| Norwegian Army | |
|---|---|
| Hæren | |
 | |
| Founded | 1628 |
| Country | |
| Allegiance | |
| Type | Army |
| Role | Ground warfare |
| Size |
|
| Part of | Norwegian Armed Forces |
| Headquarters | Bardufoss |
| Motto(s) | For alt vi har. Og alt vi er. ("For everything we have. And everything we are"). |
| Engagements | |
| Website | Official website |
| Commanders | |
| Chief of Defence | General Eirik Kristoffersen |
| Chief of the Army | Major general Lars Lervik |
The Norwegian Army (Norwegian: Hæren) is the land warfare service branch of the Norwegian Armed Forces. The Army is the oldest of the Norwegian service branches, established as a modern military organization under the command of the King of Norway in 1628. The Army participated in various continental wars during the 17th, 18th, and 19th centuries as well, both in Norway and abroad, especially in World War II (1939–1945). It constitutes part of the Norwegian military contribution as a charter member of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) since 1949.
History
Creation of the Norwegian Army
After the Kalmar War broke out in 1611, the Danish-Norwegian king, Christian IV tried to revive the leidang, with dire results. As the Norwegian peasantry had not been armed or trained in the use of arms for nearly three centuries, they were not able to fight. Soldiers deserted or were captured. The soldiers had to participate in military drills, while providing supplementary labor to the local community when not in active service. Although the army still did not represent the whole nation, as city residents were exempt from military duty, 1628 is generally regarded by historians as the year when the modern Norwegian army was born.
As a result of the Torstenson war (Danish: Torstenssonfejden, Norwegian: Hannibalfeiden, Swedish: Torstensonska kriget) lasting from 1643 to 1645, Danish–Norwegian territories were to be ceded to Sweden. This led Christian IV to invite German mercenaries to coach and command the Danish–Norwegian armed forces: a decision echoing down the centuries in traces of German vocabulary used by the Norwegian military to this day.
In the early 18th century the Swedes invaded Norway again, and this time the Norwegian army held its own, setting the stage for nearly a century of peace – the longest yet in early modern and modern Norwegian history – during which time a distinct Norwegian identity began to evolve. German ceased to be the official language of command in the army in 1772, in favour of "Dano-Norwegian".
Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars

During the French Revolutionary Wars, Denmark–Norway tried to remain neutral. But the British attack on Copenhagen 1801 forced the kingdom to leave the Second League of Armed Neutrality. The British bombardment of the Danish capital in 1807 pushed King Frederik IV to align with French Emperor Napoleon I. Hostilities reached north into Scandinavia and by 1807, Denmark-Norway was at war with Great Britain. Denmark–Norway's alliance with France and Sweden's alliance with the Great Britain led to war with Sweden 1808. Sweden made a bid to acquire Norway by way of invasion while Denmark-Norway made ill-fated attempts to reconquer territories lost to Sweden in the 17th century. As the Napoleonic era drew to a close, the anti-French victorious allies decided to sever Norway from Denmark and unite and award Norway to neighboring Sweden in 1814 at the Congress of Vienna.
The Royal Decree of 3 July 1817 decided that the Army should, among other things, consist of five infantry brigades. There were 1st Akershus, 2nd Akershus, 3rd Trondhjem, 4th Bergen and 5th Kristiansand infantry brigades. The brigades had a section called the brigade command (5th Brig.kdo.), Which was responsible for the war organization and plans.
Union with Sweden
The union with Sweden lasted until 1905, during which time the Norwegian Army retained a separate entity within the joint kingdoms. Financial budgeting, recruitment, regimental organization, and uniforms were all independent of their Swedish counterparts. The basis for recruitment for the Norwegian Army was initially one of conscription for up to five years by lot drawn amongst rural recruits only. A framework was provided by regular soldiers or hvervede, enlisted as long-service volunteers. As with other armies of the period, the payment of a substitute to serve in one's place was permitted. This system was replaced by one of universal conscription introduced in 1854. Enlistment in the active army was however still based on the drawing of ballots, with those escaping full-time service going immediately to the reserve landvern, where they received brief and basic training.
In 1884, the basis of service was further modified with the training period being reduced to 90 days. The regulars of the hvervede were reduced to a cadre of career officers, NCOs, and other specialists. The individual Norwegian recruit now passed through three stages of service with the line regiments, the militia, and the territorial reserve during the 13-year period that his liability for military service lasted. The left-wing parties of the Storting favored the substitution of part-time volunteer rifle clubs for the regular army but this was opposed by the Storting (Parliament of Norway) parliamentary majority on the basis of the doubtful effectiveness of such a force.
Independence
In June 1905, the Storting unilaterally dissolved the 91-year-old union with Sweden. After a short but tense period during which both armies were mobilized, Sweden agreed to the peaceful dissolution of the union. In 1911, six brigades were established, which by the Army Order of 1916 were called divisions. The divisions were consecutively numbered without geographical place names. The divisions corresponded to what later became district commands.
By 1920, the army of Norway was a national militia. Service was universal and compulsory, liability commencing at the age of 18 and continuing till the age of 56. The men were called out at 21, and for the first 12 years belonged to the line; then for 12 years to the landvarn. Afterwards they passed into the landatorm, in which they remained until they attained the age of 55 years. The initial training was carried out in recruits' schools; it lasted for 48 days in the infantry and garrison artillery, 62 in the mountain batteries, 72 in the engineers, 92 in the field artillery, and 102 in the cavalry. As soon as their courses were finished the men were transferred to the units to which they would permanently belong, and with them went through a further training of 30 days. Subsequent training consisted of 80 days in the second, third and seventh years of service.
The line was organized into 6 divisions of all arms, besides which there was the garrison artillery. There were 56 battalions of infantry, 5 companies of cyclists (skiers), 3 regiments of cavalry (16 squadrons), 27 four-gun field batteries, 3 batteries of mountain artillery, 9 batteries of heavy artillery, and 1 regiment and 2 battalions of engineers. The new Flying Corps was organized in 3 divisions. The divisions were of unequal strength, according to the importance of the district in which they were recruited. In event of war, each division would mobilize 2 or 3 regiments of infantry (of 3 battalions), 3 or 4 squadrons of cavalry, a battalion of field artillery (of 3 batteries), a battalion of heavy artillery, a sapper company, a telegraph company, a medical company and a company of train. Each regimental district also forms one battalion of landvarn (of 6 companies), and the other arms would form landvarn units in the same proportion. The total peace strength was 118,500 men and comprised 71,836 rifles, 228 field and 36 heavy guns. The additional numbers available on mobilization amount to 282,000 men.
The Norwegian infantry was armed with various models of the Norwegian-designed Krag–Jørgensen 6.5x55 rifles and carbines. The field artillery had Ehrhardt 7.5 cm Model 1901. The budget of the army for 1919–1920 was 1,940,000.
The divisions received in 1933 the task of establishing their own field manoeuvre brigade with the same number as the division.
World War I
With full Norwegian independence, legislation was passed strengthening the system introduced in 1885. Liability for military service was extended to 55 years of age and the period of training was lengthened to about five months. Additional localized regiments were created within a framework of six military districts, permitting more rapid mobilization of reservists. These precautions proved effective in 1914 with the outbreak of World War I. Norway's armed forces remained mobilized throughout the war, ensuring Norwegian neutrality in conjunction with that of Denmark and Sweden.
Though nominally a neutral nation during the "Great War" of World War I (1914–1918), Norway was in the unenviable position of being dependent on the warring sides for its trade. Coal from Britain was needed to keep the country going, and Norway had thus to agree that each shipload of coal leaving Britain be matched with incoming Norwegian cargoes such as copper ore and fish. This attracted the attention of the opposing German Empire and its Imperial German Navy's numerous submarines.
In 1911 the 5th Brigade was established as the Norwegian Army's district organization in Møre og Romsdal and Trøndelag. It was upgraded to the status of the 5th Division in 1916.

World War II
Despite the escalating hostilities throughout Europe in 1939 and 1940, the Norwegian government at the time failed to mobilize; leaving the Army wholly unprepared for the German invasion of April 1940. The Norwegians were organised into six divisions/districts in April 1940.[1] This amounted to approximately 19,000 men on paper. This was actually a numerically superior force to that of the Germans. However, these divisions were ill-prepared by the time the landings commenced and four were destroyed by the Germans during the initial phases of the campaign. With the German occupational forces in 1940, as with the other parts of the Armed Forces, the Army had to surrender to a superior force, but army units were the ones resisting for the longest period of time: The 6th Division led by the legendary Major General Carl Gustav Fleischer participated in the allied recapture of Narvik.
In most divisions, A force of 3 regiments (With 3,750 men in each regiment, 11,250 men in total) was the basic organization of the army. But with the 3rd and 4th Division, There was only 2 regiments (7,500 total men). Total Norwegian Division Force numbered 60,000 Men, in 16 Regiments. There was also a Few Extra Groups, like 3 Dragoon Regiments, 3 Artillery Regiments, a few Mountain artillery battalions and infantry battalions in the far north, with 2 Royal Guards companies in the south.

The greatest Norwegian accomplishment of the Second World War was the victory in the Battle of Narvik, especially the mountain war forcing the German forces all the way from the ocean to the Swedish border. In addition to the Norwegian Campaign, Norwegian soldiers joined the Norwegian resistance movement after German forces occupied Norway. The Home Front (Hjemmefronten) was the Norwegian resistance movement during Nazi Germany's occupation of Norway (1940–1945).
Norwegian soldiers also joined free Norwegian units in the United Kingdom to continue the fight against the Nazis from abroad. These units included the Norwegian Independent Company 1 and 5 Troop, No. 10 (Inter-Allied) Commando. The bulk of the Norwegian Army during the years in exile in Britain consisted of a brigade in Dumfries as well as smaller units stationed in Iceland, Jan Mayen, Svalbard and South Georgia. The 2nd Mountain Company operated in Finnmark from late 1944 under nominal Russian command. Norwegian police troops and units from this brigade took control over Finnmark in 1944 after the German retreat from the Red Army. Many former Norwegian Army members also served with the German forces.
Cold War
The Army was reconstructed after the War, based among others on the forces Norwegian Brigade in Scotland and the Norwegian police troops in Sweden as well as on Milorg. The participation in the allied occupation of Germany with the Independent Norwegian Brigade Group in Germany was a very demanding task for the Army in the period of 1946–52, but it was also a part of the reconstruction. After the war the Army was structured to meet an invasion from the East. The Army was established in all parts of the country, from 1972 in five regional "divisions" to commemorate the divisions/districts of the Second World War: East (including the inactive 6th Brigade), West, South, Trondelag, and 6th Division: North Norway.[2] The first four divisions were divided into 12 regional districts, which could, after full mobilization, embody 11 combat brigades (10 mobilization-dependent). 6th Division controlled Brigade North in Tromso, two brigade mobilization districts, and two garrisons in the northernmost Finnmark region. At the end of the Cold War the army could mobilise 13 brigades, although 10 of them were less well equipped.[3]
Post Cold War

This picture definitely changed with the fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989 and the subsequent break-up of the Soviet Union and the Warsaw Pact.
It has been downsized after the end of the Cold War, with the biggest changes taking place in the middle of the 1990s, when a number of garrisons and units were discontinued. This restructuring focused on moving from a fairly static invasion army to a flexible rapid reaction army. The Parliament in 1994 and 1995 approved a series of major organizational changes, for the Army in particular. To ensure a cost-efficient implementation, it is necessary to focus the activities in the Army on the process of transforming the army from a large mobilization army to a smaller, professional army.
The 2005–08 plan envisaged reduction of the then army from three to two brigades, but the essential and key formation was to be Brigade North. The 6 Division Command was to be organised as a mobile tactical headquarters with the capability to serve as a framework for a headquarters for multinational operations above brigade level in Norway. But to keep Brigade North operational Jane's Defence Weekly was told in May 2004 would require two brigade sets of equipment. The Army had by the end of the decade been significantly downsized from its late Cold War heights, and has for example faced criticism from within claiming that it would now only be able to defend one district of Oslo in the event of a national invasion.[4]

Norwegian contributions to international crisis management have been generated from a system that is first and foremost geared towards the rapid activation of mobilization units armed and trained for territorial defence. As a consequence, Norwegian contributions to international military operations have a high degree of sustainability, as they have a substantial number of reserve units on which to draw. However, without adaptation this force posture is to a lesser extent able to generate forces rapidly and flexibly in response to international crises. Moreover, the contributions that Norway has been able to make to international operations have tended to consist of lightly armoured mechanized infantry, well-suited for more traditional peacekeeping tasks (UNIFIL in southern Lebanon to which Norway contributed a sizable unit for over twenty years) but not sufficiently robust for missions which might entail enforcement tasks.
War in Afghanistan

Norway along with other Scandinavian countries, supported the US War on Terror. The Norwegian government was one of the strongest supporters of the war.
Norwegian Defence Minister at the time, Bjørn Tore Godal, said "the United States is Norway's most important ally. Norway is already providing intelligence assistance to the United States. If we receive a request for further support, including military support, we will, of course, respond positively, and in accordance with the obligations of article 5 of the NATO treaty."[5]
The Norwegian Army sent troops to support the NATO ISAF mission in Afghanistan, to help free Afghanistan of the Taliban. Norwegian special forces were involved in combat operations during Operation Enduring Freedom in 2002, and Norwegian Army troops during Operation Harekate Yolo in 2007.[6] About 590 Norwegians were serving in the ISAF force in 2009.[7]
According to Aftenposten, the Norwegian Army base at Meymaneh was amongst the least secure bases in Afghanistan at one point. Meymaneh is located in northwestern Afghanistan, which has become increasingly restless in recent years. Both the military and political heads of the armed forces agreed about the weakened state of the base. When the Norwegian Army was asked what they needed to defend their position, they asked for 120 troops and long-range weapons. They also requested a mobile reaction force, so that allies in the region could assist each other if they came under heavy attack.[8]
Organization
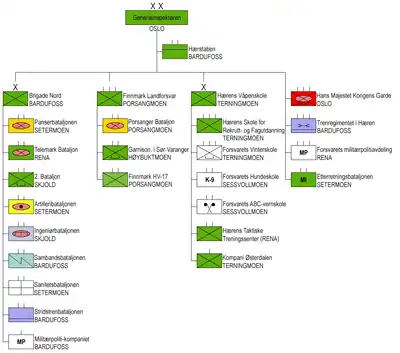
In 2009 the Army introduced the new command and control lines. The Chief of the Army (former General Inspector) now commands three subordinate operational units and five support units:[9]
- Army Staff, in Bardufoss
- Brigade Nord, in Bardufoss
- Hans Majestet Kongens Garde, in Oslo
- Finnmark Land Command
- Military intelligence Battalion, in Setermoen
- Land Warfare Centre, in Rena and Terningmoen
- Military police unit
- Operations Support Group, in Bardufoss (Maintenance, Catering, etc.)
Hans Majestets Kongens Garde (Garden)
Hans Majestet Kongens Garde is a light infantry battalion based in Oslo at Huseby camp. The main task of Garden is to protect the King and the royal family in peace, crisis and war.
After the terrorist attack in 2011, the unit also functions as a defence force in Norway’s capital Oslo and will assist the police when needed.[10]
Brigade Nord
Brigade Nord is the Norwegian Army's only major combat formation. Brigade Nord is the northernmost combat brigade in NATO and has the capabilities to plan, lead and implement operations with support from other branches of the Norwegian Defence Forces. The brigade is formed primarily around three all-arms battlegroups.[11]
2012 White Paper
According to the Norwegian MoD 2012 White Paper the Brigade Nord maneuver elements will be reorganised. Telemark Bataljonen and The Armoured Battalion will be organized as two near identical mechanized battalions composed mainly of contract personnel, but with some conscripts. The 2nd Battalion will be developed in the light infantry role, composed mainly of conscript personnel. The brigade will be equipped with organic air defence assets. The reorganization is intended to provide the brigade with 2 continuously combat ready battlegroups.[12]
Uniforms
Norwegian army field uniforms are mainly two different uniforms: M17, a lightweight field uniform for general use, both in garrison and in field. And M02: A field uniform with breathable membrane, which provides protection against moisture and wind.[13] Service uniform M10 is used as ceremonial dress and service dress; blue full dress uniform as ceremonial dress and mess dress.[14] Blue full dress uniforms are used by professional soldiers.
 Mountain gray service uniform M10.
Mountain gray service uniform M10. H.M. Guards full dress uniform.
H.M. Guards full dress uniform.
The goal of the Nordic Combat Uniform Project is to procure a common, flexible combat uniform system for the countries Finland, Sweden, Norway and Denmark. Although the uniform will be the same in the four Nordic countries, the uniforms will look different because the countries will use their own camouflage patterns.[15]
Equipment
Ranks and rank insignia
| NATO code | OF-10 | OF-9 | OF-8 | OF-7 | OF-6 | OF-5 | OF-4 | OF-3 | OF-2 | OF-1 | OF(D) | Student officer | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | Generalløytnant | Generalmajor | Brigader | Oberst | Oberstløytnant | Major | Kaptein/ Rittmester |
Løytnant | Fenrik | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NATO code | OR-9 | OR-8 | OR-7 | OR-6 | OR-5 | OR-4 | OR-3 | OR-2 | OR-1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sersjantmajor | Kommandérsersjant | Stabssersjant | Oversersjant | Sersjant 1. klasse | Sersjant | Korporal | Visekorporal 1. klasse | Visekorporal | Ledende menig | Menig | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Garrisons
| Garrisons | Brigades / Companies |
|---|---|
| Jørstadmoen |
FK KKIS(Defence command and control center) CIS TG (Communications and informations systems task group) CIS (Cyber defence academy) FOST (Defence security agency) |
| Huseby Leir |
HMKG ( His Majesty The King's guard) |
| Rena Leir |
Hærens Våpenskole (Army weapons school) Telemark Battalion and attached medical, engineer and logistics companies provided by respective battalions. HJK/Forsvarets Spesialkommando (Army and Joint special forces command) |
| Terningmoen leir |
Hærens Våpenskole (Army weapons school) HMKG school center (His Majesty The King's guard) AFA-Office (Administrative parental department) |
| Sessvollmoen |
FKL (Logistics support center) FMPS (Defence military police school), FSAN (Defence medical center) |
| Skjold | Brigade Nord
Engineer battalion and 2. battalion |
| Setermoen | Brigade Nord
Armor battalion, Intelligence battalion, Medical battalion and Artillery battalion |
| Bardufoss | Brigade Nord
Signals battalion and CSS battalion |
| Porsangermoen | Garrison of Porsanger |
| Høybuktmoen | Garrison of Sør-Varanger |
| Linderud Leir | Military Academy |
References
- ↑ Niehorster, Dr Leo. "Royal Norwegian Army, 8.04.40". niehorster.org. Retrieved 21 April 2022.
- ↑ Thomas & Volstad 1987, p. 5-6.
- ↑ John Berg, 'High Priority: Country Briefing Norway,' Jane's Defence Weekly, 12 May 2004, p. 25.
- ↑ Stian Eisenträger (28 January 2008). "Hæren kan bare forsvare én Oslo-bydel". VG.
- ↑ Steve James. "Scandinavian governments support Bush's war against terrorism". World Socialist Web Site. Retrieved 4 October 2001.
- ↑ Vegar Gystad. "Vi har trent for dette lenge". Forsvaret (in Norwegian). Archived from the original on 9 November 2007. Retrieved 15 February 2009.
- ↑ Jonathan Tidsall (24 July 2004). "Norwegian soldier killed in Afghanistan". Aftenposten. Archived from the original on 13 March 2008. Retrieved 15 February 2009.
- ↑ Catherine Stein (5 July 2008). "Norwegian base weakest in Afghanistan". Aftenposten. Retrieved 15 February 2009.
- ↑ "Generalinspektør". 26 January 2021.
- ↑ "Hans Majestet Kongens Garde". 15 March 2021.
- ↑ "Army".
- ↑ Forsvarsdepartementet. "Et Forsvar for vår tid". White Paper. Regjeringen. Archived from the original on 15 September 2012. Retrieved 22 April 2012.
- ↑ Generalinspektøren for Hæren (2016). TJ 12-3-3 Bestemmelse for Hærens uniformsantrekk.
- ↑ Forsvarsstaben (2020). Bestemmelser om uniformen.
- ↑ "Har startet testingen av Forsvarets nye uniformer." Forsvarets Forum. Retrieved November 10, 2021.
- 1 2 "Militære grader" [Military ranks]. forsvaret.no (in Norwegian). Norwegian Armed Forces. 13 October 2023. Archived from the original on 26 November 2023. Retrieved 26 November 2023.
- Thomas, Nigel; Volstad, Ron (1987). NATO Armies Today. Elite 16. Oxford: Osprey Publishing. ISBN 0-85045-822-6.


