 | |||
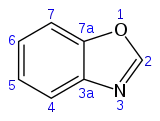
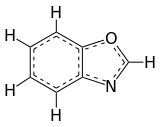 | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,3-Benzoxazole | |||
| Other names
1-Oxa-3-aza-1H-indene | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.445 | ||
PubChem CID |
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C7H5NO | |||
| Molar mass | 119.123 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | White to light yellow solid | ||
| Melting point | 27 to 30 °C (81 to 86 °F; 300 to 303 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 182 °C (360 °F; 455 K) | ||
| Insoluble | |||
| Hazards | |||
| Flash point | 58 °C (136 °F; 331 K) | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds |
oxazole indole benzofuran | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |||
Benzoxazole is an aromatic organic compound with a molecular formula C7H5NO, a benzene-fused oxazole ring structure, and an odor similar to pyridine.[1][2] Although benzoxazole itself is of little practical value, many derivatives of benzoxazoles are commercially important.
Being a heterocyclic compound, benzoxazole finds use in research as a starting material for the synthesis of larger, usually bioactive structures. Its aromaticity makes it relatively stable, although as a heterocycle, it has reactive sites which allow for functionalization.
Occurrence and applications
It is found within the chemical structures of pharmaceutical drugs such as flunoxaprofen and tafamidis. Benzoxazole derivatives are also of interest for optical brighteners in laundry detergents.[3] Benzoxazoles belong to the group of well-known antifungal agents with antioxidant, antiallergic, antitumoral and antiparasitic activity.[4]
-cis-stilbene.svg.png.webp) 4,4'-(E)-bis(benzoxazolyl)stilbene is intensely fluorescent and its derivatives are used as optical brighteners
4,4'-(E)-bis(benzoxazolyl)stilbene is intensely fluorescent and its derivatives are used as optical brightenersthiophene.svg.png.webp) 2,5-bis(benzoxazol-2-yl)thiophene is also intensely fluorescent and its derivatives are used as optical brighteners, e.g. in laundry detergents[5]
2,5-bis(benzoxazol-2-yl)thiophene is also intensely fluorescent and its derivatives are used as optical brighteners, e.g. in laundry detergents[5]
See also
- Structural isomers
- Anthranil, an analog with the oxygen atom in position 2
- Benzisoxazole, an analog with the nitrogen atom in position 2
- Analogs
- Benzimidazole, an analog with the oxygen replaced by a nitrogen
- Benzothiazole, an analog with the oxygen replaced by a sulfur
- Benzopyrrole or indole, an analog without the oxygen atom
- Benzofuran, an analog without the nitrogen atom
References
- ↑ Katritzky, A. R.; Pozharskii, A. F. (2000). Handbook of Heterocyclic Chemistry (2nd ed.). Academic Press. ISBN 0080429882.
- ↑ Clayden, J.; Greeves, N.; Warren, S.; Wothers, P. (2001). Organic Chemistry. Oxford, Oxfordshire: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-850346-6.
- ↑ E. Smulders, E. Sung "Laundry Detergents, 2. Ingredients and Products" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2012. doi:10.1002/14356007.o15_013
- ↑ Şener, E., Yalçin, İ. and Sungur, E.: QSAR of some antifungal benzoxazoles and oxazolo(4,5-b)pyridines against C. Albicans. Quant. Struct.-Act. Relat. 10 (1991) 223-228.
- ↑ Fourati, M. Amine; Maris, Thierry; Skene, W. G.; Bazuin, C. Géraldine; Prud’homme, Robert E. (3 November 2011). "Photophysical, Electrochemical and Crystallographic Investigations of the Fluorophore 2,5-Bis(5-tert-butyl-benzoxazol-2-yl)thiophene". The Journal of Physical Chemistry B. 115 (43): 12362–12369. doi:10.1021/jp207136k. PMID 21916450.