| Sulawesi shrew | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Eulipotyphla |
| Family: | Soricidae |
| Genus: | Crocidura |
| Species: | C. lea |
| Binomial name | |
| Crocidura lea | |
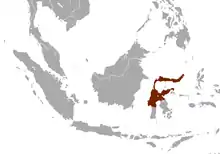 | |
| Sulawesi shrew range | |
The Sulawesi shrew (Crocidura lea) is a species of mammal in the family Soricidae. It is endemic to the central and northern provinces of Sulawesi in Indonesia. It is a fairly common species and the International Union for Conservation of Nature has assessed its conservation status as being of "least concern".
Taxonomy
The Sulawesi shrew was first described in 1921 by the American zoologists Gerrit Smith Miller Jr. and Hollister as Crocidura lea. The type locality was Temboan in North Sulawesi. Crocidura lea is part of an assemblage of shrews endemic to northern and central Sulawesi which also includes the Sulawesi white-handed shrew (Crocidura rhoditis), the black-footed shrew (Crocidura nigripes), the elongated shrew (Crocidura elongata) and the mossy forest shrew (Crocidura musseri). Crocidura lea is the smallest of this assemblage and on Sulawesi, only the Sulawesi tiny shrew (Crocidura levicula) is smaller, and it is native to eastern Sulawesi.[2]
Description
The Sulawesi shrew is one of the smallest of the white-toothed shrews; it lacks the deposits of iron in the enamel of the teeth which is seen in the red-toothed shrews. The dorsal pelage is short and velvety, being greyish-brown or reddish-brown and the underside is paler.[3]
Distribution and habitat
The Sulawesi shrew is endemic to the Indonesian island of Sulawesi where it is found in the central and northern parts of the island, at altitudes of up to about 1,000 m (3,300 ft). Its typical habitat is primary tropical forests, but it seems able to survive in secondary forests as well. The extent to which it can adapt to degraded habitat is unclear.[1]
Behaviour
The Sulawesi shrew is thought to be nocturnal but very little is known of its natural history and behaviour.[1] Like other members of its family it lives among the leaf litter and is insectivorous and is likely to eat insects and small arthropods.[3]
Status
The Sulawesi shrew is fairly common in some locations and is regularly caught in pitfall traps. The population trend is unknown but no particular threats to this species have been recognised. It has a wide range, and the International Union for Conservation of Nature has assessed its conservation status as being of "least concern".[1]
References
- 1 2 3 4 Chiozza, F. (2016). "Crocidura lea". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41328A22308315. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T41328A22308315.en. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ↑ Don E. Wilson; DeeAnn M. Reeder (2005). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference. JHU Press. p. 237. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0.
- 1 2 R. David Stone (1995). Eurasian Insectivores and Tree Shrews: Status Survey and Conservation Action Plan. IUCN. p. 15. ISBN 978-2-8317-0062-5.
