| History of Albania |
|---|
 |
| Timeline |
Ottoman Albania refers to a period in Albanian history from the Ottoman conquest in the late 15th century to the Albanian declaration of Independence and official secession from the Ottoman Empire in 1912. The Ottomans first entered Albania in 1385 upon the invitation of the Albanian noble Karl Thopia to suppress the forces of the noble Balša II during the battle of Savra. They had some previous influence in some Albanian regions after the battle of Savra in 1385 but not direct control. The Ottomans placed garrisons throughout southern Albania by 1420s and established formal jurisdiction in central Albania by 1431. Even though The Ottomans claimed rule of all Albanian lands, most Albanian ethnic territories were still governed by medieval Albanian nobility who were free of Ottoman rule. The Sanjak of Albania was established in 1420 or 1430 controlling mostly central Albania, while Ottoman rule became more consolidated in 1481, after the fall of Shkodra and League of Lezhe with the country (including areas of today's Kosovo, Montenegro and Macedonia) being mostly free in the period of 1443–1481. Albanians revolted again in 1481 but the Ottomans finally controlled Albania by 1488.
The term used in Ottoman sources for the country was Arnavudluk (Ottoman Turkish: آرناوودلق), including areas such as present-day Albania, Kosovo, western North Macedonia, southern Serbia, southern Montenegro and parts of northern Greece.[1][2]
In 1431, Many Albanian princes including Gjergj Arianiti, Zenevisi family, Andrea Thopia and Gjon Kastrioti started a war against the Ottoman Empire which resulted in defeat of Gjon Kastrioti but victory in 4 battles for Gjergj Arianiti and 1 victory for Andrea Thopia. These Albanian victories opened the way for the coming of Skanderbeg in 1443 in Kruja. Independence for most of the Albanian regions was maintained during 1443–1479, with the uprising under the lead of Skanderbeg that together with other Albanian nobles such Gjergj Arianiti, Andrea Thopia and Lek Dukagjini achieved remarkable result of 30+ victories against the Ottoman Empire.[3]
The Albanian resistance and war against Ottomans continued for 48 years. The last towns captured by the Ottomans were Shkodër in 1480, Durrës in 1501 and Himara in 1509, except for the northern part of Albania, Mirdita, which could never be fully invaded. The Ottomans seeing the impossibility to invade this place they were forced to ensure the region the right of autonomy with its own heredity princes.[4] Principality of Mirdita remained always free which was ruled by the Gjomarka family for 400 years essentially throughout the entire Ottoman period in the Balkans.[5]
Albanians would enter later on in a period of Islamization, starting in the late 14th century and early 15th century, and increasing especially in the 16th and 17th centuries. Albanians through converting to Islam would eventually dominate the Ottoman power structures disproportionally to their small population considering the large territory and huge population of the Ottoman Empire. They would become one of the most important and prestigious nations in the Empire playing an important role in the 15th and 16th centuries and especially a striking role in the 17th,18th and 19th centuries.
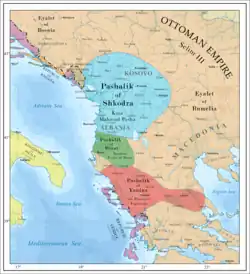
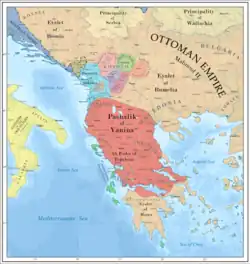
A period of the semi-independence started for local Albanian rulers in Balkans in the 1750s with the era of the so called Independent Albanian Pashas. In 1754 the autonomous Albanian Pashalik of Bushati family would be established with center the city of Shkodra called Pashalik of Shkodra. Later on the same autonomous Pashalik of Berat would be established and culminating with the Albanian Pashalik of Ali Pashe Tepelena in 1787. The Albanian Pashaliks would end in 1831 with the last one being the Bushati Pashalik. These de facto independent Albanian Pashaliks would extend from Bosnia to south of Morea ( Peloponnese) in today's southern Greece.
Meanwhile, an Ottoman Albanian commander Mehmet Ali of Egypt, would seize power in Egypt in 1805 through his Albanian mercenaries by establishing a dynasty lasting up to 1954. He would take over Sudan and many regions of Saudi Arabia by 1824 and would take over Levant later on in 1831 by even defeating Ottomans in 1833. The conflict would rise again in what is known as Egyptian-Ottoman War (1839-1841) and only European Powers would stop Mehmet Ali and his son Ibrahim Pasha to seize Constantinople and replace the Ottoman dynasty with the Albanian one by thus resolving the Oriental Crisis of 1840. Albanian communities exist up to this day in Egypt and other areas of Levant such as Syria and Palestine.
The territory which today belongs to the Republic of Albania remained part of the Ottoman Empire until it declared independence in 1912, during the Balkan Wars.
History
14th century

The Ottomans expanded their control from Anatolia to the Balkans in the middle of the 14th century. They entered European territory in 1352, and they defeated a Balkan coalition army led by Serbs, that also included some Albanians and Bosnians in the Battle of Kosovo in 1389. Ottoman pressure lessened in 1402 when the Mongol leader Timur (Tamerlane) attacked Anatolia from the east, killed the Sultan, and sparked a civil war.[7] When order was restored, the Ottomans renewed their westward progress. In 1453, Sultan Mehmed II's forces overran Constantinople and killed the last Byzantine emperor.[8]
The division of the Albanian-populated lands into small, quarreling fiefdoms ruled by independent feudal lords and tribal chiefs made them easy prey for the Ottoman armies. In 1385, the Albanian ruler of Durrës, Karl Thopia, appealed to the sultan for support against his rivals, the Balsha noble family. An Ottoman force quickly marched into Albania along the Via Egnatia and routed Balsha II in the Battle of Savra. Some of the Albanian Principalities soon started to become vassals of the Ottoman Empire after 1420. Gjirokastra became the county town of the Sanjak of Albania in 1420.[9] and than Kruja was established as the center of Sanjak of Albania after Gjergj Arianiti defeated the Ottomans between 1431 and 1435.
The Ottomans allowed Albanian clan chiefs to maintain their positions, rule and property, but they had to pay tribute, and sometimes send their sons to the Ottoman court as hostages, and provide the Ottoman army with auxiliary troops.[8] However many Albanian clans and Principalities did not recognize the Ottoman authority and did not pay tribute.
Albanian resistance

The Albanians' resistance to the Ottomans in the 14th century and especially in the 15th century won them acclaim all over Europe. Gjon Kastrioti of Krujë was one of the Albanian nobles and clan leaders who submitted to Ottoman suzerainty in 1425. He was compelled to send his four sons to the Ottoman capital to be trained for military service. The youngest, George Kastrioti (1403–68), who would become the Albanians' national hero, captured the sultan's attention. Renamed Iskander when he converted to Islam, the young man participated in military expeditions to Asia Minor and Europe becoming one of the main Ottoman generals. When appointed to administer a Balkan district, Iskander became known as Skanderbeg. After Ottoman forces under Skanderbeg's command suffered defeat in a battle near Niš (intentionally by him) present-day Serbia in 1443, Skanderbeg rushed to Krujë and tricked a Turkish pasha into surrendering the Albanian fortress. Skanderbeg then embraced Roman Catholicism and declared a holy war against the Ottoman Empire.[8]
On 1 March 1444, Albanian chieftains gathered in the cathedral of Lezhë with the prince of Montenegro and delegates from Venice and proclaimed Skanderbeg commander of the Albanian resistance. All of Albania accepted his leadership against the Ottomans, but local leaders kept control of their own districts. Under a red flag bearing Skanderbeg's heraldic emblem, an Albanian force of about 10,000-15.000 men held off Ottoman campaigns against their lands for twenty-four years when Skanderbeg was commander in chief and for another 11 years after his death.
Three times the Albanians overcame sieges of Krujë. In 1450, the Albanians routed Sultan Murad II himself. Later, they repulsed attacks led by Sultan Mehmed II in 1466 and 1467. In 1461, Skanderbeg went to the aid of his suzerain, King Alfonso I of Naples, against the kings of Sicily by practically defeating all his rivals in southern Italy. Albanians also defeated Venice in 1449 in 3 battles in Albanian–Venetian War.
Sometimes the government under Skanderbeg was unstable, however, and at times local Albanian rulers cooperated with the Ottomans against him.[8]
With political and minor material support from the Kingdom of Naples and the Vatican, resistance to the Ottoman Empire continued for 36 years.
Krujë fell to the Ottomans only in 1478, ten years after the death of Skanderbeg; Shkodër succumbed in 1479 after a failed siege in 1474 and a stronger siege in 1478 that ended with Venice ceding Shkodra to the Ottomans. The Venetians then evacuated Durrës, in 1501. The conquests triggered a great exodus of Albanian nobles to Venice and Italy, especially to the kingdom of Naples, as well as to Sicily, Romania and Egypt. Most of the Albanian refugees belonged to the Orthodox Church. The Albanians of Italy significantly influenced the Albanian national movement in future centuries, and Albanian Franciscan priests, most of whom were descended from émigrés to Italy, played a significant role in the preservation of Catholicism in Albania's northern regions.[8]
Skanderbeg's long struggle to keep Albania free became highly significant to the Albanian people, as it strengthened their solidarity, made them more conscious of their national identity, and served later as a great source of inspiration in their struggle for national unity, freedom, and national identity.[10] The memory of the mid-15th century resistance under Skanderbeg continues to be important to Albanians, and his family's banner, bearing a black two-headed eagle on a red field, became the flag under which the Albanian national movement rallied centuries later. 11 years after the death of Skenderbeg and the fall of Krujë, the Ottoman Empire gained control of the ethnic Albanian territories and made many political changes.
16th–17th centuries
The Albanian population gradually began to convert to Islam through the teachings of Bektashism, which offered considerable material advantages in Ottoman trade networks, bureaucracy and army. Many Albanians were recruited initially into the Janissary and Devşirme (in many cases sons of Albanian nobles) and later on through becoming Muslims they opened their path for very successful military and political carriers, persuading other Albanians to do so
Albanians would enter later on in the 15th and especially 16th and 17th centuries, a period of Islamization. Albanians through converting to Islam would eventually dominate the Ottoman power structures disporportinally to their small population considering the large territory and huge population of the Ottoman Empire. They would become one of the most important and prestigious nations in the Empire playing a stringing role since the 15th century, but especially in the 17th,18th and 19th centuries.
For example, 48 Grand Viziers were of Albanian origin who managed the Ottoman state approximately 190 years. Some of the most prominent Albanians during Ottoman rule were: George Kastrioti Skanderbeg, Ballaban Badera, Koca Davud Pasha, Hamza Kastrioti, Iljaz Hoxha, Pargalı Ibrahim Pasha, Mimar Sinan, Nezim Frakulla, Köprülü Mehmed Pasha, Ali Pasha, Edhem Pasha, Omer Vrioni, Patrona Halil, Haxhi Shehreti, Ali Pasha of Gucia, Ibrahim Pasha of Berat, Köprülü Fazıl Ahmed, Muhammad Ali of Egypt, Kara Mahmud Bushati, Kara Murad Pasha, Ahmet Kurt Pasha, Mustafa Bushati, Ibrahim Bushati, Sedefkar Mehmed Agha.
Albanians also played a crucial role during the Ottoman–Venetian War (1499–1503), Ottoman–Hungarian Wars and Ottoman–Habsburg wars before gaining Independence.
Ottoman Empire would be heavily dependent on Albanian Mercenaries in its warfare between the early 1600s to middle 1800s until the reforms of Tanzimat.
18th–19th centuries and the Albanian Pashaliks

The weakening of Ottoman central authority and the timar system brought anarchy to the Albanian-populated lands. In the 18th century, two Albanian centers of power emerged: Shkodër, under the Bushati family; and Ioannina, under Ali Pasha of Tepelenë. When it suited their goals, both places cooperated with the Sublime Porte, and when it was expedient to defy the central government, each acted independently.[11]
%253B_lithograph_by_George_de_la_Poer_Beresford.jpg.webp)
The Bushati family initially dominated the Shkodër region through a network of alliances with various highland tribes and later expanded in huge areas in today's Montenegro, Northern Albania, Kosovo, Macedonia, southern Serbia. Kara Mahmud Bushati attempted to establish a de juro independent principality and expand the lands under his control by playing off Austria and Russia against the Sublime Porte. In 1785, Kara Mahmud's forces attacked Montenegrin territory, and Austria offered to recognize him as the ruler of all Albania if he would ally himself with Vienna against the Sublime Porte. Seizing an opportunity, Kara Mahmud sent the sultan the heads of an Austrian delegation in 1788, and the Ottomans appointed him governor of Shkodër. When he attempted to wrest land from Montenegro in 1796, however, he was defeated and killed by an ambush in northern Montenegro. Kara Mahmud's brother, Ibrahim Bushati, cooperated with the Sublime Porte until his death in 1810, but his successor, Mustafa Pasha Bushati, proved to be recalcitrant despite participation in Ottoman military campaigns against Greek revolutionaries and rebel pashas. He cooperated with the mountain tribes and brought a large area in Balkans under his control like Kara Mahmud Bushati.[11] Visiting Albania and Ali Pasha in 1814, Charles Robert Cockerell admired Ali Pasha's governance, stating: "There is law — for everyone admits his impartiality as compared with that of rulers in other parts of Turkey — and there is commerce. He [Ali Pasha] has made roads, fortified the borders, put down brigandage, and raised Albania into a power of some importance in Europe."[12]
South of the Shkumbini River, the mostly peasant Tosks lived in compact villages under elected rulers. Some Tosks living in settlements high in the mountains maintained their independence and often escaped payment of taxes. The Tosks of the lowlands, however, were easy for the Ottoman authorities to control. The Albanian tribal system disappeared there, and the Ottomans imposed a system of military fiefs under which the sultan granted soldiers and cavalrymen temporary landholdings, or timars, in exchange for military service. By the 18th century, many military fiefs had effectively become the hereditary landholdings of economically and politically powerful families who squeezed wealth from their hard-strapped Christian and Muslim tenant farmers. The beys, like the clan chiefs of the northern mountains, became virtually independent rulers in their own provinces, had their own military contingents, and often waged war against each other to increase their landholdings and power. The Sublime Porte attempted to press a divide-and-rule policy to keep the local beys from uniting and posing a threat to Ottoman rule itself, but with little success.[13]
Ottoman-Albanian relations worsened in the year 1826 during the reign of Mahmud II, he had instigated the notorious Auspicious Incident and the turmoil that followed caused the violent dissolution of the Janissary, Devşirme and the entire Balkan Muslim leadership in Rumelia causing a new wave of revolts and instability in the gradually weakening Ottoman Empire.
After crushing the Bushatis and Ali Pasha, the Sublime Porte introduced a series of reforms, known as the tanzimat, which were aimed at strengthening the empire by reining in fractious pashas. The timars officially became large individual landholdings, especially in the lowlands. In 1835, the Sublime Porte divided the Albanian-populated lands into the vilayets of Janina and Rumelia and dispatched officials from Constantinople to administer them. This provoked a series of revolts in 1843–1844, but they were suppressed by the Ottoman army.
After 1865, the central authorities redivided the Albanian lands between the vilayets of Scutari, Janina, and Monastir. The reforms angered the highland Albanian chieftains, who found their privileges reduced with no apparent compensation, and the authorities eventually abandoned efforts to control them. Ottoman troops crushed local rebellions in the lowlands, however, and conditions there remained bleak. The religious division of the northern Albanian tribes brought them into opposition. The Muslim northern Albanian tribes participated in the Ottoman campaigns against Christian Albanian tribes, such as in 1876 when they devastated the territory populated by the Mirditë Catholics.[14] Large numbers of Tosks emigrated to join sizable Albanian émigré communities in Romania, Egypt, Bulgaria, Constantinople, southern Italy, and later the United States.[11]
20th century
.svg.png.webp)
In 1906 opposition groups in the Ottoman Empire emerged, one of which evolved into the Committee of Union and Progress, more commonly known as the Young Turks, which proposed restoring constitutional government in Constantinople, by revolution if necessary. In July 1908, a month after a Young Turk rebellion in Macedonia supported by an Albanian uprising in Kosovo and Vardar Macedonia escalated into widespread insurrection and mutiny within the imperial army, Sultan Abdül Hamid II agreed to demands by the Young Turks to restore constitutional rule. Many Albanians participated in the Young Turks uprising, hoping that it would gain their people autonomy within the empire. The Young Turks lifted the Ottoman ban on Albanian-language schools and on writing the Albanian language. As a consequence, Albanian intellectuals meeting in Manastir (present day town of Bitola) in 1908 chose the Latin alphabet as a standard script. The Young Turks, however, were set on maintaining the empire and not interested in making concessions to the myriad nationalist groups within its borders. After securing the abdication of Abdül Hamid II in April 1909, the new authorities levied taxes, outlawed guerrilla groups and nationalist societies, and attempted to extend Constantinople's control over the northern Albanian mountain men. In addition, the Young Turks legalized the bastinado, or beating with a stick, even for misdemeanors, banned carrying rifles, and denied the existence of an Albanian nationality. The new government also appealed for Islamic solidarity to break the Albanians' unity and used the Muslim clergy to try to impose the Arabic alphabet, while also banning the Albanian national flag.
The Albanians refused to submit to the Young Turks' campaign to "Ottomanize" them by force. New Albanian uprisings began in Kosovo and the northern mountains in early April 1910. Ottoman forces quashed these rebellions after three months, outlawed Albanian organizations, disarmed entire regions, and closed down schools and publications. Montenegro, preparing to grab Albanian-populated lands for itself, supported a 1911 uprising by the mountain tribes against the Young Turks regime that grew into a widespread revolt. Unable to control the Albanians by force, the Ottoman government granted concessions on schools, military recruitment, and taxation and sanctioned the use of the Latin script for the Albanian language. The government refused, however, to unite the four Albanian-inhabited vilayets into one, Albanian vilayet.
Governance
Administratively, the Ottomans divided the Albanian-inhabited lands among a number of districts, or vilayets. The Ottoman authorities did not stress conversion to Islam and the conversion was done initially by Albanian nobles in the end of the 14th century and beginning of 15th one and was gradually accepted by the mass.[13]
By 1479, the entire country, except for Durrës, Ulcinj and Bar, was under Ottoman suzerainty. Prominent viziers and pashas hailed from Albania, and were appointed to their posts long before the majority of Albanians professed Islam.
Administrative divisions

- For details of : State Organization
The Ottoman sultan considered himself God's agent on Earth, the leader of a religious—not a national—state whose purpose was to defend and propagate Islam. Non-Muslims paid extra taxes and held an inferior status, but they could retain their old religion and a large measure of local autonomy. By converting to Islam, individuals among the conquered could elevate themselves to the privileged stratum of society. In the early years of the empire, all Ottoman high officials were the sultan's bondsmen the children of Christian subjects chosen in childhood for their promise, converted to Islam, and educated to serve. Some were selected from prisoners of war, others sent as gifts, and still others obtained through devshirme, the tribute of children levied in the Ottoman Empire's Balkan lands. Many of the best fighters in the sultan's elite guard, the janissaries, were conscripted as young boys from Christian Albanian families, and high-ranking Ottoman officials often had Albanian bodyguards.[13]
Taxation
According to historian Zija Shkodra, Albania was developed as much as the rest of the Balkans . In the mountains north of the Shkumbini River, Geg herders maintained their self-governing society base on clans. An association of clans was called a bajrak.
Taxes on the northern tribes were difficult if not impossible for the Ottomans to collect because of the rough terrain and fierceness of the Albanian highlanders. Some mountain tribes succeeded in defending their independence through the centuries of Ottoman rule, engaging in intermittent guerrilla warfare with the Ottomans, who never deemed it worthwhile to subjugate them.
Until recent times, Geg clan chiefs, or bajraktars, exercised patriarchal powers, arranged marriages, mediated quarrels, and meted out punishments. The tribesmen of the northern Albanian mountains recognized no law but the Code of Lekë Dukagjini (Kanuni i Lekë Dukagjinit), a collection of tribal laws transcribed in the 14th century by a Roman Catholic priest. The code regulates a variety of subjects, including blood vengeance. Even today, many Albanian highlanders regard the canon as the supreme law of the land.[13]
Culture
Religion


Four centuries of Ottoman rule grouped the Albanian people along religious, regional, and tribal lines. In the 16th century and early 17th century, Albanians converted to Islam in large numbers. Within a century, the Muslim Albanian community was the largest religious community in the country, losing their previous entirely Orthodox and Catholic religious identity. Albanians in this time were divided into two distinct tribal and dialectal groupings: the Gegs and Tosks (see Albanian language). In the rugged northern mountains, Geg shepherds lived in a tribal society often completely independent of Ottoman rule. In the south, Muslim and Orthodox Tosks worked the land for Muslim beys, provincial rulers who frequently revolted against the sultan's authority.
In the 15th and especially 16th and 17th centuries, many Albanian converts to Islam migrated elsewhere to escape the Ottoman Empire. Some attained powerful positions in the Ottoman administration, which severely disadvantaged the Catholic community since conversion to Islam came with numerous upper-class affiliations. About 48 Albanians rose to the position of grand vizier, chief deputy to the sultan himself. In the second half of the 17th century, the Albanian Köprülü family provided 6 grand viziers, who fought against corruption, temporarily shored up eroding central government control over rapacious local beys, and won several military victories by max expanding the Ottoman states to the gates of Vienna and middle Ukraine..
As early as the 18th century, a mystic Islamic sect, the Bektashi dervishes, spread into the empire's Albanian-populated lands. Probably founded in the late 13th century in Anatolia, Bektashism became the janissaries' official faith in the late 16th century. The Bektashi sect contains features quite distinct from normative Islam and emphasizes man as a reflection of the Divine. Women, veiled, participate in Bektashi ceremonies and the celebrants use wine despite the ban on alcohol in most Islamic interpretations of the Sharia. The Bektashis became a fringe zealous religious group in southern Albania after the sultan disbanded the janissaries in 1826. Bektashi leaders played key roles in the Albanian nationalist movement of the late 19th century.
In the 19th century, the Ottoman sultans tried in vain to shore up their collapsing empire by introducing a series of reforms aimed at reining in recalcitrant local officials and dousing the fires of nationalism among its myriad peoples. The power of nationalism, however, proved too strong to counteract.
Nowadays, Albanians tend to not have strong affiliations to their varied religious identities as a result of about 50 years of Communist rule (especially under the regime of Enver Hoxha) that banned the practice of religion.
See also
References
- ↑ Anscombe 2006, p. 772: "The term 'Arnavud' was used to denote persons who spoke one of the dialects of Albanian, came from mountainous country in the western Balkans (referred to as 'Arnavudluk', and including not only the area now forming the state of Albania but also neighbouring parts of Greece, Macedonia, Kosovo, and Montenegro), organized society on the strength of blood ties (family, clan, tribe), engaged predominantly in a mix of settled agriculture and livestock herding, and were notable fighters – a group, in short, difficult to control."
- ↑ Kolovos 2007, p. 41: "Anscombe (ibid., 107 n. 3) notes that Ottoman "Albania" or Arnavudluk... included parts of present-day northern Greece, western Macedonia, southern Montenegro, Kosovo, and southern Serbia"; see also El2. s.v. "Arnawutluk. 6. History" (H. İnalcık) and Arsh, He Alvania. 31.33, 39-40. For the Byzantine period. see Psimouli, Souli. 28."
- ↑ "Albania - The World Factbook". Central Intelligence Agency.
- ↑ Gjon Marku 2017, p. 10.
- ↑ Gjon Marku 2017, p. 17.
- ↑ "Albania::The decline of Byzantium". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 16 November 2021.
- ↑ Dimitris J. Kastritsis, The Sons of Bayezid: Empire building and Representation in the Ottoman Civil War of 1402–1413, (BRILL, 2007), 1–3.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Raymond Zickel and Walter R. Iwaskiw (1994). "Albania: A Country Study ("The Ottoman Conquest of Albania")". Retrieved 9 April 2008.
- ↑ Riza, Emin (1992). "Ethnographic and open-air museums" (PDF). UNESCO, Paris. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ↑ "Albania | History, Geography, Customs, & Traditions". Encyclopædia Britannica.
- 1 2 3 Raymond Zickel and Walter R. Iwaskiw (1994). "Albania: A Country Study ("Local Albanian Leaders in the Early 19th Century")". Retrieved 9 April 2008.
- ↑ Dauti 2018, p. 37.
- 1 2 3 4 Raymond Zickel and Walter R. Iwaskiw (1994). "Albania: A Country Study ("Albanians under Ottoman Rule")". Retrieved 9 April 2008.
- ↑ Vickers, Miranda (1999). The Albanians: A Modern History. I.B.Tauris. p. 30. ISBN 978-1-86064-541-9.
- ↑ Elsie 2010, "Flag, Albanian", p. 140: "The eagle was a common heraldic symbol for many Albanian dynasties in the Late Middle Ages and came to be a symbol of the Albanians in general. It is also said to have been the flag of Skanderbeg.... As a symbol of modern Albania, the flag began to be seen during the years of the national awakening and was in common use during the uprisings of 1909-1912."
Bibliography
- Anscombe, Frederick (2006). "The Ottoman Empire in Recent International Politics - II: The Case of Kosovo" (PDF). The International History Review. 28 (4): 758–793. doi:10.1080/07075332.2006.9641103. JSTOR 40109813. S2CID 154724667. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 September 2019. Retrieved 15 October 2021.
- Dauti, Daut (30 January 2018). Britain, the Albanian Question and the Demise of the Ottoman Empire 1876-1914 (phd). University of Leeds.
- Elsie, Robert (2010). Historical Dictionary of Albania. Lanham, Maryland: Scarecrow Press (The Rowman & Littlefield Publishing Group Incorporated). ISBN 0-8108-6188-7.
- Kolovos, Elias (2007). The Ottoman Empire, the Balkans, the Greek lands: Toward a social and economic history: Studies in honor of John C. Alexander. Istanbul: Isis Press. ISBN 9789754283464.
- Gjon Marku, Ndue (2017). Mirdita House of Gjomarku Kanun. ISBN 978-1-5425-6510-3.
