The target audience is the intended audience or readership of a publication, advertisement, or other message catered specifically to the previously intended audience. In marketing and advertising, the target audience is a particular group of consumer within the predetermined target market, identified as the targets or recipients for a particular advertisement or message.[1]
Businesses that have a wide target market will focus on a specific target audience for certain messages to send, such as The Body Shop Mother's Day advertisements, which were advertising to children as well as spouses of women, rather than the whole market which would have included the women themselves.[1] Another example is the USDA's food guide, which was intended to appeal to young people between the ages of 2 and 18.[2]
The factors they had to consider outside of the standard marketing mix included the nutritional needs of growing children, children's knowledge and attitudes regarding nutrition, and other specialized details. This reduced their target market and provided a specific target audience to focus on. Common factors for target audiences may reduce the target market to specifics such as 'men aged 20–30 years old, living in Auckland, New Zealand' rather than 'men aged 20–30 years old'. However, just because a target audience is specialized doesn't mean the message being delivered will not be of interest and received by those outside the intended demographic.[3] Failures of targeting a specific audience are also possible, and occur when information is incorrectly conveyed. Side effects such as a campaign backfire and 'demerit goods' are common consequences of a failed campaign.[4] Demerit goods are goods with a negative social perception, and face the repercussions of their image being opposed to commonly accepted social values.[5]
Defining the difference between a target market and a target audience comes down to the difference between marketing and advertising. In marketing, a market is targeted by business strategies, whilst advertisements and media, such as television shows, music and print media, are more effectively used to appeal to a target audience. A potential strategy to appeal to a target audience would be advertising toys during the morning children's TV programs, rather than during the evening news broadcast.[6]
Target market
A target market is a select group of potential or current consumers, which a business decides to aim its marketing and advertising strategies at in order to sell a product or service.[7] Defining a 'target market' is the first stage in the marketing strategy of a business, and is a process of market segmentation. Market segmentation can be defined as the division of a market into its select groups, based on a variety of factors such as needs, characteristics and behaviours, so that the application of the marketing mix can be appropriate to the individual.[1] Segmentation of the market gives a business the ability to define its target market for its product or service, and apply the marketing mix to achieve the desired results.
Determining the target audience
A business must identify and understand its target audience if their marketing campaign is to be successful. It allows the business to craft their products or services to the wants and needs of customers, in order to maximise sales and therefore revenue. A successful marketing campaign connects with consumers on a personal dB level, which will help the business to develop long-term relationships with customers (Sherlock, 2014).
Not all consumers are the same. Determining the target audience is key to reaching the loyal and high-profit customers, in order to ensure a return on investment (Cahill, 1997, p. 10-11). To effectively determine the brand's target audience, marketing managers should consider the three main general aspects of target audience grouping: demographics, psychographics and consumer lifestyle (Percy, Rossiter, & Elliott, 2001, p. 65).
To determine the target audience, the business must first identify what problem their product or service solves, or what need or want it fulfills (Sherlock, 2014). The problem must be one that consumers are aware of and thus will be interested in solving. For example, a problem could be a lack of cheap air-conditioning units on the market. If a business enters the air-conditioning unit market selling their units at a low price, consumers who couldn't afford the other air-conditioning units will see this as a solution to the problem and will purchase the new units. The problem that the business solves can be identified by searching for similar businesses or business ideas. If the search is unsuccessful, then there remains a problem that the business can solve (Sherlock, 2014).
The business must determine what kind of people are facing the problem they identified. This is based on consumer demographic, psychographic, geographic information and behavior (Sherlock, 2014).
Demographic information
Demographic information involves statistical aspects of consumers such as gender, ethnicity, income, qualification and marital status (Sharma 2015). Demographic information is important to the business because it gives a basic background of the customers the business is intending to aim its marketing campaign at. This helps them to judge on a basic level how to communicate effectively with who they have identified as the target audience. Demographics are key because they provide the foundation of who the business will be targeting (Sherlock, 2014). Demographics is statistical information that does not require in-depth analysis to provide an answer, thus a business would use quantitative methods of data collection. This tiny method will provide a statistical approach to identifying the target audience.
Psychographic information
Psychographics is the use of sociological, psychological and anthropological factors, as well as consumer behavior, style of living and self-concept to determine how different market segment groups make decisions about a philosophy, person or product (Weinstein, 2014). Psychographic information can be utilized by the business to gain a deeper understanding of the consumer groups they intend to target, by analyzing the more intimate details of the consumer's lifestyle and thinking processes so as to gain an understanding of their preferences. Things like financials, interests, hobbies, and lifestyle will all be filtered by the business to create a target audience that will, in theory, be open to the product and will connect with the business through a marketing campaign aimed at them (Dowhan, 2013).
Behavioural information
Consumer behavior is the purchase decision process, what influences their purchase decision, what purposes they use the purchased good for, and their responses and attitudes to the product (Cheng et al., 2015). Cheng et al. explains that consumer's behavior is affected by messages sent by the business, which in turn affects their attitudes towards brands and products, and ultimately what products they choose to purchase (Cheng et al., 2015). When determining their target audience, a business must examine consumer behavior trends. Behavioral trends could include online purchasing instead of in-store purchasing, or modern consumers purchasing a new smartphone annually. They should then select a segment of consumers whose behavior aligns with the functionality and purpose of the product to be the intended audience for a marketing campaign. Target consumers can be identified by businesses as they will indicate that there is a demand for the product by their behavioral signals (Dowhan, 2013). Their interests, hobbies and past purchase activity provide a platform on which the business can base their marketing campaign (Dowhan, 2013).
Geographic information
Geographic information is essentially where the customer is located and is vital to the business when they are determining their target audience. This is because customers located in different geographic areas are going to encounter different things that influence their purchase decisions (Kahie, 1986). These can be any number of things, including resources, cultures, and climates, which can cause their behavior, psychographic information and influences to differ with those who are in same demographic but are geographically distant (Kahie, 1986). For example, a city or area with a heavy drinking culture will encounter high liquor sales, whereas a city or area with a minimal drinking culture will experience low liquor sales. Each country has consumers of the same demographic, but due to the cultural influence of the geographical area, their purchase decisions are different.
A basic example of a consumer profile is: males aged 35–40 who live in the US and have a university-level education (demographic), are a sociable extrovert from a top-middle economic class and live an active lifestyle (psychographic), lives in Nashville, Tennessee (geographic) and makes small and frequent purchases without considering the product's brand (behavioural). This profile will allow the business to tailor their marketing campaign to attract specific consumers.
There are many methods of demographic, psychographic, geographic and behavioral data collection. There are quantitative methods, being statistical processes such as surveys and questionnaires, and qualitative methods, being in-depth approaches such as focus groups or comprehensive interviews (Dudley et al. 2014). The different aspects of consumers are all essential to a business when it is planning a marketing campaign, as the information that the business gathers will determine what the most profitable target market for the campaign is, and how to reach this market.
The business must also look to their competitors to see what processes they are currently taking to try and solve the problem, and which consumers they are targeting (Sherlock, 2014). This will allow the business to get an idea of the type of consumer they will be targeting, and what the best way is to communicate with this type of consumer. This information can be used to allow the business to differentiate slightly from the competition in order to give them a competitive advantage once the marketing campaign begins.
Once the target audience has been identified, the business must then create content for the campaign that will resonate and effectively communicate with the consumer (Sherlock, 2014). Tracie Sherlock emphasizes that the level of content with which the business will be reaching the consumer should be of high quality, as 92% of marketers specify that high-level content is valuable for a campaign (Sherlock, 2014). This high level of content will help consumers to connect on a more personal level with the business and contribute to a successful communication process from the business to the target audience and then feedback from the target audience to the business.
Once the business has gathered data from consumers about their demographic, psychographic, geographic and behavioral situations, they can analyze this and use it to identify a rough target audience. This can be refined by the analysis of competitors' processes and targets, allowing the business to formulate a more segmented target audience. Then the segmented target audience can be refined into a clear objective of which consumers the business is targeting, thus creating the specific target audience for a marketing campaign.
Lifestyle
A lifestyle is defined as "a person's pattern of behavior" which is closely related to a consumer's personality and values (Hoyer, Macinnis, & Pieters, 2013, p. 401). The lifestyle of a customer is often determined by purchasing behavior and product preference (Lin, 2002, p. 250). This gives marketers an understanding of what type of lifestyle consumers live. A lifestyle is defined with three main sections: activities, interests, and opinions (AIO). If a marketer can conduct lifestyle research through previous purchasing behavior it gives an excellent understanding of AIOs enabling target audiences to be effectively determined (Hoyer, Macinnis, & Pieters, 2013, p. 401-403).
Vs. target market
Two key marketing terms are target audience and target market. Distinguishing the correct target market(s) and defining a target audience is a crucial step when owning a business. Although the two are very similar, it is essential to understand the differences.
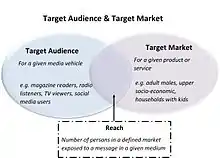
A target audience is generally associated with a business's marketing message, which highlights advantages and benefits of a business's product or service. Examples of a target audience are "company employees, society as a whole, media officials, or a variety of other groups" (Tambien, E., n.d.). Tom Duncan, author of The Principles of Advertising and IMC, and founder of the Integrated Marketing Communication (IMC) graduate program at the University of Colorado, defines target audience as "a group that has significant potential to respond positively to a brand message" (Northwestern University., n.d.) (Duncan, T., 2005). This 'group' is targeted through particular marketing communication channels such as advertising, which aim to create a positive interaction towards the brand (Tyson, R., 2014). If this is successful, the audience will play a huge role in influencing other potential customers to purchase the product or service. An example of this is when a child, part of a target audience, is positively reached through a communication channel such as a TV advertisement for toys. The child then shares this information with their parent, the target market, who will be influenced to go purchase the toy.
A target market is a selected group of consumers who share common needs or characteristics. Often these characteristics can be segmented into four different marketing groups, geographic, demographic, psychographic or behavioral (Kotler, P., Burton, S., Deans, K., Brown, L., & Armstrong, G., 2013). Once a company has defined their target market, they will aim their products, services and marketing activities towards these consumers in a way that will hopefully persuade them to purchase the product or service (Kotler, et al., 2013). The impact of this will result in either a gratifying or deficient marketing strategy.
Strategies for reaching target audiences
Reaching a target audience is a staged process, started by the selection of the sector of the target market. A successful appeal to a target audience requires a detailed media plan, which involves many factors in order to achieve an effective campaign.
The use of media is what differentiates target markets from target audiences. While target markets are marketed to with business strategies, the use of advertising and other media tools is what makes marketing to target audiences a more effective way of appealing to a select group of individuals.[6] The effectiveness of a target audience campaign is dependent on how well the company knows their market; this can include details such as behaviours, incentives, cultural differences and societal expectations.[8] Failure to identify these trends can lead to campaigns being targeted at the wrong audiences, and ultimately a loss of money or no change at all. An example of this type of failure was Chef Boyardee, who planned a campaign to appeal to teenage boys, the largest consumers of their product.[8] What they hadn't considered however was that the purchasers of their goods may be different from the consumers, which was the case, as mothers were the leading purchasers, even though the boys were consuming the product. Factors like these are considered at a more in-depth level with a detailed media plan, one that cannot be found in a simpler target market strategy.[4] Following through a media plan requires attention at every stage, and requires a range of factors to be considered. In order, these include:
- Targets
- Media types
- Media tactics
- Media vehicles
- Media units
- Media schedule
- Media promotions
- Media logistics
- Contingency plans
- Calendar
- Budget and integrated marketing[8]
Each of these sections goes into even more detail, such as media units, which includes such minute details as the length of a broadcast commercial or the size of a print advertisement.[8]
A thoroughly followed, planned and implemented media plan is required to achieve outright success in a campaign.[1] Therefore, ignoring any of the factors can lead to a miscommunication with consumers and ultimately a failure to fully reach the whole target audience effectively.[8]
Effective marketing consists of identifying the appropriate target audience, and being able to appoint the correct marketing strategy in order to reach and influence them. Four key targeting strategies largely used within businesses are; undifferentiated (mass) marketing, differentiated (segmented) marketing, concentrated (niche) marketing, and lastly micro (local or individual) marketing (Kotler, et al., 2013).
Undifferentiated (mass) marketing is a strategy used to capture a whole audience, rather than focusing on the differences in segmented markets. A business will typically design one product line and focus on what consumer demands are most frequent, in order to create a marketing program that will appeal to the greatest amount of purchases. This strategy commonly uses mass distribution and advertising to help create an admirable product and is possibly one of the most cost effective. The narrow product line, undifferentiated advertising program and absence of segmented market research and planning, all contribute to keeping the costs down. Many do not believe in this strategy, due to the high amount of competition and the difficulty in creating a product that satisfies a majority of consumers (Kotler, et al., 2013).
A differentiated (segmented) marketing strategy is when a business chooses to target multiple segments of the audience, by creating a different variations of its product for each. An example of this is V energy drinks who offer a large range of products including; V regular, V sugar free, V zero, V double espresso (V-Energy.,n.d.). Typically when using this marketing strategy, recognition of the company is widened and repeat purchasing is strengthened, with customers gaining products that are more tailored to their needs. This strategy unfortunately is not cost effective and involves a lot of research and development, as well as a whole range of promotion that is unique to each specific product. Although this strategy often has more sales than those who use an undifferentiated marketing strategy. When considering this strategy one must consider the increased sales against the increased cost (Kotler, et al., 2013).
Concentrated (niche) marketing is a "market coverage strategy in which a company goes after a large share of one or a few sub-markets (Kotler, et al., 2013)." This strategy enables companies to create a strong market position without mass production, distribution or advertising. This strategy is usually beneficial as it does not involve a lot of competition. A business is able to gain greater knowledge of their distinct segment, as they are more focused on the segmentations needs and reputation that it acquires. Many businesses using this strategy are now turning to the web to set up their shop, not only because it is cost effective but allows them to become more recognisable (Kotler, et al., 2013).
A micro-marketing strategy (local or individual) targets very narrowly compared to an undifferentiated marketing strategy. Generally a business using this strategy will adjust its product, and marketing program to fit the needs of different market segments and niches. A good example of this is shown in the real-estate industry whose goal is often to determine what type of house the client is looking for. Micro-marketing includes both local and individual marketing. Often this strategy can be costly, due to the customization and shortage of an economy of scale (Kotler, et al., 2013).
Local marketing is "tailoring brands and promotions to the needs and wants of the local customer groups, cities, neighborhoods and even specific stores (Kotler, et al., 2013)." This type of marketing does have difficulties especially when it comes to manufacturing and marketing costs, meeting the mixed requirements for each market location and brand image familiarity. New developing technologies and fragmented markets regularly exceed these obstacles (Kotler, et al., 2013).
Individual marketing refers to accommodating merchandise and marketing programs, to the desired demands of individual customers. An example of this is Coca-Cola, who enables customers to personalise their Coke cans by being able to print their name or choice of text onto the can packaging (Coca-Cola., n.d.). Despite the extra costs for the business, allowing customer to design and create a product they desire to suit their own needs, can create value and loyalty towards the business. It is also a way the business can stand out against its competitors (Kotler, et al., 2013).
Strategies for reaching target markets
Marketers have outlined four basic strategies to satisfy target markets: undifferentiated marketing or mass marketing, differentiated marketing, concentrated marketing, and micromarketing/ nichemarketing.
Mass marketing is a market coverage strategy in which a firm decides to ignore market segment differences and go after the whole market with one offer. It is type of marketing (or attempting to sell through persuasion) of a product to a wide audience. The idea is to broadcast a message that will reach the largest number of people possible. Traditionally mass marketing has focused on radio, television and newspapers as the medium used to reach this broad audience.
For sales teams, one way to reach out to target markets is through direct marketing. This is done by buying consumer database based on the segmentation profiles you have defined. These database usually comes with consumer contacts (e.g. email, mobile no., home no., etc.). Caution is recommended when undertaking direct marketing efforts — check the targeted country's direct marketing laws.
Target audiences are formed from different groups, for example: adults, teens, children, mid-teens, preschoolers, men, or women.
To market to any given audience effectively, it is essential to become familiar with your target market; their habits, behaviors, likes, and dislikes. Markets differ in size, assortment, geographic scale, locality, types of communities, and in the different types of merchandise sold. Because of the many variations included in a market it is essential, since you cannot accommodate everyone's preferences, to know exactly who you are marketing to.
To better become acquainted with the ins and outs of your designated target market legend, a market analysis must be completed. A market analysis is a documented examination of a market that is used to enlighten a business's preparation activities surrounding decisions of inventory, purchase, workforce expansion/contraction, facility expansion, purchases of capital equipment, promotional activities, improvement of daily operations and many other aspects.
Strategic planning and segmentation
Marketing organisations undertaking a strategic plan need to use target marketing in their decisions (Dibb & Simkin 1998). Target marketing is also part of the segmentation process, where groups who share the same needs and wants are segmented into specific categories. According to Dibb and Simkin, (1998) the final process of target marketing is the design of marketing mix programme. The marketing mix tools are made up of four broad groups known as the 4 Ps: product, price, place, and promotion (Kotler et al., 2014). The use of the marketing mix programme will provide sufficient data and knowledge for appropriate marketing strategies to reach the specific target audience. Target marketing strategy can be segmentation: Market segmentation demonstrates dividing the market into distinct groups that may require different products or services (Kotler et al., 2014). Using the strategy of market segmentation can allow the marketer to have sufficient knowledge of the consumer's characteristics. Knowledge of consumers' demographic, geographic, psychographic and behavioral variables can enable relevant marketing processes to reach the target audience directly.
Geographic
Geographic segmentation is the marketer's appealing to particular geographic areas such as nations, regions, countries, cities or neighborhoods (Kotler et al., 2014). Particular knowledge of geographic preferences allows businesses and organisations to modify or change their product to allocate to their market, (Kotler et al., 2014).
Demographic
This divides the market into demographic field such as age, life cycle, gender, income, occupation, education, religion, and nationality (Kotler et al., 2014). Some companies offer different products and market strategies to allocate to various age and life cycles, other companies focus on specific age of life cycle groups. Kotler et al., (2014) states an example, Disney cruise lines primarily focus on families with children large or small, and most destinations offer children and parent orientated activities. This shows that the Disney cruise line company has a specific segment of their target market being families with children.
Psychographic
Customers may be sorted based on social class, lifestyle, or personality characteristics (Kotler et al., 2014). According to Kotler et al., (2014) people who in the same demographic area can have completely different psychographic characteristics. Marketers generally segment target markets into consumer lifestyles and their social class. Social class has a large effect on preferences for cars, clothes, home furnishings, leisure activities, reading habits, and retailers (Kotler et al., 2014).
Behavioral
Consumers are divided by their knowledge, attitudes, and use of, or response to, the product (Kotler et al., 2014). Marketers can group buyers according to the occasion when they made the purchase or used the product. For example, Kotler et al. (2014) suggests that air travel is generated by occasions relative to business, vacation, or family. Another way marketers can group buyers using behavioral variables is user status and usage rate. They can be segmented into nonusers, former users, potential users, first-time users and regular users of a product, (Kotler et al., 2014). Usage rate is the segmentation into light, medium and heavy product users. According to Kotler, et al., (2014) heavy product users are usually a small percentage of the market but account for a high percentage of total consumption. Loyalty status can prove to be very significant to a marketer's product or service. Kotler et al., (2014) expresses, a reason for increasing customer loyalty is that "loyal customers are pricing insensitive compared to brand-shifting ideas."
Marketing mix
To understand the effects of marketing on audience improvement, the basic marketing principles need to be outlined, and the role that marketing strategies play in building a target audience examined. According to, Galvin (1998), marketing is considered to be as simple as selling or promoting a product or service to a client, customer or consumer who is in need of the distinct product. It is also the process of planning and executing the conception, pricing, promotion, and distribution of ideas, goods, and services to create exchanges that satisfy individual customer and organisations (Galvin, 1998). As well as segmentation, the marketing mix is a significant marketing strategy to pinpoint the target audience and further market appropriately to that audience. The marketing mix involves designing the packaging, pricing of the product, distributing of the product, and promoting or communicating about the product (Galvin, 1998). These processes are known as the 4 Ps. The market strategy and the marketing mix allow room to create value for customers and build profitable customer relationships (Kotler et al., 2014). These customer relationships can create an idea of exactly what target audience applies to the specific product, if few or more consumers have similar characteristics and purchase the product regularly for similar behavioral reasons therefore the target audience may fit within that category.
Direct marketing
Direct marketing is targeting individual consumers to both obtain an immediate response and cultivate lasting consumer relationships, (Kotler et al., 2014). According to Evans, O'Malley and Patterson, (1995) the direct marketing industry has been the fastest growing sector of marketing communications. There are multiple forms of direct marketing such as direct mail, the telephone, direct-response television, e-mail, the Internet and other tools to connect with specific consumers (Kotler et al., 2014). Evans, O'Malley and Patterson (1995) and Kotler et al. (2014) also consider leaflet drops and samples to be a form of direct marketing. Using these direct forms of communication, customers of the product or service will receive personal, efficient and easily accessed information on the product. This could influence the customer to purchase the product or service. This is arguably the most straightforward and direct process for reaching the appropriate target audience (Evans, O'Malley & Patterson, 1995).
Communication strategies
Marketing communications channels have undergone huge changes, shifting away from traditional mass-market type advertisements such as television and radio. This is due to advancements in technology and the Internet era developing brand new communication channels such as web advertising, social media and blogs (Bruhn, Schoenmueller, & Schäfer, 2012, p. 770-772 ). Many businesses such as Coca-Cola are engaging with their target audience through these modern media channels, opening up a two-way communication from brand to consumer and consumer to brand. This approach generates the brand's following through social media vehicles, which are increasingly where consumers find brand content and information. By increasing engagement with target audiences, businesses have the opportunity to increase brand equity through both traditional media and social media (Bruhn, Schoenmueller, & Schäfer, 2012, p. 781-782).
Traditional communication
Traditional media vehicles such as television, radio and press have been utilised by marketers for many years but have limitations when trying to reach an individual target audience. The advantage traditional media gives businesses is the ability to reach a huge audience. This type of marketing is commonly known as mass marketing and accounted for 70% of media spending in 2013 (Hoyer, Macinnis, & Pieters, 2013, p. 118-120). These media vehicles are better suited to a brand's attempt to stay relevant or build brand awareness in the mass market it communicates with (Bruhn, Schoenmueller, & Schäfer, 2012, p. 781-782). Although traditional media is effective in generating brand awareness, in today's market more and more consumers are online, engaged in more than one media channel at a time. Traditional media cannot target this consumer effectively where an omni-channel marketing approach is needed (Brynjolfsson, 2013). Traditional media is considered expensive for smaller businesses with limited ability to market to the intended target audience; this mass marketing approach serves the message market widely rather than deeply with the intended audience (Bruhn, Schoenmueller, & Schäfer, 2012, p. 781-782 ). To reach today's target audience effectively, traditional media such as television advertisements must be implemented in an integrated marketing communications campaign rather than the sole media vehicle to deliver a brand's message (Hoyer, Macinnis, & Pieters, 2013, p. 3-7)
Online communications
Marketers can use online media to better reach their target audience. Once marketers understand the segments of their target market they can generate a marketing message suitable for the intended target audience. Communicating to consumers through tools such as web banners, social media and email, allows direct targeting to the consumer. This serves up a custom message to a consumer who is already engaged and interested in the offering. An example of this is remarketing, which allows advertisers to see a consumer's web history, tracking them online to see exactly which websites they have visited. The marketer then has a second chance to show the consumer a related product from a previously-visited website, which the consumer had turned down earlier (Libert, Grande, & Asch, 2015).
Social media such as Twitter, Snapchat discover, Instagram, YouTube and Facebook allow two-way communication between the business and consumer which cannot be achieved by traditional media. This communication benefits both the business using social media as a tool and the consumer, as they can build meaningful relationships with the business and other consumers, creating a community around the brand. This community can provide new insights for the business, identifying problems and offering solutions through social interactions (Tsimonis & Dimitriadis, 2014, p. 328-330). When businesses have a successful social platform which generates an interactive community around a brand, it enables better relationship building, which improves the brand's image and consumer-based brand equity (Bruhn, Schoenmueller, & Schäfer, 2012, p. 781-782).
Marketers can also use online media to target preexisting communities by introducing key leaders within those communities to their product or service, in the hope that they will in turn introduce their followers to the product.[9]
The power of persuasion
The role that social influence and persuasion play has a sizable emphasis on target audience, and how the message is developed into society. How these messages are conveyed to the target audience, plays a key role tailored to the target audience to trigger deep or shallow processing, from using the best path to persuasion. The target audience analysis process requires a tremendous amount of work, to identify the characteristics of the broad target audience, refining this audience on several dimensions. The specific conformity of the target audience to the desired supporting psychological operations objective is the product of assiduous work, mainly of the target audience analysis phase of influence process, this validates the importance of this role to the overall operation enabling decision makers, to gain substantial objectives in the information environment (Topolniski, 2013).
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 Kotler, Philip; Armstrong, Gary (2005). Marketing: An Introduction. Prentice Hall. ISBN 9780133071368.
- ↑ Saltos, Etta (1999). Adapting the Food Guide Pyramid for Children: Defining the target audience.
- ↑ Zenker, Sebastian; Beckmann, Suzanne (2013). "My place is not your place - different place brand knowledge by different target groups". Journal of Place Management and Development. Bingley, United Kingdom. 6: 6–17. doi:10.1108/17538331311306078.
- 1 2 Rittenburg, Terri; Parthasarathy, Madhavan (1997). "Ethical implications of target market selection". Journal of Macromarketing. Boulder, CO. 17 (2): 49–64. doi:10.1177/027614679701700205. S2CID 153422647.
- ↑ Albers, Norman; Hubl, Lothar (1997). "Gambling Market and Individual Patterns of Gambling in Germany". Journal of Gambling Studies. 13 (2): 125–44. doi:10.1023/A:1024999217889. PMID 12913391. S2CID 25211526.
- 1 2 Ingram, David. "Target Market vs Target Audience".
- ↑ Andreasen, Alan (1994). "Social Marketing: Its definition and domain". Journal of Public Policy and Marketing. 13: 108–114. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.476.4742. doi:10.1177/074391569401300109. S2CID 15478674.
- 1 2 3 4 5 kelley, Larry; Jugenheimer, Donald (2008). Advertising Media Planning, A Brand Management Approach. M. E. Sharpe.
- ↑ Zhou, Junjie; Chen, Ying-Ju (2016-02-15). "Targeted Information Release in Social Networks" (PDF). Operations Research. 64 (3): 721–735. doi:10.1287/opre.2015.1431. ISSN 0030-364X.
References
- Ang, L. (2014). principles of integrated marketing communications. New York: Cambridge University Press.
- Bruhn, Manfred; Schoenmueller, Verena; Schäfer, Daniela B. (3 August 2012). "Are social media replacing traditional media in terms of brand equity creation?" (PDF). Management Research Review. 35 (9): 770–790. doi:10.1108/01409171211255948. S2CID 154950313. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 February 2020.
- Brynjolfsson, E. (2013, May 23). Competing in the Age of Omnichannel Retailing. Retrieved from http://sloanreview.mit.edu/article/competing-in-the-age-of-omnichannel-retailing/
- Cahill, Dennis J. (February 1997). "Target marketing and segmentation: valid and useful tools for marketing" (PDF). Management Decision. 35 (1): 10–13. doi:10.1108/00251749710160133. S2CID 41766795. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2019-03-05.
- Luo, Cheng; Bruijn, Oscar De; Chen, Yu-wang (11 April 2015). "Behavioural segmentation using store scanner data in retailing: Exploration and exploitation in frequently purchased consumer goods markets". Journal of Business and Retail Management Research. 10 (1).
- Coca-Cola. (n.d.). Share a Coke - celebrate your loved ones with personalized bottles. Retrieved from: https://buy.shareacoke.com/ Archived 2018-07-09 at the Wayback Machine
- Simkin, Lyndon; Dibb, Sally (December 1998). "Prioritising target markets". Marketing Intelligence & Planning. 16 (7): 407–417. doi:10.1108/02634509810244417.
- Dowhan, D. (2013). "Hitting Your Target". Marketing Insights. 35 (2): 32–38.
- Randle, Melanie; Mackay, Hugh; Dudley, Dorothy (1 January 2014). "A comparison of group-based research methods". Market & Social Research. 22 (1): 22–35.
- Duncan, T. (2005). Principles of advertising & IMC (2nd ed.). Chicago, IL: McGraw-Hill/Irwin.
- Evans, Martin; O′Malley, Lisa; Patterson, Maurice (July 1995). "Direct marketing: rise and rise or rise and fall?". Marketing Intelligence & Planning. 13 (6): 16–23. doi:10.1108/02634509510094147.
- Galvin, George E. (1998). The impact of target marketing on developing a culturally diverse audience (Thesis). ProQuest 304489257.
- Hoyer, W. D., Macinnis, D. J., & Pieters, R. (2013). Consumer Behavior (6th ed.).
- Kahle, Lynn R. (April 1986). "The Nine Nations of North America and the Value Basis of Geographic Segmentation". Journal of Marketing. 50 (2): 37–47. doi:10.1177/002224298605000203. S2CID 167866912.
- Kotler et al. (2014). Marketing for hospitality and tourism, (6th ed.) Pearson New International Edition.
- Kotler, P., Burton, S., Deans, K., Brown, L., & Armstrong, G. (2013). Market segmentation, targeting and positioning. In Marketing (9th ed.). NSW: Frenchs Forest, N.S.W., Pearson Australia.
- Libert, T.; Grande, D.; Asch, D. A. (16 November 2015). "What web browsing reveals about your health" (PDF). BMJ. 351 (nov16 5): h5974. doi:10.1136/bmj.h5974. PMID 26572794. S2CID 206908416. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 February 2019.
- Lin, Chin-Feng (July 2002). "Segmenting customer brand preference: demographic or psychographic". Journal of Product & Brand Management. 11 (4): 249–268. doi:10.1108/10610420210435443.
- Mittal, Banwari (11 January 2016). "Psychographics of comparison shoppers". Journal of Consumer Marketing. 33 (1): 20–31. doi:10.1108/jcm-12-2014-1268.
- Northwestern University. (n.d.). Tom Duncan - Medill - Northwestern University. Retrieved from http://www.medill.northwestern.edu/about/who-we-are/hall-of-achievement/tom-duncan.html Archived 2016-09-01 at the Wayback Machine
- Oxford Dictionary. (2016). target market - definition of target market in English from the Oxford dictionary. Retrieved from [https://web.archive.org/web/20160415081844/http://www.oxforddictionaries.com/definition/english/target-market?q=target+market Article title]
- Percy, L., Rossiter, J. R., & Elliott, R. H. (2001). Strategic advertising management. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Percy, Larry, Rossiter, John., R, Elliot, Richard. (2001). The audience considerations. Strategic Advertising Management. Retrieved from Strategic Advertising Management
- Sharma, Sakshi (December 2015). "Do Demographic Variables affect the Stress Levels of Indian Soldiers?". Vision: The Journal of Business Perspective. 19 (4): 324–335. doi:10.1177/0972262915610860. S2CID 147307704.
- Sherlock, T. (2014). "3 KEYS TO IDENTIFYING YOUR TARGET AUDIENCE". Promotional Marketing.
- Topolniski, Marius-Aurelian (2013). From Target Audience Analysis To Influence Messages In Multinational Operations. International Scientific Conference "Strategies XXI"; Bucharest. Vol. 2. pp. 395–400. ProQuest 1445001865.
- Tsimonis, Georgios; Dimitriadis, Sergios (29 April 2014). "Brand strategies in social media". Marketing Intelligence & Planning. 32 (3): 328–344. doi:10.1108/mip-04-2013-0056.
- Tyson, R. (2014, February 3). The Difference Between Your Target Market and Target Audience. Retrieved from: http://www.copypress.com/blog/how-to-resonate-with-your-target-market/
- V Movement. (2016). V MoVement | V Energy. Retrieved from http://v-energy.com.au/world-of-v/v-movement
- Weinstein, Art (16 April 2014). "Segmenting B2B technology markets via psychographics: an exploratory study". Journal of Strategic Marketing. 22 (3): 257–267. doi:10.1080/0965254X.2013.876072. S2CID 167388388.