St. Lawrence County | 089 | Canton | March 3, 1802 | Clinton County, Herkimer County, and Montgomery County | The St Lawrence River, which forms the northern border of the county and New York State | 38.19 | 107,733 | 2,821 sq mi (7,306 km2) |  |
| Saratoga County | 091 | Ballston Spa | February 7, 1791 | Albany County | A corruption of a Native American word meaning "the hill beside the river" | 282.93 | 238,797 | 844 sq mi (2,186 km2) |  |
| Schenectady County | 093 | Schenectady | March 27, 1809 | Albany County | A Mohawk word meaning "on the other side of the pine lands" | 762.35 | 160,093 | 210 sq mi (544 km2) |  |
| Schoharie County | 095 | Schoharie | April 6, 1795 | Albany County and Otsego County | A Mohawk word meaning "floating driftwood" | 48.02 | 30,063 | 626 sq mi (1,621 km2) |  |
| Schuyler County | 097 | Watkins Glen | April 17, 1854 | Chemung County, Steuben County, and Tompkins County | Philip Schuyler (1733–1804), the American Revolutionary War general and Senator from New York | 51.61 | 17,650 | 342 sq mi (886 km2) |  |
| Seneca County | 099 | Waterloo | March 24, 1804 | Cayuga County | The Seneca tribe of Native Americans | 101.18 | 32,882 | 325 sq mi (842 km2) |  |
| Steuben County | 101 | Bath | March 18, 1796 | Ontario County | Friedrich Wilhelm von Steuben (1730–1794), the Prussian general who assisted the Continental Army during the American Revolutionary War | 65.95 | 92,599 | 1,404 sq mi (3,636 km2) |  |
| Suffolk County | 103 | Riverhead | November 1, 1683 | One of 12 original counties created in the New York colony | The county of Suffolk in England | 642.84 | 1,525,465 | 2,373 sq mi (6,146 km2) |  |
| Sullivan County | 105 | Monticello | March 27, 1809 | Ulster County | John Sullivan (1740–1795), an American Revolutionary War general | 79.90 | 79,658 | 997 sq mi (2,582 km2) |  |
| Tioga County | 107 | Owego | February 16, 1791 | Montgomery County | A Native American word meaning "at the forks", describing a meeting place | 91.34 | 47,772 | 523 sq mi (1,355 km2) |  |
| Tompkins County | 109 | Ithaca | April 7, 1817 | Cayuga County and Seneca County | Daniel D. Tompkins (1774–1825), the 6th Vice President of the United States | 220.12 | 104,777 | 476 sq mi (1,233 km2) |  |
| Ulster County | 111 | Kingston | November 1, 1683 | One of 12 original counties created in the New York colony | The Irish province of Ulster, then an earldom of the Duke of York, later King James II of England | 157.04 | 182,319 | 1,161 sq mi (3,007 km2) |  |
| Warren County | 113 | Queensbury | March 12, 1813 | Washington County | Joseph Warren (1741–1775), the early American patriot and American Revolutionary War general | 75.40 | 65,599 | 870 sq mi (2,253 km2) |  |
| Washington County | 115 | Fort Edward | March 12, 1772 | Albany County | Originally Charlotte County, renamed in 1784 after George Washington (1732–1799), the American Revolutionary War general and first President of the United States | 71.92 | 60,841 | 846 sq mi (2,191 km2) |  |
| Wayne County | 117 | Lyons | April 11, 1823 | Ontario County and Seneca County | General Anthony Wayne (1745–1796), the American Revolutionary War general | 65.84 | 91,125 | 1,384 sq mi (3,585 km2) |  |
| Westchester County | 119 | White Plains | November 1, 1683 | One of 12 original counties created in the New York colony | The city of Chester in England | 1,980.854 | 990,427 | 500 sq mi (1,295 km2) |  |
| Wyoming County | 121 | Warsaw | May 14, 1841 | Genesee County | A modification of a word from the Lenape language meaning "broad bottom lands" | 66.55 | 39,666 | 596 sq mi (1,544 km2) |  |
| Yates County | 123 | Penn Yan | February 5, 1823 | Ontario County and Steuben County | Joseph C. Yates (1768–1837), eighth Governor of New York | 65.03 | 24,451 | 376 sq mi (974 km2) |  |
Defunct counties
| County |
Created [2] |
Abolished [2] |
Fate[2] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Charlotte County | 1772 | 1784 | Partitioned. Western part renamed as Washington County and eastern part transferred to Vermont. |
| Cornwall County | 1665 | 1686 | Transferred to the part of Massachusetts that later became the state of Maine and partitioned; one of the 12 original counties created in the New York colony |
| Cumberland County | 1766 | 1777 | Transferred to Vermont and partitioned |
| Dukes County | November 1, 1683 | 1692 | Transferred to Massachusetts; one of 12 original counties created in the New York colony |
| Gloucester County | 1770 | 1777 | Transferred to Vermont and partitioned |
| Mexico County | 1792 | 1796 | Never settled or incorporated, reallocated to Oneida, Oswego and Jefferson Counties. |
| Tryon County | 1772 | 1784 | Renamed as Montgomery County |
Proposed new counties
| County |
Note |
|---|---|
| Adirondack County | Would hypothetically consist of portions of northern Essex County and southern Franklin County[11] |
| Peconic County | Would hypothetically consist of the five easternmost towns in Suffolk County on Long Island.[12] |
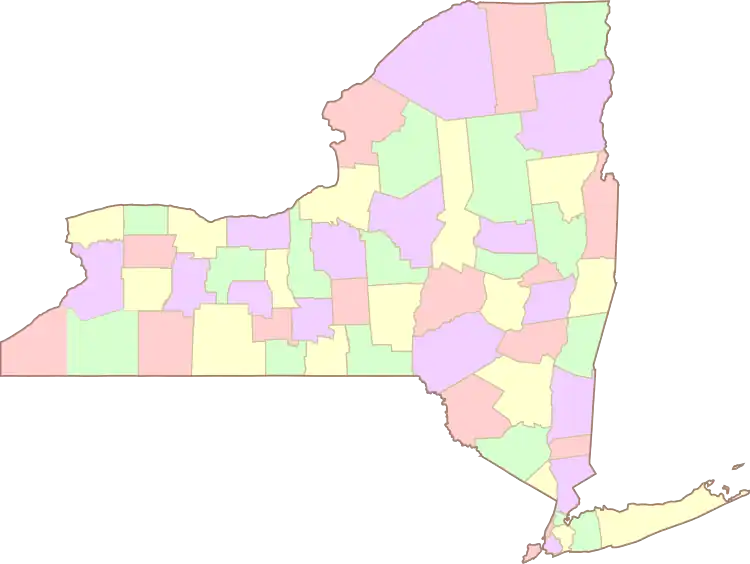
Clickable map
See also
References
- ↑ "The 12 Original Counties of New York State - Cliff Lamere". genealogy.clifflamere.com. Retrieved April 3, 2022.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "New York Formation Maps". Genealogy, Inc. Archived from the original on December 30, 2007. Retrieved January 20, 2008.
- 1 2 Beatty, Michael (2001). County Name Origins of the United States. McFarland Press. ISBN 0-7864-1025-6.
- ↑ "NY: Consolidated Chronology". digital.newberry.org. Retrieved June 8, 2023.
- ↑ Benjamin, Gerald; Nathan, Richard P. (1990). Regionalism and realism: A Study of Government in the New York Metropolitan Area. Brookings Institution. p. 59.
- ↑ "EPA County FIPS Code Listing". US Environmental Protection Agency. Archived from the original on October 8, 2012. Retrieved July 24, 2007.
- 1 2 3 "Find A County". National Association of Counties. Archived from the original on August 4, 2010. Retrieved August 9, 2010.
- ↑ Mitchell, George (1987–1988). The New York Red Book: An Illustrated Yearbook of Authentic Information Concerning New York State, Its Departments and Political Subdivisions and the Officials Who Administer Its Affairs (89th ed.). Albany, New York: Williams Press, Inc. pp. 987–988.
- ↑ "U.S. Census Bureau QuickFacts: New York". U.S. Census Bureau. July 2022. Archived from the original on March 9, 2023. Retrieved April 2, 2023.
- ↑ Legislation splitting off Bronx County from New York County was enacted in 1912 with an effective date of January 1, 1914. Prior to 1874 the entire area had been part of Westchester County. See McCarthy, Thomas C. "A 5-Borough Centennial Preface for the Katharine Bement Davis Mini-History". New York City Department of Corrections. Retrieved January 25, 2008.
- ↑ Lynch, Mike (October 30, 2007). "North Elba Supervisor Candidate Debate". Plattsburgh Press Republican. Retrieved January 20, 2008.
- ↑ Healy, Patrick (February 11, 2004). "Growth Pains and Clout Heading East in Suffolk". The New York Times. Retrieved January 20, 2008.
External links
- "Counties" at NY.gov