 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Diethyl phosphorochloridate | |
| Other names
Diethylchlorophosphate; Diethoxyphosphorus oxychloride; Diethyl chlorophosphonate; Diethyl phosphorochloride; Diethoxyphosphoryl chloride; O,O-Diethyl chlorophosphate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.011.270 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H10ClO3P | |
| Molar mass | 172.54 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Density | 1.1915 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 60 °C (140 °F; 333 K) (2 mm Hg) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
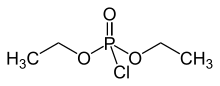
Diethyl chlorophosphate is an organophosphorus compound with the formula (C2H5O)2P(O)Cl. As a reagent in organic synthesis, it is used to convert alcohols to the corresponding diethylphosphate esters. It is a colorless liquid with a fruity odor. It is a corrosive, and as a cholinesterase inhibitor, highly toxic through dermal absorption.[1] The molecule is tetrahedral.
Synthesis and reactions
The compound is prepared by the chlorination of diethylphosphite with carbon tetrachloride (Atherton–Todd reaction).[2]
The compound is electrophilic. Controlled hydrolysis gives tetraethyl pyrophosphate. Alcohols react to vie mixed phosphate esters: [3]
- (C2H5O)2P(O)Cl + ROH → (C2H5O)2P(O)OR + HCl
The reagent is routinely employed in organic synthesis for phosphorylation of carboxylates,[4] alcohols,[5] and amines.[6]
See also
- Diethyl chlorophosphate at www.chemicalbook.com.
References
- ↑ "Haz-Map Category Details". hazmap.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2016-07-30.
- ↑ Steinberg, Geo. M. (1950). "Reactions of Dialkyl Phosphites. Synthesis of Dialkyl Chlorophosphates, Tetraalkyl Pyrophosphates, and Mixed Orthophosphate Esters". Journal of Organic Chemistry. 15 (3): 637–47. doi:10.1021/jo01149a031.
- ↑ Young, Jonathan R. (2001). "Diethyl phosphorochloridate". E-EROS Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis: 1–3.
- ↑ Michael A. Insalaco; D. Stanley Tarbell (1970). "tert-Butyl Azidoformate". Org. Synth. 50: 9. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.050.0009.
- ↑ D. C. Muchmore (1972). "Preparation and Reductive Cleavage of Enol Phosphates: 5-Methylcoprost-3-ene". Org. Synth. 52: 109. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.052.0109.
- ↑ Nick Nikolaides; Ioanna Schipor; Bruce Ganem (1995). "Conversion of Amines to Phospho Esters: Decyl Diethyl Phosphate". Org. Synth. 72: 246. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.072.0246.