53°42′50″N 6°21′1″W / 53.71389°N 6.35028°W
| Siege of Drogheda (1649) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Cromwellian Conquest of Ireland | |||||||
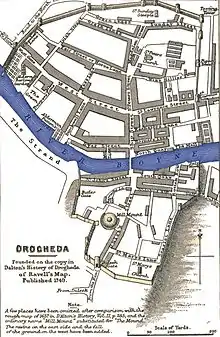 A plan of Drogheda in 1649 | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 2,547[1] | c. 12,000[2] | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| c. 2,000 killed, wounded or captured | c. 150 killed or wounded | ||||||
| 700–800 civilians killed[3] | |||||||
The siege of Drogheda took place from 3 to 11 September 1649, at the outset of the Cromwellian conquest of Ireland. The coastal town of Drogheda was held by a mixed garrison of Irish Catholics and Royalists under the command of Sir Arthur Aston, when it was besieged by English Commonwealth forces under Oliver Cromwell. After Aston rejected an invitation to surrender, the town was stormed and much of the garrison executed, along with an unknown but "significant number" of civilians. The aftermath of the siege is viewed as an atrocity which still impacts Cromwell's modern reputation.
Background
Since 1642, most of Ireland had been under the control of the Irish Catholic Confederation, who had taken much of the country in the aftermath of the 1641 Irish rebellion. Following the Execution of Charles I in January 1649, the Confederates allied with English exiles and Protestant Irish Royalists to secure Ireland for his son, Charles II of England. In June 1649, a combined Royalist/Confederate force besieged Dublin, but retreated after their defeat at Rathmines on 2 August. Some Royalist Protestants now changed sides, and James Butler, 1st Duke of Ormonde had to rally the remaining dispersed forces to put together a new field army.[4]
With troops largely composed of veterans from the New Model Army, Oliver Cromwell landed near Dublin in August 1649 to re-conquer the country on behalf of the Commonwealth of England. On 23 August, the Royalists held a Council of War at Drogheda, [lower-alpha 1] which decided to hold the town. The garrison contained four regiments totalling around 2,550 men, a mixture of Royalist and Confederate troops under Sir Arthur Aston.[5][6][lower-alpha 2] Ormonde's strategy was to avoid battle, while holding towns in the east of Ireland, relying on hunger and disease to weaken the besiegers.[7]
Cromwell's tactics at Drogheda were determined by a need to take the ports on Ireland's east coast quickly to ensure re-supply for his troops. The normal "campaigning season," when armies could live off the land, ran from spring to autumn. Since he had landed in Ireland late in the year, campaigning through the winter necessitated securing a constant re-supply from the sea.[8] He, therefore, favoured rapid assaults on fortified places using his siege artillery, rather than time-consuming blockades to secure the all-important ports.[9]
Siege

Cromwell arrived at Drogheda on 3 September and his siege guns, brought up by sea, arrived two days later.[10] His total force was about 12,000 men and eleven heavy, 48-pounder, siege artillery pieces.[2]
Drogheda's defences consisted of medieval curtain walls. These were high but relatively thin, making them vulnerable to cannon fire. Most of the town was situated on the northern bank of the River Boyne but its two main gates, the Dublin and Duleek, were south of the river along with the Millmount Fort that overlooked the defences.[11]
Cromwell positioned his forces on the south side of the River Boyne in order to concentrate them for the assault, leaving the northern side of the town open and covered by a small screen of cavalry.[12] A squadron of Parliamentarian ships also blockaded the harbour of the town.[13]
In a letter to William Lenthall, Speaker of the English House of Commons, written shortly after the storming of the town, Cromwell explained why he did not fully invest the town, an action that would have left his divided command vulnerable to an attack by a relieving force and a simultaneous sortie by the garrison, but rather concentrated his troops on the south side of Drogheda for a swift assault.
The officers and soldiers of this Garrison were the flower of their Army. And their great expectation was, that our attempting this place would put fair to ruin us: they being confident of the resolution of their men, and the advantage of the place. If we had divided our force into two-quarters to have besieged the North Town and the South Town, we could not have had such a correspondency between the two parts of our Army, but that they might have chosen to have brought their Army, and have fought with which part 'of ours' they pleased,—and at the same time have made a sally with 2,000 men upon us, and have left their walls manned; they having in the Town the number hereafter specified, but some say near 4,000.
— Oliver Cromwell.[14]
Summons to surrender
The Parliamentary commander set up his batteries at two points near the Duleek gate, on either side of St Mary's Church, where they would have an interlocking field of fire. Having opened two breaches in the walls, one to the south and the other to the east of the church, he called on the Royalists to surrender.[15]
On Monday, 10 September, Cromwell had a letter delivered to Sir Arthur Aston, which read:[16]
Sir, having brought the army of the Parliament of England before this place, to reduce it to obedience, to the end that the effusion of blood may be prevented, I thought fit to summon you to deliver the same into my hands to their use. If this be refused, you will have no cause to blame me. I expect your answer and remain your servant,
— O. Cromwell

The contemporary laws of war were clear: if surrender was refused and a garrison was taken by assault, then its defenders could lawfully be killed. That is; acceptance of a surrender of the besieged after the storming of the breach was at the discretion of the attacker.[17]
Aston refused to surrender even though the garrison of Drogheda was critically short of gunpowder and ammunition.[18] Their hope was that Ormonde, nearby at Tercroghan with some 4,000 Royalist troops, would come to their relief.[2]
Assault
At 5:00 PM, on 11 September, Cromwell ordered simultaneous assaults on the southern and eastern breaches in the walls of Drogheda. Three regiments attacked the breaches, gaining a foothold in the south but being beaten back in the east. Cromwell had to reinforce the eastern attack with two more regiments before it succeeded, the second wave climbing over "a heaped pile of their comrades' corpses."[19] At the southern breach, the defenders counterattacked. The death of their commander, Colonel Wall, caused them to fall back, allowing further Parliamentary reinforcements to be funnelled into the breach. In the fighting at the walls some 150 Parliamentarian troops, including Colonel Castle, were killed.[20]
After the death of Colonel Wall with more and more Parliamentary soldiers streaming into the breaches, the Royalist resistance at the walls collapsed. The surviving defenders tried to flee across the River Boyne into the northern part of the town while Aston and 250 others took refuge in Millmount Fort overlooking Drogheda's southern defences. Others remained stranded in the towers along the town walls, while Cromwell's troops surged into the town below them.[21]
With up to 6,000 Parliamentary troops now inside the town, Drogheda had been taken.
Massacre

Cromwell, upon riding into the town, was enraged by the sight of heaps of Parliamentarian dead at the breaches. Morrill states "it was the sight of fallen comrades that was the occasion of Cromwell issuing the order for no quarter."[19] In Cromwell's words, "In the heat of the action, I forbade them [his soldiers] to spare any that were in arms in the town...and, that night they put to the sword about two thousand men".[22]
After breaking into the town, the Parliamentarian soldiers pursued the defenders through the streets and into private properties, sacking churches and defensible positions as they went.[23] There was a drawbridge that could have stopped the attackers reaching the northern part of the town, but the defenders had no time to pull it up behind them and the killing continued in the northern part of Drogheda.[24]
Killing of prisoners
Some 200 Royalists under Aston had barricaded themselves in Millmount Fort overlooking the south-eastern gate, while the rest of the town was being sacked.[25] Parliamentarian colonel, Daniel Axtell, "offered to spare the lives of the governor and the 200 men with him if they surrendered on the promise of their lives, which they did."[19]
According to Axtell, the disarmed men were then taken to a windmill and killed about an hour after they had surrendered.[19] Aston was reportedly beaten to death with his own wooden leg, which the Parliamentarian soldiers believed had gold hidden inside.[26]
Some of the Royalists like Aston were Englishmen who had been taken prisoner and then released on military parole in England in 1647–48, but had carried on fighting for King Charles in Ireland. From the Cromwellian point of view, they had broken their parole and could be executed; from the Royalist point of view they had only agreed to parole terms in England, and Ireland was a separate jurisdiction.
Another group of about 100 Royalist soldiers sought refuge in the steeple of St Peter's Church at the northern end of Drogheda.[14] Parliamentarian soldiers led by John Hewson, on Cromwell's orders, set fire to the church steeple.[23] Around 30 of the defenders were burned to death in the fire and 50 more were killed outside when they fled the flames.[27][lower-alpha 3]

The final major concentration of Royalist soldiers was a group of 200 men who had retreated into two towers: the west gate and a round tower next to it called St. Sunday's. They were asked to surrender, but they refused, so a guard was placed on the towers and the Parliamentarians waited, confident that hunger would force them to capitulate. When the occupants of the towers surrendered, they were treated differently. Those in one tower, numbering between 120 and 140 men, had killed and wounded some of the guards. All of the officers in that tower were killed, and the ranks were decimated. The remainder of the men from the first tower, along with the soldiers in the other were deported to Barbados.[14][28]
The heads of 16 Royalist officers were cut off and sent to Dublin, where they were stuck on pikes on the approach roads.[29] Any Catholic clergy found within the town were clubbed to death or "knocked on the head" as Cromwell put it[30] including two who were executed the following day.[31]
Cromwell wrote on 16 September 1649: "I believe we put to the sword the whole number of the defendants. I do not think thirty of the whole number escaped with their lives. Those that did, are in safe custody for the Barbadoes."[32] Specifically, he listed Royalist casualties as 60 officers, 220 cavalry troopers and 2,500 infantry.[33]
However, Colonel John Hewson wrote "those in the towers being about 200, did yield to the General's mercy, where most of them have their lives and be sent to Barbados." Other reports spoke of 400 military prisoners.[3] Some of the garrison escaped over the northern wall, while according to one Royalist officer, Dungan, "many were privately saved by officers and soldiers," despite Cromwell's order for no quarter.[34] Richard Talbot, the future Jacobite and Duke of Tyrconnell, was one of the few members of the garrison to survive the sack.
At least two Royalist officers who initially received quarter were later summarily killed. Three days after the storming of the town, Sir Edmund Verney, an Englishman, was walking with Cromwell, when he was called aside by a former acquaintance who said he wished to converse with him, but instead of a friendly greeting, he was run through with a sword.[35][lower-alpha 4] Two days afterwards, Lieutenant-Colonel Richard Boyle, an Anglo-Irish Episcopalian, was dining when an English Parliamentary soldier entered and whispered something to him. Boyle stood up to follow the soldier, his hostess inquired where he was going, and he replied, "Madam, to die".[36] He was shot after leaving the room.[37]
Civilian casualties
It is not clear how many civilians died in the sack of Drogheda. Cromwell listed the dead as including "many inhabitants" of Drogheda in his report to Parliament. Hugh Peters, a military chaplain on Cromwell's council of war, gave the total loss of life as 3,552, of whom about 2,800 were soldiers, meaning that between 700 and 800 civilians were killed.[3] John Barratt wrote in 2009, "there are no reliable reports from either side that many [civilians] were killed".[38]
The only surviving civilian account of the siege is from Dean Bernard, a Protestant cleric, though a Royalist. He says that while some 30 of his parishioners were sheltering in his house, Parliamentarian troops fired in through the windows, killing one civilian and wounding another. They then broke into the house firing their weapons, but were stopped from killing those inside when an officer known to Bernard identified them as Protestants. The fate of Irish Catholic civilians may therefore have been worse.[lower-alpha 5]
The week after the storming of Drogheda, the Royalist press in England claimed that 2,000 of the 3,000 dead were civilians, a theme that was taken up both in English Royalist and Irish Catholic accounts. Irish clerical sources in the 1660s claimed that 4,000 civilians had died at Drogheda, denouncing the sack as "unparalleled savagery and treachery beyond any slaughterhouse".[39]
Debates over Cromwell's actions
Cromwell justified his actions at Drogheda in a letter to the Speaker of the House of Commons, as follows:[40]
I am persuaded that this is a righteous judgement of God on these barbarous wretches, who have imbrued their hands with so much innocent blood; and that it will tend to prevent the effusion of blood for the future, which are satisfactory grounds for such actions which cannot otherwise but work remorse and regret.
Historians have interpreted the first part of this passage, "the righteous judgement of God," in two ways. Firstly, as a justification for the massacre of the Drogheda garrison in reprisal for the Irish massacre of English and Scottish Protestants in 1641. In this interpretation, the "barbarous wretches" referred to would mean Irish Catholics.[31][lower-alpha 6]

However, as Cromwell was aware, Drogheda had not fallen to the Irish rebels in 1641, or to the Irish Confederate forces in the years that followed. The garrison was in fact English as well as Irish and comprised Catholics and Protestants of both nationalities. The first Irish Catholic troops to be admitted to Drogheda arrived in 1649, as part of the alliance between the Irish Confederates and English Royalists.[41] Historian John Morrill has argued that, in fact, it was English Royalist officers who were singled out for the most ruthless treatment—being denied quarter, executed after being taken prisoner and whose heads were publicly displayed on pikes.[42] From this viewpoint, he argued that by "barbarous wretches" Cromwell meant the Royalists, who in Cromwell's view had refused to accept "the judgement of God" in deciding the civil war in England and were needlessly prolonging the civil wars.[43]
The second part of Cromwell's statement, that the massacre would "tend to prevent the effusion of blood for the future," is accepted to mean that such harshness, including such tactics as clubbing to death and the public displaying of heads, would discourage future resistance and prevent further loss of life.[44] Another of Cromwell's officers wrote, "such extraordinary severity was designed to discourage others from making opposition." Indeed, the neighbouring garrisons of Trim and Dundalk surrendered or fled when they heard the news of what had happened at Drogheda.[26]
Some analyses by authors such as Tom Reilly, have claimed that Cromwell's orders were not exceptionally cruel by the standards of the day, which were that a fortified town that refused an offer of surrender, and was subsequently taken by assault, was not entitled to quarter.[45] However, others have argued that while, "Arthur Aston had refused a summons to surrender, thereby technically forfeiting the lives of the garrison in the event of a successful assault... the sheer scale of the killing [at Drogheda] was simply unprecedented".[46]
According to John Morrill, the massacre at Drogheda, "was without straightforward parallel in 17th century British or Irish history." The only comparable case in Cromwell's career was that at Basing House, where 100 soldiers out of 400 were killed after a successful assault. "So the Drogheda massacre does stand out for its mercilessness, for its combination of ruthlessness and calculation, for its combination of hot-and-cold bloodiness."[47]
See also
Notes
- ↑ Attendees included James Tuchet, 3rd Earl of Castlehaven, Richard Nugent, 2nd Earl of Westmeath, Sir Arthur Aston, Sir Thomas Armstrong (quartermaster-general of horse), Sir Robert Stewart and other Royalist leaders.
- ↑ Two days before Cromwell arrived, the garrison consisted of:[1]
- Artillery: one master gunner, two gunners and three gunners mates
- Cavalry: 320 in five troops, commanded by Major Butler, Captain Harpole, Sir John Dugan, Sir James Preston, Lieutenant-Colonel Dugan, Captain Plunket, Captain Fleming, and Captain Finglas
- Infantry: 2,221 in four regiments, under the command of Colonel Bryne, Colonel Wall, Sir Edmund Verney and Colonel Warren
- ↑ The precise numbers are not known. Cromwell stated that "about 100 of them possessed St. Peter's Church-steeple" (Cromwell 1649a) and Hewson reported that "the steeple was fired and then fifty of them got out at the top of the church, but the enraged soldiers put them all to the sword, and thirty of them were burnt in the fire." (Wheeler 1999, p. 87).
- ↑ The details in the Buck's letter indicates that Cromwell's order to put all those on Mill-Mount to the sword was not completely obeyed as Sir Edmund Verney was in command on the Mount (Browne & Nolan, Limited, p. 482).
- ↑ "the implications of this sequence of events for the town's Catholics do not require any further explanation ... according to the one surviving civilian account of the storming of Drogheda, the New Model Army deliberately attacked non-combatants in their homes" (Ó Siochrú 2008, p. 89).
- ↑ Mark Levene points out that "[o]nly three years before in 1646 Sir William Temple a distinguished parliamentary lawyer had published a semi-official account of the 1641 rebellion, apparently sober and factual, full of grisly detail, setting total Protestant casualties at the appalling figure of three hundred thousand" (Clifton 1999, p. 120) and so he infers that revenge played its part in the massacre and that "barbarous wretches" was an allusion to the rebels of 1641.
Citations
- 1 2 Gilbert 1879, preface xviii, xix.
- 1 2 3 Ó Siochrú 2008, p. 81.
- 1 2 3 Morrill 2007, p. 254.
- ↑ Ó Siochrú 2008, pp. 73–76.
- ↑ Reilly 1999, p. 53.
- ↑ Wheeler 1999, pp. 80–81.
- ↑ Wheeler 1999, p. 80.
- ↑ Ó Siochrú 2008, pp. 77–80.
- ↑ Lenihan 2001, p. 175.
- ↑ Wheeler 1999, p. 83.
- ↑ Wheeler 1999, pp. 83–85.
- ↑ Reilly 1999, p. 58.
- ↑ Reilly 1999, p. 63.
- 1 2 3 Cromwell 1649a, Letter to William Lenthall.
- ↑ Wheeler 1999, pp. 85–86.
- ↑ Reilly 1999, p. 64.
- ↑ Clifton 1999, p. 119.
- ↑ Reilly 1999, p. 59.
- 1 2 3 4 Morrill 2007, p. 255.
- ↑ Wheeler 1999, pp. 86–87.
- ↑ Wheeler 1999, pp. 87–88.
- ↑ Reilly 1999, p. 71.
- 1 2 Reilly 1999, p. 75 quoting Perfect Diurnall, 8 October 1649
- ↑ Wheeler 1999, p. 88.
- ↑ Reilly 1999, pp. 73–74 quoting the Moderate Intelligencer, 4 October 1649
- 1 2 Parker 2003, p. 158.
- ↑ Wheeler 1999, p. 87.
- ↑ Reilly 1999, p. 78.
- ↑ Morrill 2007, p. 256.
- ↑ Reilly 1999, p. 79.
- 1 2 Ó Siochrú 2008, p. 84.
- ↑ Cromwell 1649, Letter to John Bradshaw.
- ↑ Morrill 2007, p. 253.
- ↑ Ó Siochrú 2008, p. 87.
- ↑ Verney 1892, pp. 344–345 quoting Buck 1649, Letter
- ↑ Collins 1998, p. 79 quoting Buck 1649, Letter
- ↑ Collins 1998, p. 79.
- ↑ Barratt 2009, p. 165.
- ↑ Ó Siochrú 2008, p. 95.
- ↑ Morrill 2007, p. 257.
- ↑ Parker 2003, p. 158; Ó Siochrú 2008, p. 84
- ↑ Morrill 2007, pp. 257–258.
- ↑ Morrill 2007, p. 258.
- ↑ Morrill 2007, p. 256; Parker 2003, p. 158; Ó Siochrú 2008, p. 85
- ↑ Reilly 1999, p. .
- ↑ Ó Siochrú 2008, p. 85.
- ↑ Morrill 2007, pp. 263–265.
References
- Barratt, John (2009). Sieges of the English Civil Wars. Pen and Sword Books. p. 165. ISBN 978-1844158324.
- Browne & Nolan, Limited. The Irish ecclesiastical record (July to December 1911). Vol. 30. Dublin. p. 482.
- Buck, James (8 November 1649). .
- Clifton, Robin (1999). "'An Indiscriminate Blackness'? Massacre, Counter-Massacre, and Ethnic Cleansing in Ireland 1640–1660". In Levene, Mark; Roberts, Penny (eds.). The Massacre in History. Studies on War and Genocide, Berghahn Series. Vol. 1. Berghahn Books. pp. 119, 120.
- Collins, Sean (1998), Drogheda: Gateway to the Boyne (illustrated ed.), Dundurn, p. 79, ISBN 978-1900935081
- Cromwell, Oliver (16 September 1649). . Dublin.
- Cromwell, Oliver (17 September 1649a). . Dublin.
- Gilbert, John T., ed. (1879). A contemporary history of affairs in Ireland, from 1641 to 1652. Now for the first time published, with an appendix of original letters and documents. Dublin: the Irish Archaeological and Celtic Society – via archive.org.
- Lenihan, Padraig (2001). Confederate Catholics at War. Cork. ISBN 1-85918-244-5.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Morrill, John (2007). "The Drogheda Massacre in Cromwellian Context". In Edwards; Lenihan; Tait (eds.). The Age of Actrocity. Four Courts Press.
- Ó Siochrú, Micheál (2008). God's Executioner, Oliver Cromwell and the Conquest of Ireland. Faber & Faber. ISBN 978-0571218462.
- Parker, Geoffrey (2003). Empire War and Faith in Early Modern Europe. Penguin.
- Reilly, Tom (1999). Cromwell, An Honourable Enemy. London: Phoenix Press. ISBN 1-84212-080-8.
- Verney, Frances Parthenope (1892). Memoirs of the Verney family during the Civil War. Vol. 2. London and New York: Longmans, Green, and company. pp. 344, 345.
- Wheeler, James Scott (1999). Cromwell in Ireland. Dublin. ISBN 978-0-7171-2884-6.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link)
Further reading
- Churchill, Winston (19 November 1956). "The Curse of Cromwell". Life. Vol. 41, no. 21. ISSN 0024-3019.
- Gentles, Ian (1994). The New Model Army. Cambridge. ISBN 0-631-19347-2.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Hill, Christopher (1970). God's Englishman: Oliver Cromwell and the English Revolution. New York. ISBN 978-0-14-021438-3.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Keegan, John; Ohlmeyer, Jane, eds. (1998). The Civil Wars. Oxford. ISBN 0-19-866222-X.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link)