| Genital branch of genitofemoral nerve | |
|---|---|
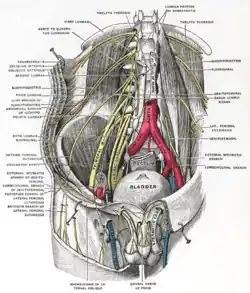 Deep and superficial dissection of the lumbar plexus (external spermatic branch of genitofemoral labeled at bottom right) | |
| Details | |
| From | Genitofemoral nerve |
| Innervates | Cremaster and dartos muscle |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | ramus genitalis nervi genitofemoralis |
| TA98 | A14.2.07.009 |
| TA2 | 6530 |
| FMA | 20560 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve, also known as the external spermatic nerve in males, is a nerve in the abdomen that arises from the genitofemoral nerve. The genital branch supplies the cremaster muscle and anterior scrotal skin in males, and the skin of the mons pubis and labia majora in females.
Structure
The genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve arises from the ventral primary divisions of L1-L2 spinal nerve roots. It passes outward on the psoas major muscle, and pierces the fascia transversalis, or passes through the deep inguinal ring. It then descends within the spermatic cord. In males, it passes through to the scrotum, where it supplies the cremaster, dartos muscle and gives a few filaments to the skin of the scrotum. In females, it accompanies the round ligament of the uterus, where it terminates as the nerve supplying the skin of the labia majora and mons pubis.[1] : 343
Function
The genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve is responsible for the motor portion of the cremasteric reflex, which describes contraction of the cremasteric muscle when the skin of the superior medial part of the thigh is touched.[1] : 262
See also
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 953 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 953 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- Anatomy photo:36:07-0305 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Inguinal Region, Scrotum and Testes: Layers of the Spermatic Cord"