In geometry, a bicone or dicone (from Latin: bi-, and Greek: di-, both meaning "two") is the three-dimensional surface of revolution of a rhombus around one of its axes of symmetry. Equivalently, a bicone is the surface created by joining two congruent, right, circular cones at their bases.
A bicone has circular symmetry and orthogonal bilateral symmetry.
Geometry
For a circular bicone with radius R and height center-to-top H, the formula for volume becomes
For a right circular cone, the surface area is
- where is the slant height.
| Bipyramid name | Digonal bipyramid | Triangular bipyramid (See: J12) |
Square bipyramid (See: O) |
Pentagonal bipyramid (See: J13) |
Hexagonal bipyramid | Heptagonal bipyramid | Octagonal bipyramid | Enneagonal bipyramid | Decagonal bipyramid | ... | Apeirogonal bipyramid |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyhedron image | 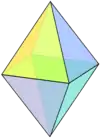 |
 |
 |
 |
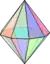 |
 |
... | ||||
| Spherical tiling image |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Plane tiling image | |
| Face config. | V2.4.4 | V3.4.4 | V4.4.4 | V5.4.4 | V6.4.4 | V7.4.4 | V8.4.4 | V9.4.4 | V10.4.4 | ... | V∞.4.4 |
| Coxeter diagram | ... |
See also
References
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.