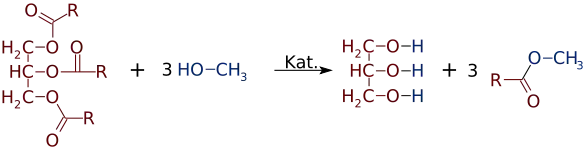Fatty acid methyl esters (FAME) are a type of fatty acid ester that are derived by transesterification of fats with methanol. The molecules in biodiesel are primarily FAME, usually obtained from vegetable oils by transesterification. They are used to produce detergents and biodiesel.[1] FAME are typically produced by an alkali-catalyzed reaction between fats and methanol in the presence of base such as sodium hydroxide, sodium methoxide[2] or potassium hydroxide. One of the reasons for FAME use in biodiesel instead of free fatty acids is to nullify any corrosion that free fatty acids would cause to the metals of engines, production facilities and so forth. Free fatty acids are only mildly acidic, but in time can cause cumulative corrosion unlike their esters. As an improved quality, FAMEs also usually have about 12-15 units higher cetane number than their unesterified counterparts.[3]
Other details
Every microorganism has its specific FAME profile (microbial fingerprinting). After triglycerides, fatty acids and certain other lipids of some cultured microbes are esterified, they become volatile enough for analysis with gas chromatography which is used to create FAME profile.[4] These profiles can be used as a tool for microbial source tracking (MST) to identify pathological bacteria strains[5] and for characterizing new species of bacteria.
For example, a profile created from cultured bacteria from some water sample can be compared to a profile of known pathological bacteria to find out if the water is polluted by feces or not.[5]
In June 2022, Polycyclopropanated fatty acid methyl ester (POP-FAME) fuels were biosynthesized from Streptomyces coelicolor bacteria, which have energy densities of more than 50MJ/L larger than the most widely used aviation and rocket fuels.[6]
See also
References
- ↑ Anneken, David J.; Both, Sabine; Christoph, Ralf; Fieg, Georg; Steinberner, Udo; Westfechtel, Alfred (2006). "Fatty Acids". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a10_245.pub2. ISBN 9783527306732. OCLC 910197915.
- ↑ Vyas, Amish P.; Verma, Jaswant L.; Subrahmanyam, N. (2010). "A review on FAME production processes". Fuel. 89 (1): 1–9. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2009.08.014. ISSN 0016-2361.
- ↑ Schobert, Harold H. (2013). Chemistry of Fossil Fuels and Biofuels. Cambridge, NY: Cambridge University Press. pp. 62–64. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511844188. ISBN 9780511844188. OCLC 823724682.
- ↑ Sekora, Nicholas S.; Lawrence, Kathy S.; Agudelo, Paula; van Santen, Edzard; McInroy, John A. (2009). "Using FAME Analysis to Compare, Differentiate, and Identify Multiple Nematode Species". Journal of Nematology. 41 (3): 163–173. PMC 3380492. PMID 22736811.
- 1 2 Duran, Metin; Haznedaroğlu, Berat Z.; Zitomer, Daniel H. (2006). "Microbial source tracking using host specific FAME profiles of fecal coliforms". Water Research. 40 (1): 67–74. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2005.10.019. PMID 16360192.
- ↑ Cruz-Morales, Pablo; Yin, Kevin; Landera, Alexander; Cort, John R.; Young, Robert P.; Kyle, Jennifer E.; Bertrand, Robert; Iavarone, Anthony T.; Acharya, Suneil; Cowan, Aidan; Chen, Yan; Gin, Jennifer W.; Scown, Corinne D.; Petzold, Christopher J.; Araujo-Barcelos, Carolina (2022-07-20). "Biosynthesis of polycyclopropanated high energy biofuels". Joule. 6 (7): 1590–1605. doi:10.1016/j.joule.2022.05.011. ISSN 2542-4785. S2CID 250189786.