 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
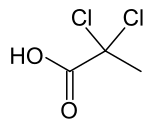
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,2-Dichloropropanoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.840 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1760 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H4Cl2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 142.96 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless oil |
| Density | 1.40 g/cm3 (20 °C) |
| Melting point | 20 °C (68 °F; 293 K) |
| Boiling point | 190 °C (374 °F; 463 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  | |
| Danger | |
| H315, H318, H412 | |
| P264, P273, P280, P302+P352, P305+P351+P338, P310, P321, P332+P313, P362, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
2,2-Dichloropropionic acid is the organic compound with the formula CH3CCl2CO2H.[1] It is a colorless liquid that freezes near room temperature.
Occurrence and use
Its sodium salt once was marketed under the name Dalapon as a selective herbicide used to control perennial grasses.[2]
It is an inhibitor of some enzymes that process pyruvate.[3]
References
- ↑ Samel, Ulf-Rainer; Kohler, Walter; Gamer, Armin Otto; Keuser, Ullrich (2005). "Propionic Acid and Derivatives". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a22_223. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- ↑ "Dalapon". pmep.cce.cornell.edu. Retrieved 2016-08-31.
- ↑ Halestrap, A. P. (1975). "The mitochondrial pyruvate carrier. Kinetics and specificity for substrates and inhibitors". Biochemical Journal. 148 (1): 85–96. doi:10.1042/bj1480085. PMC 1165509. PMID 1156402.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.