An International Motor Insurance Card System is an arrangement between authorities and insurance organizations of multiple states to ensure that victims of road traffic accidents do not suffer from the fact that injuries or damage sustained by them were caused by a visiting motorist rather than a motorist resident in the same country.
Additionally to extending the insurance coverage territorial scope such systems have the benefit for motorists to avoid the need to obtain insurance cover at each of the frontiers of the countries which they visit.
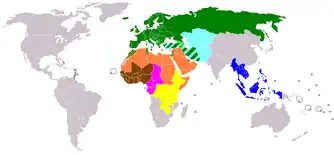
There are multiple motor insurance systems around the world, established on regional basis. The first was the Green Card system established in 1949 in Europe, but later other regions followed suit.
Green card system

The Council of Bureaux (COB)[1] maintains an international motor insurance card system in and around Europe where the certificate issued is known by the name green card. In 1949 the system was established in the framework of UNECE. At later stage the EU and EFTA were involved and reflecting the deepening of the links with them the CoBx secretariat was relocated from London to Brussels in 2006.[2]
Around 300,000 motor accidents a year were covered in Europe by the green card system during the year 2004 according to a survey.[3]
In 2016, the green card system counts around 377,666 international accidents within the green card area.[4]
At the origin, the green card was checked while crossing the border. However, inside the European single market the green card is no longer checked at internal borders. Insurance for motorized vehicles remains mandatory within the European union. Some countries (such as France and Belgium [3]) have kept the green card as their national/domestic system of insurance, which make the green card a compulsory requirement in those nations.[5]
A green card is usually issued when the insurance policy starts; but in some cases the green card is only issued later, upon request.[6] Insurers do not make people pay to have a green card, but intermediaries, including insurance brokers, are allowed in the UK to charge an administration fee.[7]
In each member state of the green card system the insurance companies established green card bureaux operating with the recognition and approval of the government and the activities of the Green Card Bureaux are established by law or regulation in each of the countries participating in the system. Each green card bureau has two functions:
- As a "bureau of the country of the accident", it has responsibility in accordance with national legal provisions for compulsory third party motor insurance for the handling and settlement of claims arising from accidents caused by visiting motorists.
- As a "guaranteeing bureau" it guarantees certificates of motor insurance ("green cards"), which are issued by its member insurance companies to their policyholders.
36 of the 47 Countries participating in the Green Card system have replaced the Green Card by a Multilateral Agreement which means the Green Card is no longer a required document when crossing the borders between those countries. There are three types of green card member states as per the multilateral agreement. [8][9]
- EEA members (EU member states, Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway)
- members under section III of the Internal Regulations of the Council of Bureaux (which refers to the multilateral agreement) with the EEA members: Andorra, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, Serbia, Switzerland and the United Kingdom.[10]
- the rest of the green card members
Membership and geographic limits
The green card system is primarily a European system. It presently includes most, but not all European countries, and some of their neighbors, in most cases bordering the Mediterranean Sea. The position of the COB is that the green card system could be joined by the countries "west of the Urals and the Caspian Sea and countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea", but this rule is not followed strictly as Iran and Iraq fall outside of the area as described.
| Country | Year | Single "box" (EEA) box[11][12] |
|---|---|---|
| (1949) | single box as an EEA member | |
| (1949) | linked to EEA by a Multilateral Agreement | |
| (1949) | single box as an EEA member | |
| (1949) | single box as an EEA member | |
| (1949) | single box as an EEA member | |
| (1949) | single box as an EEA member | |
| (1949) | single box as an EEA member until Brexit
linked to EEA by a Multilateral Agreement[13] | |
| (1949) | single box as an EEA member | |
| (1949) | single box as an EEA member | |
| (1949) | single box as an EEA member | |
| (1949) | single box as an EEA member | |
| (1949) | single box as an EEA member | |
| (1949) | single box as an EEA member | |
| (1949) | single box as an EEA member | |
| (1951) | single box as an EEA member | |
| (1953) | single box as an EEA member | |
| (1953) | single box as an EEA member | |
| (1953) | single box as an EEA member | |
| (1954) | single box as an EEA member | |
| (1954) | linked to EEA by a Multilateral Agreement | |
| (1958) | single box as an EEA member | |
| (1960) | single box as an EEA member | |
| (1964) | Independent box | |
| (1965) | single box as an EEA member | |
| (1969)[lower-alpha 5] | Independent box | |
| (1969)[lower-alpha 6] | Independent box | |
| (1970) | single box as an EEA member | |
| (1971) | single box as an EEA member | |
| (1976)[lower-alpha 8] | Independent box | |
| (1985) | single box as an EEA member | |
| (1992) | Independent box | |
| (1992) | single box as an EEA member | |
| (1992) | single box as an EEA member | |
| (1992) | single box as an EEA member | |
| (1994) | Independent box | |
| (1996) | linked to EEA by a multilateral agreement | |
| (1996) | linked to EEA by a Multilateral Agreement | |
| (1996) | single box as an EEA member | |
| (1997) | Independent box | |
| (1997) | Independent box | |
| (1998) | single box as an EEA member | |
| (2003) | Independent box | |
| (2003) | single box as an EEA member | |
| (2009)[15] | Independent box. Suspended from June 2023.[16] | |
| (2012)[18] | linked to EEA by a Multilateral Agreement | |
| (2016) | Independent box |
Additionally, insurance companies or national bureaux of some countries participate in the Green card system through foreign national bureaux:
 Liechtenstein through Switzerland; Liechtenstein is part of the single box as an EEA member
Liechtenstein through Switzerland; Liechtenstein is part of the single box as an EEA member Monaco through France
Monaco through France San Marino through Italy
San Marino through Italy.svg.png.webp) Vatican City through Italy
Vatican City through Italy
Former member states:
 Iraq[lower-alpha 7] (1982–1992)[19]
Iraq[lower-alpha 7] (1982–1992)[19] Israel[lower-alpha 9] (1968-2022)[20]
Israel[lower-alpha 9] (1968-2022)[20]
According to recommendation of the Management Committee of CoBx it is strongly recommended that the geographical scope of the Green card System should be restricted to the following additional states, in accordance with the European and Mediterranean rule: Algeria, Libya, Egypt, Lebanon, Syria, Georgia and possibly upon further consideration Armenia. Instead of expansion further than that, it is recommended to examine arrangements of cooperation with other motor insurance systems.[21] In 2012 it was decided to add Kazakhstan to the list of potential members since part of it lies west of the Urals.[17]
Countries that are currently candidates for membership are:
In 2008 the Economic Cooperation Organization asked the CoBx for cooperation and since some of its members are outside the geographical scope of the Green card system, it was suggested that the ECO members would establish their regional motor insurance system - the White card system. At the same time there are discussion whether the scope of the Green card system should be expanded to all UNECE members or to abandon geographical limitations in exchange for criteria based on the density of trade exchanged by road between the candidate country and the existing members of the System.
In 2011 Kosovo[23] submitted application for membership, but it was concluded that the conditions of vehicle license plate international recognition and UN membership are not fulfilled.[17]
The UNECE Afro-Eurasian[24] members states currently outside the Green card system are: Armenia (candidate), Georgia (candidate), Kazakhstan (potential candidate),[17] Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan.
Other states, falling within the defined geographical scope of the Green card system (or participating in cooperation activities in the Mediterranean region such as the EMP and/or the UfM), but not participating are:
EU/EEA laws
In the single market of the EU and the EEA, international insurance between member states are regulated by specific EU/EEA laws related to insurance against civil liability in respect of the use of motor vehicles, and to the enforcement of the obligation to insure against such liability. Those were amended several times and have been codified:
- 1st EU Directive, amended by Council Directive 72/430/EEC of 19 December 1972 or Council Directive 72/166/EEC of 24 April 1972
- 2nd Council Directive 84/5/EEC of 30 December 1983
- 3rd Council Directive 90/232/EEC of 14 May 1990
- 4th Directive: Directive 2000/26/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 May 2000
- 5th Directive 2005/14/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 11 May 2005 amending Council Directives 72/166/EEC, 84/5/EEC, 88/357/EEC and 90/232/EEC and Directive 2000/26/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council.
- Codified Directive (2009/103/EC)[25]
- 6th Directive: DIRECTIVE (EU) 2021/2118
Article 7 (of 2009/103/EC) deals with national measures concerning vehicles normally based on the territory of third countries:
Each Member State shall take all appropriate measures to ensure that vehicles normally based in the territory of a third country which enter the territory in which the Treaty is in force shall not be used in its territory unless any loss or injury caused by those vehicles is covered, in accordance with the requirements of the laws of the various Member States on compulsory insurance against civil liability in respect of the use of vehicles, throughout the territory in which the Treaty is in force.
In 2021, new rules are considered to introduce EU-harmonized “Claims History Statement” and to ease prices comparison with free-of-charge and independent price comparison tools. New harmonization set guarantees for personal injuries to € 6 450 000 per accident or € 1 300 000 per injured party or/and for damage to property, € 1 300 000 per accident for vehicles going faster than 14 km/h.[26]
UK withdrawal agreement
After the UK withdrew from the EU it ceased to be an EEA member state. From that date, and until the European Commission waived the obligation in Commission Implementing Decision (EU) 2021/1145 of 30 June 2021,[13] in force since 2 August 2021, a physical copy of a green card had to be carried to drive a British registered vehicle in the EU. Since the obligation was waived the UK Government page on the subject now states: "You do not need to carry a green card when you drive in the EU (including Ireland), Andorra, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, Serbia, and Switzerland. You still need valid vehicle insurance. You may need to carry a green card to drive in other countries, including: Albania, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Moldova, Russia, Turkey, Ukraine" [27]
Orange card system
The Orange card system is established between most of the members of the Arab League and is applicable primarily in the Middle East and North Africa.
Participants are: Algeria, Bahrain, Egypt, Iraq, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco (Green card member), Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Somalia, Sudan, Syria, Tunisia (Green card member), United Arab Emirates and Yemen.
The non-participating AL members are: Comoros, Djibouti and Palestine.
Blue card system
The Blue card system is established between the 10 members of ASEAN and is applicable in South East Asia.[28]
Pink card system
The Pink card system is established between the members of the CEMAC and is applicable in Central Africa.
Participants are: Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Congo, Gabon and Equatorial Guinea.
Canada also uses a pink card system, more formally known as "Canada Inter-Province", which is accepted in all provinces and territories of Canada and throughout the United States.
Brown card system
The Brown card system is established between most of the members of the ECOWAS and is applicable in Western Africa.
Participants are: Benin, Burkina Faso, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal, Sierra Leone and Togo.
The non-participating ECOWAS member is Cabo Verde.
Yellow card system
The Yellow card system is established between most of the members of the COMESA and is applicable primarily in Eastern Africa.
Participants are: Burundi, DR Congo, Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Kenya, Malawi, Rwanda, Sudan, Tanzania, Uganda, Zambia and Zimbabwe.
The non-participating COMESA members are: Comoros, Egypt (Orange card member), Eswatini, Libya (Orange card member), Madagascar, Mauritius, Seychelles, Somalia (Orange card member), and Tunisia (Green and Orange card member).
White card system
There is a proposal for the establishment of White card system between the members of the ECO, if the Green Card system territorial scope could not be expanded to include all of them.
Participants are: Afghanistan, Azerbaijan (Green card member), Iran (Green card member), Kazakhstan (Green card potential candidate), Kyrgyzstan (UNECE member), Pakistan, Tajikistan (UNECE member), Turkey (Green card member), Turkmenistan (UNECE member), Uzbekistan (UNECE member).
See also
- Green card (disambiguation) - for other uses of the term, besides a motor insurance certificate.
- Vehicle insurance in France.
Notes
- 1 2 Czechoslovakia joined the Green Card system in 1949. After dissolution in 1993, the Czech Republic and Slovakia remained members.
- ↑ The Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia joined in 1954 and its membership was later continued by the State Union of Serbia and Montenegro and finally the Republic of Serbia.
- 1 2 Mediterranean member of the green card system.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Member state or prospective member for both Green card and Orange card.
- ↑ Morocco was affiliate member between 1969 and 2003 when affiliate membership status type was abolished.
- ↑ Tunisia was affiliate member between 1969 and 2003 when affiliate membership status type was abolished.
- 1 2 Member of the green card system that is located neither in Europe nor borders the Mediterranean Sea.
- ↑ Iran was an affiliate member between 1976 and 2003 when affiliate membership status type was abolished.
- ↑ Israel was affiliate member between 1968 and 2003 when affiliate membership status type was abolished.
References
- ↑ "History of the CoB | Council of Bureaux". www.cobx.org. Retrieved 2022-07-23.
- ↑ "CoBx history, 2006". Cobx.org. Archived from the original on 2013-06-05. Retrieved 2013-06-09.
- 1 2 "House of Lords - European Union - Minutes of Evidence". publications.parliament.uk.
- ↑ "Stats" (PDF). www.nbi-ngf.ch. Retrieved 2020-09-28.
- ↑ "About the CoB". Archived from the original on 2018-05-14. Retrieved 2018-05-07.
- ↑ "Driving in Europe, car insurance and car accidents". www.ecc-netitalia.it.
- ↑ "Stats" (PDF). www.abi.org.uk. Retrieved 2020-09-28.
- ↑ "The Green Card | Council of Bureaux". www.cobx.org. Retrieved 2022-07-23.
- ↑ "CoB System Map | Council of Bureaux". www.cobx.org. Retrieved 2022-07-23.
- ↑ Commission Implementing Decision (EU) 2021/1145 of 30 June 2021 on the application of Directive 2009/103/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council with regard to checks on insurance against civil liability in respect of the use of motor vehicles normally based in Montenegro and the United Kingdom (Text with EEA relevance), 2021-07-13, retrieved 2022-07-23
- ↑ "About the CoB". Archived from the original on 2020-09-20. Retrieved 2020-06-22.
- ↑ EU directive, article 14 single premium
- 1 2 Commission Implementing Decision (EU) 2021/1145 of 30 June 2021 on the application of Directive 2009/103/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council with regard to checks on insurance against civil liability in respect of the use of motor vehicles normally based in Montenegro and the United Kingdom (Text with EEA relevance), 2021-07-13, retrieved 2022-07-23
- ↑ Report to UNECE, 2009 The new member states join the Green Card system with transitional status until monitoring over them is lifted.
- ↑ Russia applied for membership in 2002 and was candidate until 2009 when it joined the Green card system.
- ↑ "Россию исключили из системы «Зеленая карта». Страховки действительны еще десять дней". Banki.ru (in Russian). 2023-06-23.
- 1 2 3 4 "ECE/TRANS/SC.1/2012/1 - (CoB) Report from the President" (PDF). Retrieved 2013-06-09.
- ↑ Participating through Serbia until 2012.[17]
- ↑ Iraq was affiliate member from 1982 until it was suspended in 1992 following UN sanctions. In 2003, with the abolition of affiliate membership status type, it was decided that members suspended for more than five years will have to rejoin following the regular procedure for new member states.
- ↑ "Green Card Bureaux | Council of Bureaux". www.cobx.org. Retrieved 2022-07-23.
- ↑ "CoBx news, Issue No. 31 (May 2010)". Cobx.org. Archived from the original on 2013-06-05. Retrieved 2013-06-09.
- ↑ "Report of the President of the Council of Bureaux, 2010" (PDF). Retrieved 2013-06-09.
- ↑ "CoBx note on Kosovo". Cobx.org. Archived from the original on 2013-05-29. Retrieved 2013-06-09.
- ↑ North American members of UNECE are Canada and the United States.
- ↑ "Directive 2009/103/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 September 2009 relating to insurance against civil liability in respect of the use of motor vehicles, and the enforcement of the obligation to insure against such liability (Text with EEA relevance)". EU. 16 September 2009. Retrieved 2020-06-23.
- ↑ "Parliament adopts new rules to improve protection of road accident victims | News | European Parliament". 21 October 2021.
- ↑ "Vehicle insurance".
- ↑ "PROTOCOL 5 - ASEAN SCHEME OF COMPULSORY MOTOR VEHICLE INSURANCE". Protocol No. 5 of 8 April 2001 (PDF). Fifth Annual ASEAN Finance Ministers Meeting. p. 8-9.