51°25′05″N 0°31′48″E / 51.418°N 0.530°E
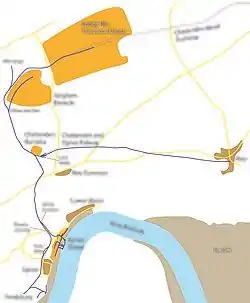 The route of the Chattenden and Upnor Railway | |
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Headquarters | Chattenden |
| Locale | England |
| Dates of operation | 1885–1961 |
| Successor | Abandoned |
| Technical | |
| Track gauge | 2 ft 6 in (762 mm) |
The Chattenden and Upnor Railway (also known as the Lodge Hill and Upnor Railway[1]) was a narrow gauge railway serving the military barracks and depot at Upnor, Kent and associated munitions and training depots. It started life in the early 1870s as a standard-gauge railway. The 2 ft 6 in (762 mm) narrow gauge working began in 1885, initially in a mixed gauge formation with the standard gauge, and post circa 1903 2 ft. 6 in. gauge exclusively. In the latter form the line continued in use until the end of 1961.
History
Precursors
The first railway at Chattenden was a standard gauge line laid by the Royal Engineers in the early 1870s. This was used to bring building materials from a wharf at Upnor to be used in the construction of the Chattenden Munitions Depot.[2] According to a report in the issue of "Iron" dated Saturday 29 May 1875: "A detachment of non-commissioned officers and men of the Royal Engineers, commanded by Lieutenant Barker, on Saturday left the School of Military Engineering at Chatham for Upnor, where they will be quartered for some time, as they are to be employed to lay down lines of rails to connect forts on the Thames and Medway with the new powder magazines to be constructed at Chattenden Roughs, a few miles from the old magazines at Upnor Castle. It is expected that more than forty miles of these railways will be constructed."[3] This railway fell out of use when the building work was completed.[2]
An 18 in (457 mm) railway is thought to have been laid to help with the construction of the standard gauge line. An 0-4-0ST locomotive, called Burgoyne, built by Manning Wardle in 1873 (works no. 448), would have been used in construction, although it may also have been used on the Chatham Eastern Defences 18 inch gauge railway and worked on Borstal Prison construction work. Burgoyne was identical as built to Busy Bee (Manning Wardle 424 of 1872 for the Admiralty at Chatham Dockyard) and was a member of the classic Manning Wardle '6 by 8' 0-4-0ST specification.
Opening
In 1885, members of the Royal School of Military Engineering laid an experimental 2 ft 6 in (762 mm) gauge railway on the trackbed of the standard gauge line, initially retaining the standard gauge as a third rail in at least some places. The steep gradients involved allowed the engineers to test the effectiveness of narrow-gauge railways over hilly terrain (according to an article in 'The Locomotive' magazine in 1903, some standard gauge was still extant at this stage). The last standard gauge locomotives were transferred to the Royal Arsenal at some stage between 1898 and 1906.The 1885 gauge adaptation was at the behest of Royal Engineers officers such as Major John Hogg, who were mindful of the shortcomings of the 18 inch gauge lines laid during the abortive Suakin Campaign of the Spring that year. At the time 2 ft 6 in (762 mm) gauge railways were being used extensively in the North-West Frontier Province of India.[4] Sadly, although no steam locomotives of the Royal Engineers era on the C. & U.R. currently survive, probably the main legacy of the railway in this era was the use of 36 2 ft. 6 in. gauge Bagnall 2-4-2ST's supplied to the Indian States Military Railways in 1901-5 as a Strategic Reserve. Examples saw use in Mesopotamia during World War One and two survive in India today. The locomotives, although of a different wheel arrangement, showed a marked family resemblance to Bagnall 1514 of 1897 (see below).
World Wars
The Chattenden and Upnor Railway line was taken over by the Admiralty on 1 April 1906.[2] Two new locomotives, Fisher and Chevalier were purchased just after the start of the First World War to deal with the rise in munitions traffic. In 1918, five Greenwood and Batley battery-electric locomotives were purchased, to work the lines into the munitions stores where steam locomotives were a fire risk.[1]
In 1931 the railway had 91 powder wagons, 16 box wagons to carry ammunition, 17 assorted wagons for ballast, an officers‘ carriage, 7 workmen‘s carriages, 3 brake vans, and a breakdown van.
Two final steam locomotives, Burnett Hall and Norbury were purchased in 1933 and 1934.[1] These were the main locomotives in use at the start of the Second World War. In 1943, the first of a series of diesel locomotives were purchased.[1]
Closure
By 1896, the last 1⁄4 mile (0.40 km) of the Hoo branch had been lifted,[5] with the remainder removed by 1909.[6]
By 1941, the section of the branch from Upnor to the Tank Field signal box was mostly out of use, and the remaining section to Pontoon Hard (Upper Upnor) was closed.[4] The rest of the line closed on 31 December 1961.[2] The track was lifted in December 1965.[1]
Passenger services
The line was never opened to the public, but passenger services were run for munitions workers. In 1891 there were nine passenger trains running each day.[1]
During the Second World War, passenger trains were revived using bogie carriages built by Charles Roberts & Co. Ltd. in 1942. These continued until 19 May 1961.[2]
Route

The railway started at the Lodge Hill munitions depot, at interchange sidings with the standard gauge Chattenden Naval Tramway. It curved around the west end of Chattenden Magazines Enclosure to Lutnor Junction, where a branch ran back into the magazines. The main line continued southeast for 1⁄4 mile (0.40 km) to Chattenden Barracks, where the line's locomotive sheds and workshops were located. A long branch ran east from here to the village of Hoo.[6]
South of Chattenden Barracks, the line rose on an embankment to cross the A228 road on an overbridge. It then continued south to Upnor Junction, where two branches ran down to the bank of the River Medway. One branch ran west past Tank Field, to the Upper Pontoon Hard near Frindsbury. The other ran into the Upnor Depot.[7]
The railway had several sections of steep gradients. From Upnor Depot to Church Crossing the line rose at 1 in 26, from there to Upnor Junction the gradient was 1 in 30. There was also a section of 1 in 34 approaching the west gate of Lodge Hill depot.[1]
Accidents
On 17 March 1907, Colonel Brabazon, the senior officer at Lodge Hill Depot, had a photograph taken of the 78 employees. The locomotive Lancashire hauled a special train to bring all the employees up to the depot. The driver was in the group, waiting for the photograph to be taken when the locomotive began to move. It ran away on the downhill gradient in the direction of Upnor and derailed on the curve around Issingham Barracks. The line only had a 5-ton jackscrew and a large crew spent most of the next day re-railing the locomotive.[1]
Standard Gauge Locomotives
Built for the Army
| Name/Number | Builder | Type | Date | Works number | Image | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steam Sapper No. 5 | Aveling & Porter | 2-2-0 GT Single Cylinder | 1872 | 830 | The 'Steam Sappers' were mainly Aveling and Porter road locomotives (one of which, Steam Sapper No. 8 saw use during the Anglo-Ashanti Conflict of 1873-4) although three of their number were fitted with rail wheels, one for trial purposes and two as built. It seems that Nos. 5 and 9 constituted the original mechanical power on the C. & U. R. The main advantage of these single cylinder machines lay in the fact that they could be put to use to drive stationary machinery but their lack of springing and slow overall speed would have ensured that they would have been of limited use in ordinary service. | |
| Steam Sapper No. 9 | Aveling & Porter | 2-2-0 GT Single Cylinder | 1872 | 722 | Originally delivered to War Department, Shoeburyness as a road locomotive. Fitted with rail wheels in 1873 at transferred to the Chattenden system. | |
| Steam Sapper No. 12 | Aveling & Porter | 2-2-0 GT Single Cylinder | 1877 | 1316 | ||
| Royal Engineer | Manning Wardle & Co. | 0-4-0ST Outside Cylinder | 1876 | 602 | Later sold to Wm. Rigby & Co., Erith | |
| Vauban | Manning Wardle & Co. | 0-4-0ST Outside Cylinder | 1885 | 937 | Built for Suakin Campaign. To Royal Arsenal Railways, Woolwich as Thor circa 1903. To W.D. Slough 1918. Scrapping date unknown. | |
| Burgoyne | Manning Wardle & Co. | 0-6-0ST Inside Cylinder | 1885 | 949 | Built for Suakin Campaign. To Royal Arsenal Railways, Woolwich as Kimberley circa 1903. To J. F. Wake, Darlington 11/1919. Scrapped after 6/1925. | |
| Manning Wardle & Co. | 0-4-0ST Outside Cylinder | 1885 | 962 | Built for Suakin Campaign. To Royal Arsenal Railways, Woolwich as Lord Roberts circa 1903. Scrapped 1/1916 after re-instatement 6/1914. | ||
2 ft. 6 in. Gauge Locomotives
Built for the Army
| Name/Number | Builder | Type | Date | Works number | Image | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon | Yorkshire Engine Company | 0-4-2T | 1885 | 404 |  |
Scrapped by 1914[8] |
| Sulphur | Yorkshire Engine Company | 0-4-2T | 1885 | 405 | Identical to Carbon.[9] Scrapped 1932[10] | |
| Yorkshire | John Fowler | 0-4-4T | 1887[11] | 5350 |  |
Scrapped after sighting near Strood Station 1932. |
| Cheshire[4] | W.G. Bagnall | 0-4-2T | 1890 | 1260 | Lower leading part of mainframe with coupled wheels and cylinders detachable and exchangeable with Cumberland
Experimental design for potential front line use. Ex-War Department, Crewe. Scrapped after sighting near Strood Station 1932.[8] | |
| Lancashire | Yorkshire Engine Company | 0-4-4T | 1891 | 462 |  |
Scrapped after sighting near Strood Station in 1932.[8] |
| Cumberland | Lowca Engineering Company | 0-4-2T[10] | 1893 | 220 | Lower leading part of mainframe with coupled wheels and cylinders detachable and exchangeable with Cheshire
Experimental design for potential front line use. Withdrawn by 1904 advertised for sale and scrapped circa 1909. | |
| Stafford, later Eardley Wilmot | W.G. Bagnall | 0-6-0T | 1897 | 1513 | ex-War Department, South Africa, 1901. Renamed Eardley Wilmot 1915. Scrapped in 1941.[10] | |
| Bagnall | W.G. Bagnall | 0-6-0ST | 1897 | 1514 | ex-War Department, South Africa, 1901. Scrapped after sighting near Strood Station 1932[10] | |
| Lord Kitchener | Yorkshire Engine Company | 0-6-2T | 1902 | 711 |  |
New.[11] To Chatham Dockyard for scrap 1948; scrapped 1954. |
| Pioneer | Yorkshire Engine Company | 2-6-2ST | 1903[10] | 757 |  |
Experimental design for potential front line use. Oil Fired as built. Bar frames. To Woolmer Instructional Military Railway in 1905. To the Pentewan Railway in 1912.[1] To Government 1918. For Sale at Newbury Racecourse 1922 shortly afterwards scrapped. |
| none[12] | Richard Hornsby & Sons | 0-6-6-0DM | 1903 | 6234 | .jpg.webp) |
Hornsby-Akroyd 20 hp compression-ignition (semi-diesel) engine. Underpowered, inefficient transmission, noisy and difficult to start. Disposal unknown. |
| Ascension[13] | Avonside Engine Company | 0-4-0T | 1904 | 1480 | To Admiralty, Hoo Fort, by 1928.[1] |
Built for the Admiralty
| Name/Number | Builder | Type | Date | Works number | Image | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eardley Wilmot | McEwan Pratt | 0-6-0PM | 1911 | not known |  |
Unfinished when McEwan Pratt went into receivership in 1911. Completed at Chatham Dockyard but never successful. 80 hp 4cyl petrol engine. Offered for sale as scrap 1922.[14] |
| Chevallier | Manning Wardle | 0-6-2T | 1915 | 1677 |  |
Sold to the Bowaters Paper Railway in 1950, subsequently sold to the Great Whipsnade Railway[15] |
| Fisher | Dick Kerr and Company | 0-6-2T | 1915 | 13996 | Scrapped 1954[10] | |
| Burnett Hall[4] | Avonside | 0-4-2T | 1933 | 2070 | Scrapped 1956. Nameplate on display at Amberley Museum. | |
| Norbury[4] | Peckett | 0-4-2T | 1934 | 1868 | Scrapped 1955. Nameplate on display at Amberley Museum. | |
| 83 | Ruston and Hornsby | 4wDM | 1943 | 213838 | Sold 1960[10] | |
| Yard No. 92[10] | Hunslet | 0-6-0DM | 1946 | 3301 | Sold 1961[10] | |
| Yard No. 84 | Ruston and Hornsby | 4wDM | 1947 | 242919 | To RNAD Crombie[10] | |
| Yard No. 85[10] | Drewry | 0-6-0DM | 1949 | 2263 |  |
Transferred to RNAD Ernsettle in October 1960,[10] then to the Welshpool and Llanfair Light Railway in 1968 and named Chattenden |
| Yard No. 44[10] | Hibberd Planet | 4wDM | 1954 | 3687 |  |
Sold to the Welshpool and Llanfair Light Railway in 1962,[10] named Upnor Castle, sold to the Ffestiniog Railway and regauged to 1 ft 11+1⁄2 in (597 mm) |
| Yard No. 45[1] | Ruston and Hornsby | 4wDM | 1952 | 268878 | Moved to RNAD Ernsettle in November 1960. |
Battery-electric
A large number of battery-electric locomotives were used, mainly to move munitions around the Lodge Hill depot. Six supplied in 1928 were also suitable for use on the main line. They had central cabs with large square-cornered windows and tramway skirts covering the wheels. These were replaced by six Greenwood and Batley 8-ton locomotives built between 1938 and 1945.[1]
The rest of the battery-electric fleet were motorised wagons without cabs that were restricted to use in the depot. Twenty-four were supplied by Greenwood and Batley in batches between 1918 and 1948. Seven came from Wingrove & Rogers and two were built in the workshops at Lodge Hill.[1]
Rolling Stock
| Number | Type | Size | Version | Builder | Year | Image | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Brake Van | v1 | Oldbury | Angled bay window sides | |||
| Brake Van | v1a | Oldbury | Straight bay window sides | ||||
| 212 | Brake Van | v2 | |||||
| 213 | Brake Van | v2 | Converted to Breakdown Van | ||||
| Four Wheel Coach | v1 | ||||||
| Four Wheel Coach | v2 | Converted to Ambulance Van | |||||
| Combination Coach | v1 | ||||||
| Combination Coach | v2 | Wickham & Co. | 1957 | ||||
| 196 | Bogie Coach | v2 | Cravens | 1941 | In preservation at the Sittingbourne and Kemsley Light Railway | ||
| 198 | Bogie Coach | v2 | Cravens | 1941 | |||
| 199 | Bogie Coach | v2 | Cravens | 1941 | In preservation at the Sittingbourne and Kemsley Light Railway | ||
| 200 | Bogie Coach | v2 | Cravens | 1941 | In preservation at the Sittingbourne and Kemsley Light Railway | ||
| 202 | Bogie Coach | v1 | |||||
| 204 | Bogie Coach | v1 | Under restoration at the Sittingbourne and Kemsley Light Railway | ||||
| 12 | Bogie Van | 10T | Oldbury | ||||
| 16 | Bogie Flat | 10T | Leeds Forge Co. | ||||
| 18 | Bogie Well Wagon | 10T | |||||
| 19 | Bogie Low Side | 10T | Leeds Forge Co. | ||||
| 20 | Bogie Low Side | 10T | R.Y. Pickering | ||||
| 21 | Bogie Low Side | 10T | R.Y. Pickering | ||||
| 26 | Bogie Low Side | 10T | R.Y. Pickering | ||||
| 27 | Bogie Low Side | 10T | R.Y. Pickering | ||||
| 28 | Bogie Low Side | 10T | R.Y. Pickering | ||||
| 32 | Bogie Low Side | 10T | Cravens | ||||
| 33 | Bogie Low Side | 10T | Cravens | ||||
| 35 | Bogie Low Side | 10T | Cravens | ||||
| 38 | Bogie Low Side | 10T | Cravens | ||||
| 41 | Bogie Low Side | 10T | Cravens | ||||
| 45 | Bogie Low Side | 10T | |||||
| 48 | Bogie High Side | 10T | v1 | ||||
| 60 | Bogie High Side | 10T | v2 | Cravens | |||
| 65 | Bogie High Side | 10T | v2 | Cravens | |||
| 66 | Bogie High Side | 10T | v2 | Cravens | |||
| 53 | Powder Van | 3T | v1 | Wood Frames. Height modified to match 5T. Early photo (probably renumbered at a later date). | |||
| 69 | Powder Van | 3T | v1b | ||||
| 99 | Powder Van | 3T | v1 | Wood Frames | |||
| 110 | Powder Van | 3T | v1a | ||||
| 111 | Powder Van | 3T | v1 | Wood Frames | |||
| 130 | Powder Van | 3T | v1a | ||||
| 158 | Powder Van | 3T | v5 | Angled Roof | |||
| 179 | Powder Van | 3T | v4 | Angled Roof | |||
| 106 | Powder Van | 5T | v5a | Angled Roof | |||
| 68 | Powder Van | 5T | v2 | ||||
| 97 | Powder Van | 5T | v2 | ||||
| 121 | Powder Van | 5T | v6 | ||||
| 142 | Powder Van | 5T | v6 | ||||
| 69 | Powder Van | 5T | v3 | Early photo (probably renumbered at a later date as a 3T van was also numbered 69). | |||
| 112 | Powder Van | 5T | v3 | ||||
| 128 | Powder Van | 5T | v3 | ||||
| 137 | Powder Van | 5T | v3 | ||||
| 140 | Powder Van | 5T | v3 | ||||
| 171 | Powder Van | 5T | v3 |
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Yeatman, D. (December 1966). "Lodge Hill and Upnor Railway". The Industrial Railway Record. The Industrial Railway Society. 12: 277–292.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "The Chattenden & Upnor Railway". The Railway Magazine. January 1962.
- ↑ "Letters to the Editor". The Industrial Railway Record. 15: 118. September 1967.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Hayton, J. Roland (May 1941). "The Chattenden & Upnor Narrow-Gauge Railway". The Railway Magazine. pp. 207–211.
- ↑ Ordnance Survey (1896). County Series: Kent (Map). 1:2500.
- 1 2 Ordnance Survey (1909). County Series: Kent (Map). 1:10560.
- ↑ Hayton, J. Roland (June 1937). "Light Railways of the Hundred of Hoo". The Railway Magazine. pp. 395–397.
- 1 2 3 "Letters to the Editor". The Industrial Railway Record. 14: 79. June 1967.
- ↑ Halton, Peter (October 1966). "Chattenden & Upnor Railway". The Narrow Gauge. No. 42. The Narrow Gauge Railway Society. pp. 13–15.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Lyne, R.M. (1983). Military Railways in Kent. Ramsgate: North Kent Books. ISBN 0-948305-04-5.
- 1 2 "Letters to the Editor". The Industrial Railway Record. 14: 73. June 1967.
- ↑ Smithers, Mark (2016). The Royal Arsenal Railways. Pen and Sword. p. 112.
- ↑ ""W.D." locomotives of earlier years". The Railway Magazine. December 1941. pp. 586–587.
- ↑ "Ministry of Munitions Locomotives". The Industrial Railway Record. 55: 304. August 1974.
- ↑ "Whipsnade Steam". The Railway Magazine. November 1973. p. 575.
- Thomas, Cliff (2002). The Narrow Gauge in Britain & Ireland. Atlantic Publishers. ISBN 1-902827-05-8.
- Mitchell, Vic; Smith, Keith (2000). Kent Narrow Gauge. Middleton Press. ISBN 1-901706-45-1.