| Ambitle | |
|---|---|
 Feni Islands seen from space, with Ambitle (left) and Babase (right). | |
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 450 m (1,480 ft)[1] |
| Prominence | 450 m (1,480 ft) |
| Listing | Volcanoes of Papua New Guinea |
| Coordinates | 4°05′S 153°39′E / 4.08°S 153.65°E[1] |
| Dimensions | |
| Length | 15 km (9.3 mi) |
| Width | 10 km (6.2 mi) |
| Area | 87 km2 (34 sq mi) |
| Geography | |
| Location | Bismarck Archipelago, Papua New Guinea |
| Geology | |
| Mountain type | Stratovolcano |
| Last eruption | 350 BCE ± 100 years[1] |
Ambitle is a volcanic island which, together with Babase, another volcanic island, is one of the two Feni Islands in the Bismarck Archipelago. The island is located within the Papua New Guinea's New Ireland Province, to the east of the island of New Ireland.
Ambitle is a stratovolcano, reaching 450 metres (1,480 feet) above sea level. It last erupted in about 350 BCE based on radiocarbon dating. Its caldera, 3 kilometres (2 miles) wide, contains thermal areas on its western side. Venting of hydrothermal water also occurs in coral reefs to the west of this island.[1]
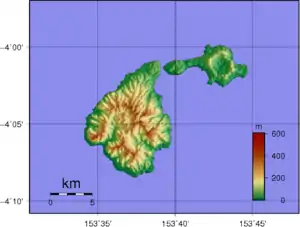
Topographic map of Feni Islands. Ambitle is the larger island on the left.
References
- 1 2 3 4 "Ambitle". Global Volcanism Program. Smithsonian Institution. Retrieved 2023-06-04.
Further reading
- Pichler, Thomas; Dix, George R. (May 1996). "Hydrothermal venting within a coral reef ecosystem, Ambitle Island, Papua New Guinea". Geology. Geological Society of America. 24 (5): 435–438. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(1996)024<0435:HVWACR>2.3.CO;2.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.