
Carrier Routing System (CRS) is a modular and distributed core router developed by Cisco Systems Inc that enables service providers to deliver data, voice, and video services over a scalable IP Next-Generation Network (NGN) infrastructure. In a network topology, these routers are generally positioned in the core or edge of a service provider network. They are also used by Over-the-top content providers and large enterprises. It supports a wide range of interface speeds and types such as channelized OC3, OC12 to OC768 on Packet over SONET and from 1GE, 10GE all the way to 100GE on the Ethernet technologies. A standalone CRS-3 system can handle 2.2Tbit/s and a multi-chassis system could be designed to handle 322Tbit/s.
Architecture
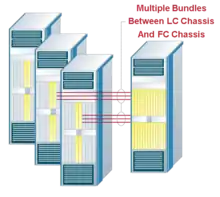
A standalone Carrier Routing System is deployed with a Line card chassis (LCC). The three main functional units of this LCC are the Line cards, Switching fabric and Route processor. The Line card consists of the physical interface card and a modular services card. The physical connectivity could be using fiber-optic cables or using Twisted pair cables. The routing decisions are made by the route processor and the switching fabric takes care of the routing based on the Route processor input. The CRS runs IOS XR which is said to be designed for high-end carrier grade routers and was launched with CRS-1. In a multi-chassis deployment, the Line card chassis is used along with another variety of chassis called as the Fabric Card Chassis (FCC). The architecture enables scalability by increasing the number of Line Card Chassis and/or Fabric Card Chassis. In both single- and multi-chassis configurations, the CRS switch fabrics are based on a three-stage Beneš architecture. In a single-chassis system, the three switching stages—S1, S2, and S3—are all contained on one fabric card. In a multi-chassis system, the S2 stage is contained within the Fabric Card Chassis, with the S1 and S3 stages resident in the Line Card Chassis.
The CRS Line card chassis comes in three different flavors: 4-slot, 8-slot and 16-slot. The number of slots indicates the number of line cards that the chassis can accommodate. There is only one variety of Fabric card chassis.
 4-slot
4-slot 8-slot
8-slot 16-slot
16-slot
Deployment
- Internet service providers
- Mobile network operators
- Over-the-top content
- Wireline services
- Service providers: P, PE, Peering
- Large enterprises
Product Portfolio
CRS-X
Cisco Systems has announced the addition of a new product to its existing CRS family, the Carrier Routing System X, or CRS-X (C-R-S-Ten), which is expected to be 10 times faster than the first CRS model (CRS-1) the company offered, back in 2004.[1] CRS-X is said to be a 400Gbit/s per slot system and is backward compatible with the previous generation HW. At the time of launch, CRS-X family has three different flavors of physical interface card (40x10GE, 4x100GE and 2x100GE-Flex-40) apart from the improved fabric and modular service cards.
| Model | Number of slots | Aggregate switching capacity |
|---|---|---|
| CRS-X 16 Slot | 16 | 12.8 Tbit/s |
| CRS-X 16 Slot: Back-to-Back | 32 | 25.6 Tbit/s |
| CRS-X Multi-Chassis | Up to 1152 | Up to 921.6 Tbit/s |
Cisco states that the CRS-X can be used in back-to-back & multi-chassis deployments and that CRS-1, CRS-3 & CRS-X can co-exist in a multi-chassis setup. The press release (reference) also claims that, the CRS-X 400 GE Line Card with Cisco AnyPort Technology uses Cisco’s CMOS photonic CPAK to reduce power consumption, heat dissipation and increase 100 GE port densities by a factor of three compared to competitive solutions. The Universal Port concept adds the option of using a 100G port as 2 ports of 40G or 10 ports of 10G. 40G can again be used as 4 ports 10G. This product will go up against Juniper Networks’ T4000 and PTX core routing systems and perhaps Alcatel-Lucent’s 7950 XRS.
CRS-3
The CRS-3 is the second generation of the CRS series launched in March, 2010. In CRS-3 each line card slot has a capacity of 140Gbits/s, which is more than three times the capacity of the previous CRS-1 generation. The architecture is retained as in the previous generation and hardware is compatible with the CRS-1 system. Apart from the single-chassis system and the multi-chassis system, CRS-3 supports back-to-back configuration as well. In this configuration, two Line Card Chassis are connected back-to-back and there is no Fabric Card Chassis involved as in the case of a multi-chassis configuration. This configuration works only for the 8-slot and 16-slot chassis models. CRS-3 also supports IPoDWDM. This solution reduces transport elements, while supporting multilayer features such as proactive protection and control plane interaction, reducing operating expenses and capital costs. AT&T Corporation tested the CRS-3 in a live-network using the 100 Gb Ethernet backbone and the Dutch telco KPN Telecom selected the CRS-3 platform for their new NextGen IP backbone.[2]
| Model | Number of slots | Max. Full-Duplex throughput per system | Link to product-specs |
|---|---|---|---|
| CRS-3 4 slot single shelf | 4 | 1.12 Tbit/s | Cisco CRS-3 4-Slot Single-Shelf System |
| CRS-3 8 slot single shelf | 8 | 2.24 Tbit/s | Cisco CRS-3 8-Slot Single-Shelf System |
| CRS-3 16 slot single shelf | 16 | 4.48 Tbit/s | Cisco CRS-3 16-Slot Single-Shelf System |
| CRS-3 multishelf platform | 1152 | 322 Tbit/s | Cisco CRS-3 24-Slot Fabric-Card Chassis |
CRS-1
CRS-1 is the first generation of Carrier Routing System launched in 2004. This replaced the Cisco 12000 routers which were used as core routers. Each slot of CRS-1 has a capacity of 40Gbit/s. CRS-1 supports both standalone and multi-chassis configurations.
| Model | Number of slots | Max. Full-Duplex throughput per system | Link to product-specs |
|---|---|---|---|
| CRS-1 4 slot single shelf | 4 | 320 Gbit/s | Introducing the 4 slots CRS-1 Interactive presentation CRS-1:4 |
| CRS-1 8 slot single shelf | 8 | 640 Gbit/s | Introducing the 8 slots CRS-1 Cisco CRS-1 8-Slot Single-Shelf System |
| CRS-1 16 slot single shelf | 16 | 1.2 Tbit/s | Presentation of 16 slots CRS-1 Cisco CRS-1 16-Slot Single-Shelf System |
| CRS-1 multishelf platform | 1152 | 92 Tbit/s | General brochure for the CRS-1 series Cisco CRS-1 24-Slot Fabric-Card Chassis |
See also
References
- ↑ Cisco newsroom Cisco Adds Carrier Routing System X (CRS-X) Core Router to Industry-Leading CRS Family Archived June 9, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ Press coverage Cisco CRS-3 router Archived June 9, 2011, at the Wayback Machine, visited 5 August 2010
External links
- New Cisco core router boasts 10X capacity of original
- X' Marks Cisco's NewCore-Router Upgrade
- Cisco Plans To DoubleThe Speed Of The Internet
- Introduction to CRS - video
- Cisco CRS-1 & CRS-3
- Cisco IOS XR Software General Information
- Major CRS-1 Deployments
- Source
- Cisco CRS 1 News Release
- Cisco CRS-1 Architecture Inside Analysis(Chinese Version)
- Cisco CRS-3 Press Release
- Cisco says new monster CRS-3 router paves way for more powerful Internet