Department of Meuse-Inférieure | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1795–1814 | |||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||
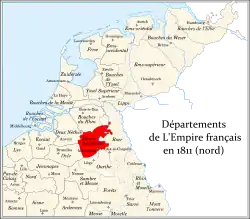 Meuse-Inférieure and other annexed departments | |||||||||||||||
| Status | Department of the French First Republic and the French First Empire | ||||||||||||||
| Chef-lieu | Maastricht 51°0′N 5°35′E / 51.000°N 5.583°E | ||||||||||||||
| Official languages | French | ||||||||||||||
| Historical era | French Revolutionary Wars | ||||||||||||||
• Creation | 1 October 1795 | ||||||||||||||
• Treaty of Paris, disestablished | 30 May 1814 | ||||||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||||||
• 1814[1] | 267,249 | ||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
| Today part of | |||||||||||||||
Meuse-Inférieure ([møz ɛ̃.fe.ʁjœʁ] "Lower Meuse"; Dutch: Beneden-Maas; German: Unteren-Maas) was a department of the French First Republic and French First Empire in present-day Belgium, Netherlands and Germany. It was named after the river Meuse. Its territory corresponded largely with the present-day provinces of Belgian and Dutch Limburg. It was created on 1 October 1795, when the Austrian Netherlands and the Prince-Bishopric of Liège were officially annexed by the French Republic.[2] Before this annexation, its territory was part of the County of Loon, the Austrian Upper Guelders, the Staats-Oppergelre, the County of Horne, the Abbacy of Thorn, Maastricht and part of the Lands of Overmaas. The lands of the original medieval Duchy of Limburg were associated with the Overmaas lands, lying to their south. The two regions had long been governed together and referred to collectively with both names, but the original Duchy lands were not part of this new entity.
The Chef-lieu of the department was Maastricht. The department was subdivided into the following three arrondissements and cantons:
- Maastricht: Bilzen, Galoppe, Heerlen, Malines-sur-Meuse, Maastricht (2 cantons), Meerssen, Oirsbeek, Rolduc and Tongres.
- Hasselt: Béringue, Looz, Hasselt, Herck-la-Ville, Peer and Saint-Trond.
- Roermond: Achel, Brée, Maaseik, Niederkrüchten, Ruremonde, Venlo and Weert.
After Napoleon was defeated in 1814, the department (excluding Niederkrüchten and Herzogenrath which were assigned to the Kingdom of Prussia and are located in the present-day state of North Rhine-Westphalia) became part of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands, as the Province of Limburg (with a part of the Roer département).
In subsequent events starting in 1830, a part of this kingdom split out to become Belgium. By 1839 it was settled that the Hasselt canton of Limburg, plus significant parts of the other two, went into Belgium, while the rest remained in the Netherlands. Both provinces have kept the name Limburg.
Administration
Prefects
The Prefect was the highest state representative in the department.
| Term start | Term end | Office holder |
|---|---|---|
| 29 March 1800[3] | 2 November 1801 | François Becays Ferrand dit Ferrand de Lacaussade |
| 2 November 1801[4] | 31 January 1806 | Pierre Loysel |
| 31 January 1806[5] | 30 May 1814 | Jean-Baptiste Roggieri |
Secretaries-General
The Secretary-General was the deputy to the Prefect.
| Term start | Term end | Office holder |
|---|---|---|
| 2 March 1800 | 30 May 1814 | M.J. Reintjens |
Subprefects of Hasselt
| Term start | Term end | Office holder |
|---|---|---|
| 17 April 1800[1] | 13 October 1813 | Jean Baptiste Bertrand Arnoul |
| 13 October 1813[1] | 21 November 1813 | Briche |
| 21 November 1813[1] | 6 January 1814 | Billig |
| 6 January 1814[1] | 30 May 1814 | Baumes |
Subprefects of Maastricht
The office of Subprefect of Maastricht was held by the Prefect until 1811.
| Term start | Term end | Office holder |
|---|---|---|
| 11 January 1811[1] | 30 May 1814 | Van den Rhoër |
Subprefects of Roermond
| Term start | Term end | Office holder |
|---|---|---|
| 17 April 1800[1] | 3 May 1801 | Magniet |
| 3 May 1801[1] | 24 July 1811 | Liger |
| 24 July 1811[1] | 30 May 1814 | Brandes |
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Tulard, Jean & Marie-José (2014). Napoléon et 40 millions de sujets: La centralisation et le premier empire. p. 330. ISBN 9791021001480.
- ↑ Duvergier, Jean-Baptiste (1835). Collection complète des lois, décrets, ordonnances, réglemens et avis du Conseil d'état, t. 8. p. 300.
- ↑ Archives Nationales. "BECAYS FERRAND DIT FERRAND DE LACAUSSADE, François". francearchives.fr. Retrieved 26 June 2019.
- ↑ Archives Nationales. "LOYSEL, Pierre". francearchives.fr. Retrieved 26 June 2019.
- ↑ Archives Nationales. "ROGGIERI, Jean-Baptiste". francearchives.fr. Retrieved 26 June 2019.
