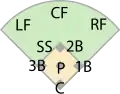
In the sport of baseball, each of the nine players on a team is assigned a particular fielding position when it is their turn to play defense. Each position conventionally has an associated number, for use in scorekeeping by the official scorer: 1 (pitcher), 2 (catcher), 3 (first baseman), 4 (second baseman), 5 (third baseman), 6 (shortstop), 7 (left fielder), 8 (center fielder), and 9 (right fielder).[1] Collectively, these positions are usually grouped into three groups: the outfield (left field, center field, and right field), the infield (first base, second base, third base, and shortstop), and the battery (pitcher and catcher). Traditionally, players within each group will often be more able to exchange positions easily (that is, a second baseman can usually play shortstop well, and a center fielder can also be expected to play right field); however, the pitcher and catcher are highly specialized positions and rarely will play at other positions.
Fielding
Fielders must be able to catch the ball well, as catching batted balls before they bounce is one way they can put the batter out, as well as create opportunities to prevent the advance of, and put out other runners. In addition, they must be able to throw the ball well, with many plays in the game depending on one fielder collecting the hit ball and then throwing it to another fielder who, while holding the ball in their hand/glove, touches either a runner or the base the runner is forced to run to in order to record an out. Fielders often have to run, dive, and slide a great deal in the act of reaching, stopping, and retrieving a hit ball, and then setting themselves up to transfer the ball, all with the end goal of getting the ball as quickly as possible to another fielder. They also run the risk of colliding with incoming runners during a tag attempt at a base.
Fielders may have different responsibilities depending on the game situation. For example, when an outfielder is attempting to throw the ball from near the fence to one of the bases, an infielder may need to "cut off" the throw and then act as a relay thrower to help the ball cover its remaining distance to the target destination.[2]
As a group, the outfielders are responsible for preventing home runs by reaching over the fence (and potentially doing a wall climb) for fly balls that are catchable. The infielders are the ones who generally handle plays that involve tagging a base or runner, and also need quick reflexes in order to catch a batted ball before it leaves the infield. The pitcher and catcher have special responsibilities to prevent base stealing, as they are the ones who handle the ball whenever it has not been hit. The catcher will also sometimes attempt to block the plate in order to prevent a run being scored.
Other roles
Other team personnel
See also
References
- ↑ Spatz, Lyle (2012). Historical Dictionary of Baseball. Scarecrow Press. p. 3. ISBN 9780810879546.
- ↑ "Baseball Positions & Responsibilities". SportsRec. Retrieved 2021-08-19.