| Septal nasal cartilage | |
|---|---|
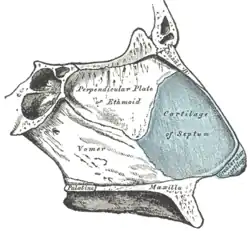 Bones and cartilages of the septum of the nose. Right side (cartilage of the septum visible as the blue structure at right) | |
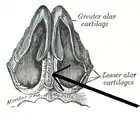 Cartilages of the nose, seen from below (cartilage of septum visible in blue at bottom center) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Cartilago septi nasi |
| TA98 | A06.1.01.013 |
| TA2 | 946 |
| FMA | 59503 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The septal nasal cartilage (cartilage of the septum or quadrangular cartilage) is composed of hyaline cartilage.[1] It is somewhat quadrilateral in form, thicker at its margins than at its center, and completes the separation between the nasal cavities in front.
Its anterior margin, thickest above, is connected with the nasal bones, and is continuous with the anterior margins of the lateral cartilages; below, it is connected to the medial crura of the major alar cartilages by fibrous tissue.
Its posterior margin is connected with the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid; its inferior margin with the vomer and the palatine processes of the maxillae.
References
- ↑ Saladin, Kenneth S. (2012). Reeder, Greg (ed.). Supplement to Accompany Kenneth S. Saladin's Anatomy & Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function (6th ed.). New York, NY: McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-747213-9. OCLC 1027903304.
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 992 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 992 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- Anatomy figure: 33:02-01 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Diagram of the skeleton of medial (septal) nasal wall."
- Atlas image: rsa1p7 at the University of Michigan Health System - "Nasal septum, lateral view"
- lesson9 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (nasalseptumbonescarti)