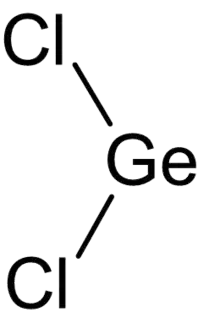
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Germanium dichloride | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Dichlorogermanylidene | |
| Other names
Dichlorogermylene Germanium(II) chloride | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.162 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| GeCl2 | |
| Molar mass | 143.546 g/mol |
| Appearance | white-pale yellow solid |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Germanium dichloride is a chemical compound of germanium and chlorine with the formula GeCl2. It is a yellow solid. Germanium dichloride is an example of a compound featuring germanium in the +2 oxidation state.
Preparation
Solid germanium dichloride can be produced by comproportionation by passing germanium tetrachloride, GeCl4, over germanium metal at 300 °C and reduced pressure (0.1 mmHg).[1]
- GeCl4 + Ge → 2 GeCl2
Germanium dichloride is also formed from the decomposition of trichlorogermane, GeHCl3, at 70 °C. Trichlorogermane is generated when germanium reacts with hydrogen chloride.[1] This reaction involves dehydrohalogenation.
- GeHCl3 → GeCl2 + HCl
Another route to germanium dichloride is the reduction of germanium tetrachloride with hydrogen at 800 °C.[1]
- GeCl4 + H2 → GeCl2 + 2HCl
Reactions
GeCl2 is hydrolysed to give yellow germanium(II) hydroxide, which on warming gives brown germanium monoxide:[1]
- GeCl2 + 2 H2O ⇌ Ge(OH)2(s) + 2 HCl
- Ge(OH)2 → GeO + H2O
Alkalizing a solution containing germanium(II) ions:
- Ge2+ + 2 OH− → Ge(OH)2
Germanium oxides and hydroxides are amphoteric. Solutions of GeCl2 in HCl are strongly reducing.[2] With chloride ion, ionic compounds containing the pyramidal GeCl−3 ion have been characterised, for example [3] With rubidium and caesium chloride compounds, e.g. RbGeCl3 are produced; these have distorted perovskite structures.[1]
Germanium dichloride reacts with tetraethylammonium chloride to give the trichlorogermanate:[4]
- GeCl2 + Et4NCl → Et4NGeCl3
Dichlorogermylene
Molecular GeCl2 is often called dichlorogermylene, highlighting its resemblance to a carbene. The structure of gas-phase molecular GeCl2 shows that it is a bent molecule, as predicted by VSEPR theory.[5] The dioxane complex, GeCl2·dioxane, has been used as a source of molecular GeCl2 for reaction syntheses, as has the in situ reaction of GeCl4 and Ge metal. GeCl2 is quite reactive and inserts into many types of chemical bonds.[6] Usually, germanium dichloride is generated from germanium dichloride dioxane.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 376. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ↑ Egon Wiberg, Arnold Frederick Holleman (2001) Inorganic Chemistry, Elsevier ISBN 0-12-352651-5
- ↑ Kociok-Köhn, G.; Winter, J. G.; Filippou, A. C. (1999). "Trimethylphosphonium trichlorogermanate(II)". Acta Crystallogr. C. 55 (3): 351–353. doi:10.1107/S010827019801169X.
- ↑ Parshall, G. W. (1974). "Tetraethylammonium Trichlorogermanate(l-) and Trichlorostannate(l-)". Inorganic Syntheses. 15: 222–225. doi:10.1002/9780470132463.ch48. ISBN 9780470132463.
- ↑ Tsuchiya, Masaki J.; Honjou, Hiroaki; Tanaka, Keiichi; Tanaka, Takehiko (1995). "Millimeter-wave spectrum of germanium dichloride GeCl2. Equilibrium structure and anharmonic force field". Journal of Molecular Structure. 352–353: 407–415. Bibcode:1995JMoSt.352..407T. doi:10.1016/0022-2860(95)08830-O.
- ↑ Egorov, M.P.; Gaspar, P. (1994). "Germanium: Organometallic chemistry". Encyclopedia of Inorganic chemistry. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 0-471-93620-0.