| Vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia | |
|---|---|
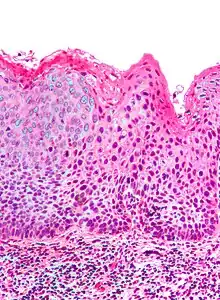 | |
| Micrograph of (classic) vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia III. H&E stain. | |
| Specialty | Gynecology |
Vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN) refers to particular changes that can occur in the skin that covers the vulva. VIN is an intraepithelial neoplasia, and can disappear without treatment. VINs are benign but if the changes become more severe, there is a chance of cancer developing after many years, and so it is referred to as a precancerous condition.[1]
Classification
Medically speaking, the term denotes a squamous intraepithelial lesion of the vulva that shows dysplasia with varying degrees of atypia. The epithelial basement membrane is intact and the lesion is thus not invasive but has invasive potential.
The terminology of VIN evolved over several decades. In 1989[2] the Committee on Terminology, International Society for the Study of Vulvar Disease (ISSVD) replaced older terminology such as vulvar dystrophy, Bowen's disease, and Kraurosis vulvae by a new classification system for Epithelial Vulvar Disease:
- Nonneoplastic epithelial disorders of vulva and mucosa:
- Lichen sclerosus
- Squamous hyperplasia
- Other dermatoses
- Mixed neoplastic and nonneoplastic disorders
- Intraepithelial neoplasia
- Squamous vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN), previously classified as VIN 1-3:
| Source | Mild dysplasia | Moderate dysplasia | Severe dysplasia / carcinoma in situ | HPV-negative lesion with atypical keratinocytes in the basal cell layer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WHO 2003[3] | Vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN) 1 | VIN 2 | VIN 3 | VIN 3 |
| WHO 2014 and ISSVD 2015[3] | Low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LSIL) | High-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL) | Intraepithelial neoplasia, differentiated type | |
- Non-squamous intraepithelial neoplasia
- Extramammary Paget's disease
- Tumors of melanocytes, noninvasive
- Non-squamous intraepithelial neoplasia
- Invasive disease (vulvar carcinoma)
The ISSVD further revised this classification in 2004, replacing the three-grade system with a single-grade system in which only the high-grade disease is classified as VIN.
VIN is subdivided into: (Robbins Pathological Basis of Disease, 9th Ed)
Classic vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia: associated with developing into the warty and basaloid type carcinoma. This is associated with carcinogenic genotypes of HPV and/or HPV persistence factors such as cigarette smoking or immunocompromised states.
Differentiated vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia also known as VIN Simplex: is associated with vulvar dermatoses such as lichen sclerosus. It is associated with atypia of the squamous epithelium.
Risk factors
The exact cause of VIN is unknown. Studies are being done to determine the cause of VIN. The following factors have been associated with VIN:
- HPV (Human Papilloma Virus)
- HSV-2 (Herpes simplex Virus - Type 2)
- Smoking
- Immunosuppression
- Chronic vulvar irritation
- Conditions such as Lichen Sclerosus
Diagnosis
The person may have no symptoms, or local symptomatology including itching, burning, and pain. The diagnosis is always based on a careful inspection and a targeted biopsy of a visible vulvar lesion.
The type and distribution of lesions varies among the two different types of VIN. In the Usual type VIN, seen more frequently in young patients, lesions tend to be multifocal over an otherwise normal vulvar skin. In the differentiated type VIN, usually seen in postmenopausal women, lesions tend to be isolated and are located over a skin with a vulvar dermatosis such as Lichen slerosus.[4]
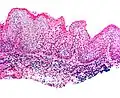 Micrograph of vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia III. H&E stain.
Micrograph of vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia III. H&E stain.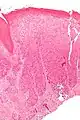 Micrograph of differentiated vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia. H&E stain.
Micrograph of differentiated vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia. H&E stain.
Prevention
Vaccinating girls with HPV vaccine before their initial sexual contact has been claimed to reduce incidence of VIN.[6]
References
- ↑ "Vulval intra-epithelial neoplasia (VIN)". Macmillan Cancer Support. Archived from the original on 2010-06-26. Retrieved 2010-06-09.
- ↑ Ridley CM, Frankman O, Jones IS, et al. (May 1989). "New nomenclature for vulvar disease: International Society for the Study of Vulvar Disease". Hum. Pathol. 20 (5): 495–6. doi:10.1016/0046-8177(89)90019-1. PMID 2707802.
- 1 2 Schnürch, H.; Ackermann, S.; Alt, C.; Barinoff, J.; Böing, C.; Dannecker, C.; et al. (2016). "Diagnosis, Therapy and Follow-up Care of Vulvar Cancer and its Precursors. Guideline of the DGGG and DKG (S2k-Level, AWMF Registry Number 015/059, November 2015". Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 76 (10): 1035–1049. doi:10.1055/s-0042-103728. PMC 5066425. PMID 27765958.
- 1 2 "Vulvar Disease | Research and Education". ISSVD. Retrieved 2022-04-20.
- ↑ Sideri M, Jones RW, Wilkinson EJ, Preti M, Heller D,. Scurry J, Haefner H, Neill S. 2004 Modified Terminology, ISSVD Vulvar Oncology Subcommittee. Journal of Reproductive Medicine. 2005;50:807-10.
- ↑ "FDA Approves Expanded Uses for Gardasil to Include Preventing Certain Vulvar and Vaginal Cancers". Food and Drug Administration. 2008-09-12. Retrieved 2010-02-13.