Metamorphic series include the Barrovian and Buchan series of metamorphic rocks. George Barrow was a geologist in Scotland who discovered the Barrovian series.[1] These are also called metamorphic facies series. A metamorphic facies series is a sequence of metamorphic facies which plot in a temperature-pressure diagram along a line, and this line represents a certain geothermal gradient. They are not the same as metamorphic zones, as these are defined as a region on a geological map where the pressure-temperature conditions for an index mineral (a mineral that indicates the approximate metamorphic grade of a rock), were appropriate for these minerals to form.[2][3]
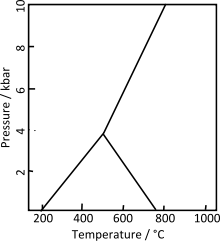
The Buchan and Barrovian facies series relate to this diagram of Al2SiO5 polymorphs (also called a petrogenetic grid), with increasing temperature along the x-axis and increasing pressure along the y-axis. See Metamorphism#Regional
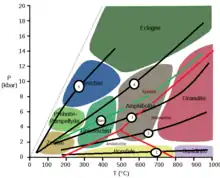
The figure above shows different metamorphic series for different rocks. The names Buchan and Barrovian facies series are often used in another context, i.e. for the kyanite-andalusite-sillimanite polymorphs. However, Buchan facies series plot along line 3 and Barrovian at somewhat higher pressure and with the appearance of kyanite. The facies series have connections to plate tectonics. Facies series 1 is typical of contact metamorphism, but also found in regional metamorphosed rocks. Facies series 2 correlates with volcanic arc environments, and so on: 3. Collisional mountain belts, regional metamorphism 4. Stable continents and 5. Accretionary prisms. Original image: Woudloper.
- Buchan metamorphism has the facies series greenschist-amphibolite-granulite
- Barrovian metamorphism has the same facies series but has approximately 1 kbar more pressure so these rocks form kyanite[4]
References
- ↑ "Regional metamorphism". Tulane University. Retrieved 23 August 2019.
- ↑ Philpotts,A. and Klein,C. Earth Materials, 2013, Cambridge University Press: New York, pp. 398–399.
- ↑ Marshak, S.2015.Earth: Portrait of a Planet, pp. 245–249.
- ↑ Tulane University
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.