 8-simplex |
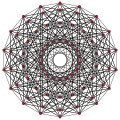 Heptellated 8-simplex |
 Heptihexipentisteriruncicantitruncated 8-simplex (Omnitruncated 8-simplex) |
| Orthogonal projections in A8 Coxeter plane (A7 for omnitruncation) | ||
|---|---|---|
In eight-dimensional geometry, a heptellated 8-simplex is a convex uniform 8-polytope, including 7th-order truncations (heptellation) from the regular 8-simplex.
There are 35 unique heptellations for the 8-simplex, including all permutations of truncations, cantellations, runcinations, sterications, pentellations, and hexications. The simplest heptellated 8-simplex is also called an expanded 8-simplex, with only the first and last nodes ringed, is constructed by an expansion operation applied to the regular 8-simplex. The highest form, the heptihexipentisteriruncicantitruncated 8-simplex is more simply called a omnitruncated 8-simplex with all of the nodes ringed.
Heptellated 8-simplex
| Heptellated 8-simplex | |
|---|---|
| Type | uniform 8-polytope |
| Schläfli symbol | t0,7{3,3,3,3,3,3,3} |
| Coxeter-Dynkin diagrams | |
| 7-faces | |
| 6-faces | |
| 5-faces | |
| 4-faces | |
| Cells | |
| Faces | |
| Edges | 504 |
| Vertices | 72 |
| Vertex figure | 6-simplex antiprism |
| Coxeter group | A8×2, [[37]], order 725760 |
| Properties | convex |
Alternate names
- Expanded 8-simplex
- Small exated enneazetton (soxeb) (Jonathan Bowers)[1]
Coordinates
The vertices of the heptellated 8-simplex can bepositioned in 8-space as permutations of (0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,2). This construction is based on facets of the heptellated 9-orthoplex.
A second construction in 9-space, from the center of a rectified 9-orthoplex is given by coordinate permutations of:
- (1,-1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0)
Root vectors
Its 72 vertices represent the root vectors of the simple Lie group A8.
Images
| Ak Coxeter plane | A8 | A7 | A6 | A5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Graph |  |
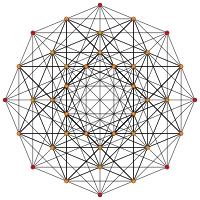 |
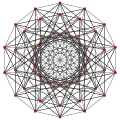 |
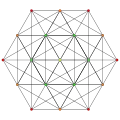 |
| Dihedral symmetry | [[9]] = [18] | [8] | [[7]] = [14] | [6] |
| Ak Coxeter plane | A4 | A3 | A2 | |
| Graph |  |
 |
 | |
| Dihedral symmetry | [[5]] = [10] | [4] | [[3]] = [6] |
Omnitruncated 8-simplex
| Omnitruncated 8-simplex | |
|---|---|
| Type | uniform 8-polytope |
| Schläfli symbol | t0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7{37} |
| Coxeter-Dynkin diagrams | |
| 7-faces | |
| 6-faces | |
| 5-faces | |
| 4-faces | |
| Cells | |
| Faces | |
| Edges | 1451520 |
| Vertices | 362880 |
| Vertex figure | irr. 7-simplex |
| Coxeter group | A8, [[37]], order 725760 |
| Properties | convex |
The symmetry order of an omnitruncated 8-simplex is 725760. The symmetry of a family of a uniform polytopes is equal to the number of vertices of the omnitruncation, being 362880 (9 factorial) in the case of the omnitruncated 8-simplex; but when the CD symbol is palindromic, the symmetry order is doubled, 725760 here, because the element corresponding to any element of the underlying 8-simplex can be exchanged with one of those corresponding to an element of its dual.
Alternate names
- Heptihexipentisteriruncicantitruncated 8-simplex
- Great exated enneazetton (goxeb) (Jonathan Bowers)[2]
Coordinates
The Cartesian coordinates of the vertices of the omnitruncated 8-simplex can be most simply positioned in 9-space as permutations of (0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8). This construction is based on facets of the heptihexipentisteriruncicantitruncated 9-orthoplex, t0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7{37,4}
Images
| Ak Coxeter plane | A8 | A7 | A6 | A5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Graph |  |
 |
 |
 |
| Dihedral symmetry | [[9]] = [18] | [8] | [[7]] = [14] | [6] |
| Ak Coxeter plane | A4 | A3 | A2 | |
| Graph |  |
 |
 | |
| Dihedral symmetry | [[5]] = [10] | [4] | [[3]] = [6] |
Permutohedron and related tessellation
The omnitruncated 8-simplex is the permutohedron of order 9. The omnitruncated 8-simplex is a zonotope, the Minkowski sum of nine line segments parallel to the nine lines through the origin and the nine vertices of the 8-simplex.
Like all uniform omnitruncated n-simplices, the omnitruncated 8-simplex can tessellate space by itself, in this case 8-dimensional space with three facets around each ridge. It has Coxeter-Dynkin diagram of ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() .
.
Related polytopes
This polytope is one of 135 uniform 8-polytopes with A8 symmetry.
| A8 polytopes | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
t0 |
t1 |
t2 |
t3 |
t01 |
t02 |
t12 |
t03 |
t13 |
t23 |
t04 |
t14 |
t24 |
t34 |
t05 |
t15 |
t25 |
t06 |
t16 |
t07 |
t012 |
t013 |
t023 |
t123 |
t014 |
t024 |
t124 |
t034 |
t134 |
t234 |
t015 |
t025 |
t125 |
t035 |
t135 |
t235 |
t045 |
t145 |
t016 |
t026 |
t126 |
t036 |
t136 |
t046 |
t056 |
t017 |
t027 |
t037 |
t0123 |
t0124 |
t0134 |
t0234 |
t1234 |
t0125 |
t0135 |
t0235 |
t1235 |
t0145 |
t0245 |
t1245 |
t0345 |
t1345 |
t2345 |
t0126 |
t0136 |
t0236 |
t1236 |
t0146 |
t0246 |
t1246 |
t0346 |
t1346 |
t0156 |
t0256 |
t1256 |
t0356 |
t0456 |
t0127 |
t0137 |
t0237 |
t0147 |
t0247 |
t0347 |
t0157 |
t0257 |
t0167 |
t01234 |
t01235 |
t01245 |
t01345 |
t02345 |
t12345 |
t01236 |
t01246 |
t01346 |
t02346 |
t12346 |
t01256 |
t01356 |
t02356 |
t12356 |
t01456 |
t02456 |
t03456 |
t01237 |
t01247 |
t01347 |
t02347 |
t01257 |
t01357 |
t02357 |
t01457 |
t01267 |
t01367 |
t012345 |
t012346 |
t012356 |
t012456 |
t013456 |
t023456 |
t123456 |
t012347 |
t012357 |
t012457 |
t013457 |
t023457 |
t012367 |
t012467 |
t013467 |
t012567 |
t0123456 |
t0123457 |
t0123467 |
t0123567 |
t01234567 |
Notes
References
- H.S.M. Coxeter:
- H.S.M. Coxeter, Regular Polytopes, 3rd Edition, Dover New York, 1973
- Kaleidoscopes: Selected Writings of H.S.M. Coxeter, edited by F. Arthur Sherk, Peter McMullen, Anthony C. Thompson, Asia Ivic Weiss, Wiley-Interscience Publication, 1995, ISBN 978-0-471-01003-6
- (Paper 22) H.S.M. Coxeter, Regular and Semi Regular Polytopes I, [Math. Zeit. 46 (1940) 380-407, MR 2,10]
- (Paper 23) H.S.M. Coxeter, Regular and Semi-Regular Polytopes II, [Math. Zeit. 188 (1985) 559-591]
- (Paper 24) H.S.M. Coxeter, Regular and Semi-Regular Polytopes III, [Math. Zeit. 200 (1988) 3-45]
- Norman Johnson Uniform Polytopes, Manuscript (1991)
- N.W. Johnson: The Theory of Uniform Polytopes and Honeycombs, Ph.D.
- Klitzing, Richard. "8D uniform polytopes (polyzetta)". x3o3o3o3o3o3o3x - soxeb, x3x3x3x3x3x3x3x - goxeb