
Philip the Tetrarch (c. 26 BCE. - 34 CE), sometimes called Herod Philip II by modern writers (see "Naming convention"), son of Herod the Great and his fifth wife, Cleopatra of Jerusalem, ruled over the northeast part of his father's kingdom between 4 BCE and 34 CE. He was a half-brother of Herod Antipas and Herod Archelaus and should not be confused with Herod II, whom some writers call Herod Philip I.
Territory
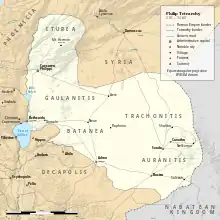
Philip ruled territories which the Gospel of Luke lists as Iturea and Trachonitis[1] and Flavius Josephus lists as Gaulanitis, Trachonitis and Paneas[2] as well as Batanea, Trachonitis, Auranitis, and "a certain part of what is called the House of Zenodorus".[3] The city of Caesarea Philippi served as the capital of his tetrarchy.
Marriage and dynasty
Philip married his niece Salome, the daughter of Herodias and Herod II (sometimes called Herod Philip I, and also a member of the Herodian dynasty). This Salome appears in the Bible in connection with the beheading of John the Baptist. However, there would have been a great difference in their ages: Salome was born in ~14 CE, at which time Herod Philip was 39 years old. The gospels of Matthew and Mark state that the Herodias whom Herod Antipas married was the wife of Antipas' brother "Philip", a fact supported by Josephus, who indicated she was the wife of Herod II (a.k.a. Philip I).
It is possible that the 'Salome' he was married to was a half-sister by that same name, a daughter of Herod the Great and his 8th wife Elpis. This sibling Salome was born in ~14 BCE, and so only five years younger than Herod Philip (a more realistic age gap). But this would also be the only known occurrence of the children of Herod the Great intermarrying, even if from different mothers. Marriage to 1st cousins and uncles, however, was relatively common in the so-called Herodian dynasty.
It is known that Philip the Tetrarch rebuilt the city of Caesarea Philippi, calling it by his own name to distinguish it from the Caesarea on the sea-coast, which was the seat of the Roman government.
Naming convention
There is no contemporary evidence for Philip the Tetrarch's use of the name "Herod Philip" (Greek: Ἡρώδης Φίλιππος, Hērōdēs Philippos) as a dynastic title, as did occur with his brothers Herod Antipas and Herod Archelaus. Herod II is sometimes called "Herod Philip I" (because both the Gospel of Matthew[4] and Gospel of Mark[5] call the husband of Herodias "Philip"), and then Philip the Tetrarch is called "Herod Philip II".[6][7] Kokkinos says, "The stubborn insistence of many theologians in referring to Herod III as 'Herod Philip' is without any value...No illusory Herod Philip ever existed."[7][pp. 223–233]; [266] Philip the Tetrarch, "unlike his brothers, did not use Herod as a dynastic name."[8] Philip's half-brothers, Archelaus and Antipas, had adopted the name of Herod, "presumably" for a dynastic claim from Herod the Great.[9]
Family tree of the Herodian dynasty
| Antipater the Idumaean procurator of Judea | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1.Doris 2.Mariamne I 3.Mariamne II 4.Malthace | Herod I the Great king of Judea | 5.Cleopatra of Jerusalem 6.Pallas 7.Phaidra 8.Elpis | Phasael governor of Jerusalem | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) Antipater heir of Judaea | (2) Alexander I prince of Judea | (2) Aristobulus IV prince of Judea | (3) Herod II Philip prince of Judea | (4) Herod Archelaus ethnarch of Judea, Idumea | (4) Herod Antipas tetrarch of Galilea & Perea | (5) Philip the Tetrarch of Iturea & Trachonitis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tigranes V of Armenia | Alexander II prince of Judea | Herod Agrippa I king of Judea | Herod V ruler of Chalcis | Aristobulus Minor prince of Judea | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tigranes VI of Armenia | Herod Agrippa II king of Judea | Aristobulus ruler of Chalcis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gaius Julius Alexander ruler of Cilicia | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gaius Julius Agrippa quaestor of Asia | Gaius Julius Alexander Berenicianus proconsul of Asia | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lucius Julius Gainius Fabius Agrippa gymnasiarch | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See also
References
- ↑ Luke 3:1
- ↑ "Flavius Josephus, Anitquities XVII., 8 : 1".
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ↑ "Flavius Josephus, Anitquities XVII., 11 : 4".
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ↑ Matthew 14:3
- ↑ Mark 6:17
- ↑ Note: It is an example of the great difficulty in establishing the relationships of various holders of the same name in the same area or family - especially in the Herodian dynasty.
- 1 2 Kokkinos (1998).
- ↑ Bowman & al., eds. (2001 [1996]). Refers to him throughout as Philip, or Philip the Tetrarch.
- ↑ Bury & al., eds. (1965 or before)
Bibliography
- Vol. 10: The Augustan empire, 44 B.C.–A.D. 70. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help)- J. B. Bury; S.A. Cook; F.E. Adcock; M.P. Charlesworth; N.H. Baynes, eds. (1965) [latest reprint]. ~.
- Bowman, Alan K.; Champlin, Edward; Lintott, Andrew, eds. (2001) [1996]. ~. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521264308. Retrieved 25 February 2022.
- Kokkinos, Nikos (1998). "The Herodian Dynasty: Origins, Role in Society and Eclipse". Journal for the Study of the Pseudepigrapha, Supplement Series. Sheffield: Sheffield Academic Press: 236–240.
External links
- Philip the Tetrarch entry in historical sourcebook by Mahlon H. Smith
- Herod Philip II biographical entry