| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
28 seats in the House of Assembly 15 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 60.89% ( | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
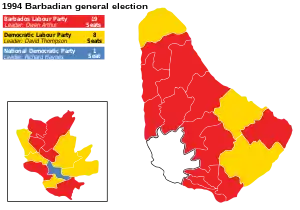 Results by constituency | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
.svg.png.webp) |
|---|
Early general elections were held in Barbados on 6 September 1994.[1] The result was a victory for the opposition Barbados Labour Party, which won 19 of the 28 seats, with its leader Owen Arthur becoming Prime Minister. The ruling Democratic Labour Party led by David Thompson was reduced to only eight seats. The National Democratic Party became the first third party to win a seat since the Barbados National Party in 1966, with NDP leader, Richard Haynes, winning St. Michael South Central.[2] Voter turnout was 60.9%.[1]
Results
 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Votes | % | Seats | +/– | |
| Barbados Labour Party | 60,504 | 48.34 | 19 | +9 | |
| Democratic Labour Party | 47,979 | 38.33 | 8 | –10 | |
| National Democratic Party | 15,980 | 12.77 | 1 | +1 | |
| Independents | 700 | 0.56 | 0 | 0 | |
| Total | 125,163 | 100.00 | 28 | 0 | |
| Valid votes | 125,163 | 99.48 | |||
| Invalid/blank votes | 659 | 0.52 | |||
| Total votes | 125,822 | 100.00 | |||
| Registered voters/turnout | 206,642 | 60.89 | |||
| Source: Caribbean Elections | |||||
References
- 1 2 Dieter Nohlen (2005) Elections in the Americas: A data handbook, Volume I, p90 ISBN 978-0-19-928357-6
- ↑ "Barbados General Election Results - 6 September 1994". Caribbean Elections. Archived from the original on 31 August 2020. Retrieved 25 October 2020.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.

.jpg.webp)
