 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
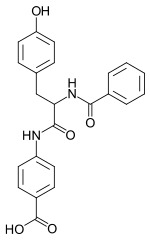
| Preferred IUPAC name
4-[(2S)-2-Benzamido-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanamido]benzoic acid | |
| Other names
(S)-4-((2-(benzoylamino)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl) -1-oxopropyl)amino)benzoic acid (S)-p-(α-benzamido-p-hydroxyhydrocinnamamido) benzoic acid Benzoyltyrosyl-p-aminobenzoic acid (Btpaba)Chymex N-benzoyl-L-tyrosyl-p-aminobenzoic acid P-((N-benzoyl-L-tyrosin)amido)benzoic acid Chymex (trade name) | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| Abbreviations | Btpaba |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.048.484 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C23H20N2O5 | |
| Molar mass | 404.4153 g/mol |
| Pharmacology | |
| V04CK03 (WHO) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Bentiromide is a peptide used as a screening test for exocrine pancreatic insufficiency and to monitor the adequacy of supplemental pancreatic therapy. Bentiromide is not available in the United States or Canada; it was withdrawn in the US in October 1996.[2]
Side effects
Headache and gastrointestinal disturbances have been reported in patients taking bentiromide.[2]
Mechanism of action
Bentiromide is given by mouth as a noninvasive test. It is broken down by the pancreatic enzyme chymotrypsin, yielding p-aminobenzoic acid (PABA). The amount of PABA and its metabolites excreted in the urine is taken as a measure of the chymotrypsin-secreting activity of the pancreas.
Chemistry
- XLogP=3.201
- H_bond_donor=4
- H_bond_acceptor=5
Synthesis
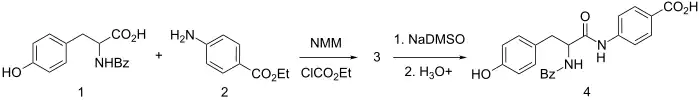
It is synthesized by amide formation between ethyl p-aminobenzoate and N-benzoyl-tyrosine using N-methyl-morpholine and ethyl chlorocarbonate for activation. The resulting L-amide is selectively hydrolyzed by sequential use of dimsyl sodium (NaDMSO) and dilute acid to give bentiromide (4).
See also
References
- ↑ Bentiromide – Compound Summary, PubChem.
- 1 2 Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information on bentiromide.
- ↑ P. L. De Benneville, N. J. Greenberger, DE 2156835; eidem, U.S. Patent 3,801,562 (1972, 1974 both to Rohm & Haas).
- ↑ Debenneville, Peter L.; Godfrey, William J.; Sims, Homer J.; Imondi, Anthony R. (1972). "New substrates for a pancreatic exocrine function test". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 15 (11): 1098. doi:10.1021/jm00281a002. PMID 4654657.