 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Aiviosin |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Veterinary Use |
| License data |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Macrolide antibiotic |
| ATCvet code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII |
|
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.058.284 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
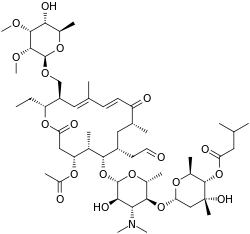
| Formula | C53H87NO19 |
| Molar mass | 1042.267 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| |
| |
Tylvalosin, sold under the brand name Aiviosin, is a macrolide antibiotic used for the treatment of bacterial infections in swine.[3] It is used as tylvalosin tartrate.[3]
Medical uses
Tylvalosin is indicated for the control of porcine proliferative enteropathy associated with Lawsonia intracellularis infection in groups of swine intended for slaughter and female swine intended for breeding in buildings experiencing an outbreak of PPE.[3] Not for use in male swine intended for breeding; and for the control of swine respiratory disease associated with Bordetella bronchiseptica, Glaesserella (Haemophilus) parasuis, Pasteurella multocida, Streptococcus suis, and Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae in groups of swine intended for slaughter and female swine intended for breeding in buildings experiencing an outbreak of swine respiratory disease.[3] Not for use in male swine intended for breeding.[3]
References
- ↑ "Aiviosin- tylvalosin granule". DailyMed. 29 November 2021. Retrieved 13 December 2023.
- ↑ "Aiviosin- tylvalosin tartrate granule, for solution". DailyMed. 29 November 2021. Retrieved 13 December 2023.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "Freedom of Information Summary Aiviosin NADA 141-336" (PDF). Retrieved 13 December 2023.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from US Food and Drug Administration. United States Department of Health and Human Services.
This article incorporates public domain material from US Food and Drug Administration. United States Department of Health and Human Services.