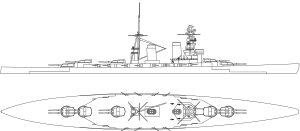
 Design for the Amagi class | |
| Class overview | |
|---|---|
| Builders |
|
| Operators | Imperial Japanese Navy |
| Preceded by | Kongō class |
| Succeeded by | Design B-65 |
| Built | 1920–1922 |
| Planned | 4 |
| Completed | 1 (converted into an aircraft carrier) |
| Cancelled | 3 |
| Lost | 1 |
| Scrapped | 3 |
| General characteristics | |
| Type | Battlecruiser |
| Displacement |
|
| Length | 251.8 m (826 ft) |
| Beam | 30.8 m (101 ft) |
| Draft | 9.5 m (31 ft) |
| Installed power |
|
| Propulsion | 4 shafts; 4 steam turbines |
| Speed | 30 knots (56 km/h; 35 mph) |
| Range | 8,000 nmi (15,000 km; 9,200 mi) at 14 knots (26 km/h; 16 mph) |
| Complement | 1,600 |
| Armament |
|
| Armor |
|
The Amagi class (天城型, Amagi-gata) was a series of four battlecruisers planned for the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) as part of the Eight-eight fleet in the early 1920s. The ships were to be named Amagi, Akagi, Atago, and Takao. The Amagi design was essentially a lengthened version of the Tosa-class battleship, but with a thinner armored belt and deck, a more powerful propulsion system, and a modified secondary armament arrangement. They were to have carried the same main battery of ten 41 cm (16.1 in) guns and been capable of a top speed of 30 knots (56 km/h; 35 mph).
Limitations imposed by the 1922 Washington Naval Treaty prevented the class from being completed as designed. However, the treaty had a limited allowance for hulls already under construction to be converted into aircraft carriers. Amagi and Akagi were both intended for conversion, but an earthquake damaged the hull of Amagi so extensively that the ship was scrapped. Akagi was reconstructed as an aircraft carrier and served with distinction as part of the Kido Butai during the Second World War, participating in the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor before being sunk at the Battle of Midway.
Design
Dimensions and machinery
The ships had a planned displacement of 41,217 tonnes (40,566 long tons) and 47,000 t (46,000 long tons) at full load. The class design was 250 m (820 ft) long at the waterline, and 251.8 m (826 ft) overall. The ships would have had a beam of 30.8 m (101 ft) and a draft of 9.5 m (31 ft)[1] and would have used four propeller shafts, powered by Gihon steam turbines. The design staff intended to use turbines, which were to be powered by 19 Kampon water-tube boilers, eleven of which were oil-fired, while the other eight were to have mixed oil and coal for fuel. This system was designed to provide 131,200 shaft horsepower (97,800 kW) for a top speed of 30 knots (56 km/h; 35 mph). The planned fuel stores amounted to 3,900 tons of oil and 2,500 tons of coal. The ships had a planned cruising speed of 14 knots (26 km/h; 16 mph), and with full fuel stores, the ships would have had a maximum range of 8,000 nautical miles (15,000 km; 9,200 mi).[1]
Armament
The ships were to be equipped with a main battery of ten 41 cm (16.1 in) L/45 guns[A 1] guns in five twin-gun turrets, although an L/50 gun tested in 1920 might have been used instead. The guns fired 1,000 kg (2,200 lb) armor-piercing projectiles with a 224 kg (494 lb) propellant charge at 790 m/s (2,600 ft/s), at a rate of fire between 1.5 and 2.5 rounds per minute. Each gun had 90 rounds and an approximate barrel life of 250–300 shots. The turrets would have been arranged along the centerline: two superfiring turrets fore, and three in line aft of the superstructure. The gun turrets weighed 1,004 tons (1,020 mt), and allowed for depression of −5 degrees and elevation of 30 degrees.[2]
The secondary battery was to have consisted of sixteen 14 cm (5.5 in) L/50 guns mounted in casemates along the center of the ship. These guns fired 38 kg (84 lb) projectiles and used 10.33–10.97 kg (22.8–24.2 lb) of propellant at a muzzle velocity of 850–855 m/s (2,790–2,810 ft/s). The guns had a maximum elevation of 25 degrees, which enabled a maximum range of 17.5 km (10.9 mi).[3] Four, later increased to six, 12 cm (4.7 in) L/45 anti-aircraft guns were to have been mounted amidships, along with eight 61 cm (24 in) above-water torpedo tubes.[1]
Armor
It was planned that the Amagi class would be protected by a main belt 254 mm (10.0 in) thick, sloped at 12 degrees, and a torpedo bulkhead 73 mm (2.9 in) thick. The main battery barbettes were designed to have between 230–280 mm (9.1–11.0 in) of armor plating, and the conning tower would have had armor ranging in thickness from 76 mm (3 in) to a maximum of 356 mm (14.0 in). Deck armor was to have been 98 mm (3.9 in) thick.[1]
Background
Experiences in the Russo-Japanese War convinced naval war planners that more fast capital ships were needed, so on 4 April 1907, the Imperial Defence Council approved an "Eight-eight" policy. This plan originally called for a fleet of eight battleships and eight armored cruisers that would all be under ten years old (later changed to eight battlecruisers and reduced to eight years old). However, the advent of the dreadnought battleship crippled this plan at the beginning; given Japan's weak and underdeveloped economy and the enormous strain that had been put on it during the Russo-Japanese War (Japan emerged from the war victorious, but bankrupt),[4] the launch of HMS Dreadnought was a "disaster" for Japan.[5]
In 1907, Japan was halfway to the eight-eight, with two newly delivered battleships (the Katori class) in the fleet and two more (the Satsuma class) and four armored cruisers authorized or under construction. In addition, three more battleships and four armored cruisers had been authorized, though not funded. However, naval technology was changing; older battleships, including all of Japan's battleships in commission or under construction,[A 2] were quickly rendered obsolete with the commissioning of HMS Dreadnought (hence the terms dreadnought and pre-dreadnought), and armored cruisers were seemingly useless in the face of the new battlecruisers being laid down by Great Britain and Germany. The IJN recognized this, and proposed in 1909 that two battlecruisers be ordered from British plans, with one to be built in Great Britain and one to be built at home. These two ships became the Kongō class. Another pair of Kongos were later built in Japan.[5]
In 1910, there was still authorization for one battleship and four armored cruisers. This battleship, a more heavily armored version of the Kongō-class battlecruisers, became Japan's first super-dreadnought, Fusō. With these ships, Japan appeared to be getting closer to the eight-eight goal; however, these new ships represented a "new level of naval strength" for the IJN, and they made all previous Japanese capital ships obsolete. This meant that any naval planner aiming for an eight-eight fleet would have to call for seven more battleships and four more battlecruisers[5] at a time when Japan was trying to weather a worldwide economic depression.[4]
After proposals from the IJN in 1911 and 1912 for massive shipbuilding programs, the Cabinet compromised down to a "four-four" plan; under this, three new battleships (the other Fusō-class ship and the two Ise-class ships) and no new battlecruisers were authorized.[6] The Navy did not agree, and instead called for an "eight-four" fleet, while the Imperial Defence Council called for the original eight-eight. The Cabinet relented, and by July 1914, it was decided to aim first for an eight-four fleet, followed by the eight-eight fleet. The eight-four plan was presented to the Diet of Japan in 1915; it aimed to have the eight battleships and four battlecruisers by 1923 with the building of two Nagato-class and two Tosa-class battleships. The problem with this was that the old plan intended all of the ships of the eight-eight fleet to be under eight years old; by the time these new ships were completed, Fusō and the first two Kongō ships would be past their replacement age.[7]
The plan was approved in 1917, along with funding for two battlecruisers which became the Amagi class. In late 1917, the Navy proposed to expand the eight-four plan by adding two more battlecruisers; this was approved, and two more Amagi-class ships were ordered. However, having eight 41 cm (16 in) gun ships (four battleships and four battlecruisers) on order put an enormous financial strain on Japan, which was spending about a third of its national budget on the Navy. The massive size and scale of its building program was rapidly driving up the cost of naval construction and armament.[7]
Construction, cancellation, and conversion

Akagi was the first ship of the class to be laid down; construction began on 6 December 1920 at the naval yard in Kure. Amagi followed ten days later at the Yokosuka naval yard. The projected completion dates for the first pair of ships were December and November 1923, respectively. Atago was laid down in Kobe at the Kawasaki shipyard on 22 November 1921, and was projected to be finished in December 1924. Takao, the fourth and final ship of the class, was laid down at the Mitsubishi shipyard in Nagasaki on 19 December 1921, and was also projected to be completed in December 1924.[1] The ships were named after several mountains: Amagi, Akagi, Atago, and Takao.[A 3] Takao was initially to have been named Ashitaka after Mount Ashitaka.[8]
The Washington Naval Treaty, signed in February 1922, greatly reduced the tonnage allowed for capital ships in the signatory nations. The treaty also instituted a moratorium on new warship construction; battlecruisers canceled under this included one class each from Japan, the United States, and Great Britain: the Amagi class, the Lexington class and the G3 class, respectively.[9] The treaty did allow for battleship and battlecruiser hulls currently under construction to be converted into aircraft carriers, but only if these new carriers were kept under a 27,000-ton limit. Considering that the Amagi class were designed to displace 47,000 t (46,000 long tons; 52,000 short tons) at full load in their battlecruiser configuration,[1] this would have been a rather difficult displacement to obtain. However, the Americans also had the same problem when designing a conversion of their Lexington class, so an exception, spearheaded by US Assistant Secretary of the Navy Theodore Roosevelt Jr., was added to the treaty that gave the five signatories the option of converting up to two capital ships that were under construction to 33,000-ton aircraft carriers.[10][11] This resulted in the United States and Japan quickly reordering two ships each. Japan chose Amagi and Akagi, the two ships nearest to completion, for conversion.[1] Their guns were turned over to the Imperial Japanese Army for use as coastal artillery; three of their main gun turrets were installed in Tokyo Bay, at Busan, Korea, and on Iki Island in the Strait of Tsushima. The rest of their guns were placed in reserve and scrapped in 1943.[12]

The September 1923 Great Kantō earthquake in Tokyo caused significant stress damage to the hull of Amagi. The structure was too heavily damaged to be usable, and conversion work was abandoned. Amagi was stricken from the navy list and sold for scrapping, which began on 14 April 1924. The other two ships, Atago and Takao, were officially canceled two years later (31 July 1924) and were broken up for scrap in their slipways.[1] The incomplete Tosa-class battleship Kaga, on which work had stopped on 5 February 1922, was reordered as a carrier to replace Amagi.[13]
Akagi's career as an aircraft carrier

The conversion of Akagi began on 19 November 1923, and was completed in March 1927. However, the strange assortment of flight decks fitted on Akagi—a main landing deck superimposed over two short take-off decks—proved unsatisfactory, and the ship was withdrawn from active service in 1935 for modernization. The lower two flight decks were removed, the main deck was lengthened to 250 m (820 ft), and a third elevator was added.[14] Refitting was completed in 1938.[15] Akagi supported operations off China in early 1939 and 1940, and underwent an overhaul in November 1940.[15]
Akagi served as Vice Admiral Chūichi Nagumo's flagship in the attack on Pearl Harbor on 7 December 1941.[16] Nagumo's Kido Butai—composed of the carriers Akagi, Kaga, Hiryū, Sōryū, Shōkaku, and Zuikaku, supported by escorts—launched two waves of airstrikes on the American base at Pearl Harbor in a devastating surprise attack. American losses included four battleships and two destroyers sunk and nearly 200 aircraft destroyed.[17][18][19]
On 19 February 1942, aircraft from Akagi, Hiryū, Sōryū, and Kaga participated in the bombing of Darwin, Australia.[19][20] On 27 February, their bombers severely damaged the old American carrier USS Langley, which was subsequently scuttled by her escort.[21]
Akagi and the carriers Hiryū and Sōryū were sent in March 1942 with a mixed force of battleships, cruisers, and destroyers to the Indian Ocean to engage the British fleet there and to support planned attacks on Ceylon. In the Easter Sunday Raid on 5 April, aircraft from the carriers struck the British base at Colombo, destroying a number of aircraft and sinking an armed merchant cruiser and the old destroyer HMS Tenedos in the harbor.[19][22] The Japanese fleet also spotted the heavy cruisers HMS Dorsetshire and HMS Cornwall at sea; both ships were sunk in an overwhelming air attack.[19] On 9 April the carriers attacked British installations at Trincomalee, destroying aircraft and sinking the carrier HMS Hermes, the destroyer HMAS Vampire, and the corvette HMS Hollyhock.[23]
Battle of Midway
In late May 1942, in an effort to draw out and destroy the elusive American carriers, Japanese forces organized attacks on the Aleutian Islands in Alaska and Midway Atoll in the Western Pacific.[24] Nagumo, aboard Akagi, led Kaga, Sōryū, and Hiryū and the support ships of the First Carrier Striking Force to Midway.[25][26] In the initial attack, Japanese planes neutralized a small force of fighter aircraft and inflicted heavy damage to American installations.[24][27] Torpedo planes and dive-bombers sent from Midway to harry the Japanese fleet had little effect, but the Japanese attack plan had been deciphered by codebreakers, and the American carriers' planes were already en route.[28] Torpedo bombers from USS Hornet, USS Enterprise, and USS Yorktown joined the attack in succession, forcing the Japanese carriers to maneuver violently to avoid torpedoes and rendering them unable to launch additional aircraft.[29] American dive-bombers, arriving late after difficulty locating the fleet, soon landed fatal strikes on Akagi, Kaga, and Sōryū.[29] Yorktown, handicapped by hits from Hiryū's bombers, managed to return to the fight only to take two torpedo hits a couple of hours later.[29] The burning Yorktown was abandoned, but her scouts pinpointed Hiryū's location, and bombers from Enterprise put Hiryū out of action with four bomb strikes.[29] Japan lost all four carriers of the First Carrier Striking Force at Midway.[30]
Notes
- ↑ L/45 denotes the length of the gun barrels; in this case, the gun is 45 calibers, meaning that the gun is 45 times long as it is in diameter.
- ↑ While the Satsuma-class battleships were technically "semi-dreadnoughts" due to their heavy secondary battery, they were still made obsolete by Dreadnought.
- ↑ Conway's All the World's Fighting Ships (p. 235) states that Takao was named for the town of Takao, Formosa, and some sources repeat this. However, the name Takao for Japanese warships predated the renaming of the town, and Lacroix (p. 122) states that the name was simply re-used for the battlecruiser.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Gardiner and Gray (1984), p. 235
- ↑ DiGiulian, Tony (19 April 2007). "Japanese 41 cm/45 (16.1") 3rd Year Type, 40 cm/45 (16.1") 3rd Year Type". Navweaps.com. Archived from the original on 24 January 2009. Retrieved 18 January 2009.
- ↑ DiGiulian, Tony (23 August 2007). "Japanese 5.5"/50 (14 cm) 3rd Year Type". Navweaps.com. Archived from the original on 6 January 2009. Retrieved 18 January 2009.
- 1 2 Gardiner and Gray (1984), p. 222
- 1 2 3 Gardiner and Gray (1984), p. 223
- ↑ Gardiner and Gray (1984), pp. 222–223
- 1 2 Gardiner and Gray (1984), p. 224
- ↑ Katagiri, p. 93
- ↑ See: Washington Naval Treaty, Chapter II, Part III, Section II
- ↑ Friedman (1983), p. 43
- ↑ See: Washington Naval Treaty, Chapter I, Article IX
- ↑ Gibbs & Tamura (1982), pp. 192, 194
- ↑ Gardiner and Gray eds. (1984), p. 232
- ↑ Stille, p. 12
- 1 2 Kotani, Ken. "Pearl Harbor: Japanese planning and command structure" in Marston (2005), pp. 32–33
- ↑ "Akagi (Aircraft Carrier, 1927–1942)". Naval History & Heritage Command. 21 March 1999. Archived from the original on 10 May 2010. Retrieved 6 October 2009.
- ↑ Hoyt (2001), pp. 225–228
- ↑ Kotani, Ken. "Pearl Harbor: Japanese planning and command structure" in Marston (2005), pp. 40–41
- 1 2 3 4 Ireland (1998), p. 190
- ↑ Hoyt (2001), p. 260
- ↑ "Langley". Dictionary of American Naval Fighting Ships. Navy Department, Naval History and Heritage Command. Retrieved 6 October 2009.
- ↑ Hoyt (2001), p. 268
- ↑ Ireland (1998), p. 191
- 1 2 Ireland (1998), p. 197
- ↑ Love, Robert. "The Height of Folly" in Marston (2005), p. 89
- ↑ Hoyt (2001), p. 293
- ↑ Hoyt (2001), p. 295
- ↑ Love, Robert. "The Height of Folly" in Marston (2005), p. 93
- 1 2 3 4 Ireland (1998), p. 200
- ↑ Love, Robert. "The Height of Folly" in Marston (2005), p. 97
Bibliography
- DiGiulian, Tony. "Navweaps.com: Naval Weapons, Naval Technology and Naval Reunions". Bucks County, Pennsylvania.
- Friedman, Norman (1983). U.S. Aircraft Carriers: An Illustrated Design History. Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 0-87021-739-9. OCLC 8763586.
- Gardiner, Robert; Gray, Randal, eds. (1985). Conway's All the World's Fighting Ships 1906–1921. Annapolis: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 0-87021-907-3. OCLC 12119866.
- Gibbs, Jay & Tamura, Toshio (1982). "Question 51/80". Warship International. XIX (2): 190, 194–195. ISSN 0043-0374.
- Hoyt, Edwin P. (2001). Japan's War: The Great Pacific Conflict. New York: Cooper's Square Press. ISBN 0-8154-1118-9.
- Ireland, Bernard (1998). Jane's Naval History of World War II. London: HarperCollins. ISBN 0-00-472143-8.
- Katagiri, Daiji (1988). Ship Name Chronicles of the Imperial Japanese Navy Combined Fleet. Japan: Kōjinsha. ISBN 4-7698-0386-9.
- Lacroix, Eric (1997). Japanese Cruisers of the Pacific War. Annapolis: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 0-87021-311-3.
- Marston, Daniel, ed. (2005). The Pacific War Companion. Oxford: Osprey Publishing Ltd. ISBN 1-84176-882-0.
- Stille, Mark (2005). Imperial Japanese Navy Aircraft Carriers 1921–45. Oxford: Osprey Publishing. ISBN 1-84176-853-7. OCLC 57638857.
- "Washington Naval Treaty" of 1922. Washington Naval Conference.
- Dictionary of American Naval Fighting Ships. Naval History & Heritage Command, United States Department of the Navy. Print publications 1959–1991; digital version available at the Online DANFS Project.