| Cigale | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Role | |
| Manufacturer | Aubert Aviation |
| Designer | Paul Aubert |
| First flight | 25 February 1938 |
| Number built | ca. 35 |
The Aubert PA-20 Cigale (English: Cicada), PA-204 Cigale Major and PA-205 Super Cigale were a family of high-wing cabin monoplanes built in France in the years immediately before and immediately after World War II. The original Cigale was shown at the 1938 Paris Salon but its development was interrupted by the War. The Cigale was a high wing cantilever monoplane of conventional configuration with fixed, tailwheel undercarriage.
Development
The original two-seat PA-20 Cigale first flew in 1938 powered by a Train 6T. Various refinements were made, including a change to a Renault 4Pei engine, and the aircraft was redesignated PA-201 Cigale. This original aircraft was destroyed during the course of World War II, but in 1945, Paul Aubert returned to the design, building another aircraft to the PA-201 standard. This went on to prove highly successful when flown competitively in 1945 and 1946. Aubert further modified his design into a four-seater, flying the PA-204 Cigale Major on 21 April 1947, and soon building a second example to this standard.
One of the PA-204s was subsequently re-engined first with a SNECMA 4L in 1951 (PA-204S), and then with a Lycoming O-290-D2B (PA-204L) in 1955 and a Lycoming O-320 in 1956 (PA-205 Super Cigale). With this engine, Aubert was finally satisfied with the design and built around thirty production examples, eight of which went to Aéroclub Air France.
Variants
- PA-20 Cigale
- Pre-war prototype two-seat trainer.[1]
- PA-201 Cigale
- Post-war development.[1]
- PA-204 Cigale-Major
- Improved four-seat variant with a Renault 4Pei inverted inline engine. Prototype flew in 1949, with production from 1954.[1][2]
- PA-204S Super Cigale
- Further developed with a Régnier 4L02 engine.[1]
- PA-204L Super Cigale
- Final production variant with an Avro Lycoming engine with a range of power output between 135 and 180 hp.[1]
Specifications (PA-204L)
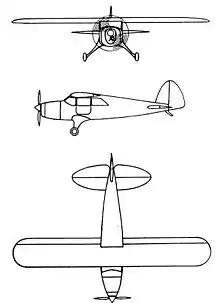
Data from The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Aircraft,[1][3]
General characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Capacity: 3 passengers
- Length: 7.50 m (24 ft 7 in)
- Wingspan: 10.00 m (32 ft 10 in)
- Height: 2.40 m (7 ft 10 in)
- Wing area: 12.90 m2 (138.9 sq ft)
- Aspect ratio: 7.8
- Empty weight: 640 kg (1,411 lb)
- Max takeoff weight: 1,250 kg (2,756 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × Lycoming O-320 flat-four piston engine, 110 kW (150 hp)
- Propellers: 2-bladed Hartzell constant-speed propeller
Performance
- Maximum speed: 255 km/h (158 mph, 138 kn)
- Cruise speed: 230 km/h (140 mph, 120 kn) 70% power
- Landing speed: 90 km/h (56 mph; 49 kn)
- Range: 1,880 km (1,170 mi, 1,020 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 4,500 m (14,800 ft)
- Rate of climb: 4.5 m/s (890 ft/min) at sea level
- Take-off run: 230 m (755 ft)
- Landing run: 120 m (394 ft)
- Fuel consumption: 32 L/h (8 gal/h; 7 imp gal/h)
References
- Bridgman, Leonard (1955). Jane's All The World's Aircraft 1955–56. New York: The McGraw-Hill Book Company.
- Taylor, Michael J. H. (1989). Jane's Encyclopedia of Aviation. London: Studio Editions. p. 83.
- World Aircraft Information Files. London: Bright Star Publishing. pp. File 889 Sheet 83.
- The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Aircraft (Part Work 1982-1985). Orbis Publishing.
External links