| 1962 North Indian Ocean cyclone season | |
|---|---|
 Season summary map | |
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | May 15, 1962 |
| Last system dissipated | December 13, 1962 |
| Strongest storm | |
| Name | Twelve |
| • Maximum winds | 140 km/h (85 mph) (3-minute sustained) |
| • Lowest pressure | 974 hPa (mbar) |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Depressions | 13 |
| Deep depressions | 10 |
| Cyclonic storms | 5 |
| Very severe cyclonic storms | 1 |
| Total fatalities | 50,769 total, 142 missing |
| Total damage | $34.5 million (1962 USD) |
| Related articles | |
The 1962 North Indian Ocean cyclone season had no official bounds, but cyclones tend to form between April and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northern Indian Ocean. There are two main seas in the North Indian Ocean—the Bay of Bengal to the east of the Indian subcontinent and the Arabian Sea to the west of India. The official Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre in this basin is the India Meteorological Department (IMD), while the Joint Typhoon Warning Center releases unofficial advisories. An average of four to six storms form in the North Indian Ocean every season with peaks in May and November.[1] The IMD includes cyclones occurring between the meridians 45°E and 100°E in the season.[2]
Systems
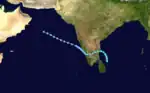
Cyclonic Storm One
| Cyclonic storm (IMD) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | May 15 – May 22 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 75 km/h (45 mph) (3-min); 994 hPa (mbar) |
Cyclonic Storm One existed from May 15 to May 22.[3] The storm moved from east to west.
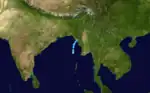
Deep Depression Two
| Deep depression (IMD) | |
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | May 24 – May 25 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 30 km/h (15 mph) (3-min); 992 hPa (mbar) |
Deep Depression Two existed from May 24 to May 25.[4] The storm moved from south to north.
Depression Three
| Depression (IMD) | |
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | May 28 – May 30 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 35 km/h (25 mph) (3-min); |
Depression Three existed from May 28 to May 30.[5] The storm moved from east to west.
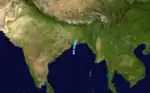
Depression Four
| Depression (IMD) | |
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | June 6 – June 8 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 45 km/h (30 mph) (1-min); |
Depression Four existed from June 6 to June 8.[6] The storm moved from south to north.
Deep Depression Five
| Deep depression (IMD) | |
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | July 11 – July 13 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 55 km/h (35 mph) (3-min); 982 hPa (mbar) |
Deep Depression Five existed from July 11 to July 13.[7]
Depression Six
| Depression (IMD) | |
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | July 8 – July 15 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 45 km/h (30 mph) (1-min); |
Depression Six existed from July 8 to July 15.[8] The storm stalled for several days in Western India from July 8 to July 13, then moved west into the northern Arabian Sea. The tropical depression later dissipated on July 15, and generally moved westward in its eight-day lifetime.
Deep Depression Seven
| Deep depression (IMD) | |
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | September 8 – September 14 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 35 km/h (25 mph) (3-min); |
Deep Depression Seven existed from September 8 to September 15.[9] The storm moved from east to west throughout its lifetime. It formed on September 8 in the western Bay of Bengal and made landfall on eastern India on September 8. The depression crossed India and traced the western coast of the country from September 10 to September 14, making two sharp turns along the way. The storm dissipated in the extreme northern Arabian Sea on Septemebr 15.
Deep Depression Eight
| Deep depression (IMD) | |
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | September 16 – September 21 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 85 km/h (50 mph) (3-min); |
Deep Depression Eight existed from September 16 to September 21.[10] The storm moved from east to west.
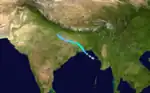
Cyclonic Storm Nine
| Cyclonic storm (IMD) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | September 19 – September 25 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 90 km/h (55 mph) (3-min); 990 hPa (mbar) |
Cyclonic Storm Nine existed from September 19 to September 25.[11] The storm moved from east to west.
Deep Depression Ten
| Deep depression (IMD) | |
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | October 22 – October 26 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 75 km/h (45 mph) (3-min); 1000 hPa (mbar) |
Deep Depression Ten existed from October 22 to October 26.[12] The storm moved from south to north.
Severe Cyclonic Storm Harriet
| Severe cyclonic storm (IMD) | |
| Category 1 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) | |
 | |
| Duration | October 26 – October 30 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 100 km/h (65 mph) (3-min); 990 hPa (mbar) |
After making landfall in Thailand, the system continued westward, then curved to the northeast, probably regathering strength and making landfall near Chittagong in East Pakistan on October 30 before rapidly dissipating.[13]
The destruction from Tropical Storm Harriet took the lives of at least 769 residents of Thailand's southern provinces. Another 142 people were also deemed missing as of November 4, with over 252 severe injuries. Damage at the time was estimated to be over $34.5 million (1962 USD) to government buildings, agriculture, homes and fishing fleets.[14][15]
In East Pakistan, the cyclone killed 50,000 people.[16]
Very Severe Cyclonic Storm Twelve
| Very severe cyclonic storm (IMD) | |
| Category 1 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | November 26 – November 29 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 140 km/h (85 mph) (3-min); 974 hPa (mbar) |
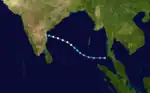
Severe Cyclonic Storm Twelve developed on November 26. It was the strongest tropical cyclone of the season, peaking with winds of 140 km/h (85 mph). The system dissipated on November 29.[17] The storm moved from east to west and made a Tropical Storm-equivalent landfall on eastern India.
Severe Cyclonic Storm Thirteen
| Severe cyclonic storm (IMD) | |
| Category 1 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | December 9 – December 13 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 95 km/h (60 mph) (3-min); 990 hPa (mbar) |
The final storm of the season, Severe Cyclonic Storm Thirteen, developed on December 9. It lasted four days, dissipating on December 13.[18] The storm moved from weat to east.
Season effects
This is a table of all storms in the 1962 North Indian Ocean cyclone season. It mentions all of the season's storms and their names, duration, peak intensities (according to the IMD storm scale), damage, and death totals. Damage and death totals include the damage and deaths caused when that storm was a precursor wave or extratropical low, and all of the damage figures are in 1962 USD.
| Name | Dates | Peak intensity | Areas affected | Damage (USD) |
Deaths | Refs | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Category | Wind speed | Pressure | ||||||
| One | May 15–22 | Cyclonic storm | 75 km/h (45 mph) | 994 hPa (29.35 inHg) | Sri Lanka, India | Unknown | Unknown | |
| Two | May 24–25 | Deep Depression | 30 km/h (20 mph) | 998 hPa (29.47 inHg) | Myanmar, East Pakistan | Unknown | Unknown | |
| Three | May 28–30 | Depression | 35 km/h (20 mph) | 1,004 hPa (29.65 inHg) | Arabian Peninsula | Unknown | Unknown | |
| Four | June 6–8 | Depression | Not specified | 1,004 hPa (29.65 inHg) | East Pakistan | Unknown | Unknown | |
| Five | July 11–13 | Deep Depression | 55 km/h (35 mph) | 982 hPa (29.00 inHg) | India | Unknown | Unknown | |
| Six | June 6–8 | Depression | Not specified | Not specified | Pakistan, India | Unknown | Unknown | |
| Season aggregates | ||||||||
| 13 systems | May 15 – December 13 | 140 km/h (85 mph) | 974 hPa (28.76 inHg) | 34.5 million | 769 and missing 142 | |||
See also
- North Indian Ocean tropical cyclone
- List of tropical cyclone records
- 1962 Atlantic hurricane season
- 1962 Pacific hurricane season
- 1962 Pacific typhoon season
- Australian region cyclone seasons: 1961–62 1962–63
- South Pacific cyclone seasons: 1961–62 1962–63
- South-West Indian Ocean cyclone seasons: 1961–62 1962–63
References
- ↑ "IMD Cyclone Warning Services: Tropical Cyclones". India Meteorological Department. Archived from the original on 4 November 2008. Retrieved May 10, 2013.
- ↑ "Report on Cyclonic Disturbances Over the North Indian During 2008". India Meteorological Department. January 2009. Archived from the original (PDF) on May 29, 2009. Retrieved May 10, 2013.
- ↑ India Meteorological Department (1962). "Annual Summary — Storms & Depressions: Cyclonic Storm in the Bay of Bengal and Depression in the Arabian Sea" (PDF). India Weather Review. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: 1–3. Retrieved May 12, 2013.
- ↑ India Meteorological Department (1962). "Annual Summary — Storms & Depressions: Deep depression in the Bay of Bengal" (PDF). India Weather Review. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: 3–4. Retrieved May 12, 2013.
- ↑ India Meteorological Department (1962). "Annual Summary — Storms & Depressions: Depression in the Arabian Sea" (PDF). India Weather Review. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: 4–5. Retrieved May 12, 2013.
- ↑ India Meteorological Department (1962). "Annual Summary — Storms & Depressions: Depression in the Bay of Bengal" (PDF). India Weather Review. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: 5–6. Retrieved May 12, 2013.
- ↑ India Meteorological Department (1962). "Annual Summary — Storms & Depressions: Deep depression in the Bay of Bengal" (PDF). India Weather Review. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: 6–7. Retrieved May 12, 2013.
- ↑ India Meteorological Department (1962). "Annual Summary — Storms & Depressions: Depression in the Arabian Sea" (PDF). India Weather Review. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: 7. Retrieved May 12, 2013.
- ↑ India Meteorological Department (1962). "Annual Summary — Storms & Depressions: Depression in the Bay of Bengal and Deep Depression in the Arabian Sea" (PDF). India Weather Review. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: 7–9. Retrieved May 12, 2013.
- ↑ India Meteorological Department (1962). "Annual Summary — Storms & Depressions: Deep depression in the Bay of Bengal" (PDF). India Weather Review. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: 9–10. Retrieved May 12, 2013.
- ↑ India Meteorological Department (1962). "Annual Summary — Storms & Depressions: Cyclonic Storm in the Bay of Bengal" (PDF). India Weather Review. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: 10–11. Retrieved May 12, 2013.
- ↑ India Meteorological Department (1962). "Annual Summary — Storms & Depressions: Deep depression in the Bay of Bengal" (PDF). India Weather Review. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: 11–12. Retrieved May 12, 2013.
- ↑ India Meteorological Department (1962). "Annual Summary — Storms & Depressions: Severe Cyclonic Storm in the Bay of Bengal" (PDF). India Weather Review. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: 13–14. Retrieved May 12, 2013.
- ↑ "Thai Storm Toll Put at 769". The New York Times. November 4, 1962. p. 17.
- ↑ "Harriet's Terrible Toll". The Miami News. November 2, 1962. p. 28. Retrieved May 12, 2011.
- ↑ Damen, Michiel. "CYCLONE HAZARD IN BANGLADESH" – via www.academia.edu.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ↑ India Meteorological Department (1962). "Annual Summary — Storms & Depressions: Severe Cyclonic Storm in the Bay of Bengal" (PDF). India Weather Review. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: 14–15. Retrieved May 12, 2013.
- ↑ India Meteorological Department (1962). "Annual Summary — Storms & Depressions: Severe Cyclonic Storm in the Bay of Bengal" (PDF). India Weather Review. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: 16–17. Retrieved May 12, 2013.
External links
- India Meteorological Department
- Joint Typhoon Warning Center Archived 2015-08-09 at the Wayback Machine