Horsham Township | |
|---|---|
 Horsham Township municipal building | |
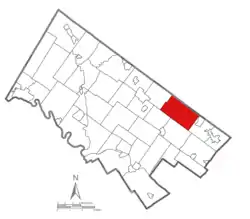 Location of Horsham Township in Montgomery County | |
 Horsham Township Location of Horsham Township in Pennsylvania  Horsham Township Horsham Township (the United States) | |
| Coordinates: 40°11′57″N 75°09′59″W / 40.19917°N 75.16639°W | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Pennsylvania |
| County | Montgomery |
| Settled | 1681 |
| Established | 1717 |
| Government | |
| • Type | Council-manager |
| Area | |
| • Total | 17.32 sq mi (44.9 km2) |
| • Land | 17.32 sq mi (44.9 km2) |
| • Water | 0.00 sq mi (0.0 km2) |
| Elevation | 262 ft (80 m) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 26,147 |
| • Estimate (2016)[3] | 26,645 |
| • Density | 1,500/sq mi (580/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC-5 (EST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-4 (EDT) |
| ZIP Codes | 18914, 19002, 19040, 19044, 19454 |
| Area codes | 215, 267, and 445 |
| FIPS code | 42-091-35808 |
| Website | www |
Horsham Township is a home rule municipality in Montgomery County, Pennsylvania. It is located ten miles north of Center City Philadelphia. The township, incorporated in 1717, is one of the oldest original municipalities in Montgomery County. Although it retains the word "Township" in its official name, it has been governed by a Home Rule Charter since 1975 and is therefore not subject to the Pennsylvania Township Code.[4] The population was 26,564 at the time of the 2020 census.
Horsham Township is made up of several community areas including Horsham (19044) and portions of the Hatboro (19040), Ambler (19002), Chalfont (18914) and North Wales (19454) ZIP codes.
History

Horsham Township is named after the town of Horsham in Sussex in the South of England. Horsham is one of several townships in Montgomery County whose name and size were determined by master survey lines drawn by William Penn's engineers as they first plotted this part of the colony for sale and settlement. Parallel lines, projected at intervals of a mile and a half and extending in a northwesterly direction from settlements along the Delaware, served not only as base lines for measurement of individual land grants but also as courses for future highways. County Line Road, Horsham Road, and Welsh Road are examples of highways so laid out. The effect of these survey lines upon the development pattern of Eastern Montgomery County is very much in evidence today.
In 1684, the entire township of 17 square miles (44 km2) was made available to individual purchasers. Samuel Carpenter, from the town of Horsham in Sussex, England, after which the township is named, purchased 5,000 acres (20 km2), 4,200 acres (17 km2) within the present boundaries of the township. In 1709, Carpenter, then Treasurer of Pennsylvania, began to sell tracts of land to migrating Quakers. In 1717, Horsham Township was established as a municipal entity by a vote of the people.
In 1718, Sir William Keith, then provincial governor of Pennsylvania, acquired 1,200 acres (4.9 km2) of Carpenter's land on which he erected a house in keeping with the dignity of his office. The development of Keith's "plantation" proved to be a step in establishing closer ties between Horsham and neighboring communities, particularly those of Hatboro and Willow Grove. He was responsible for the construction of the present Easton Road (PA Highway 611) from the old York Road junction at Willow Grove to his mansion on County Line Road in 1722.
The first significant settlement in the Township centered around the junction of Horsham and Easton Roads and was known as Horshamington. Keith's extension of Easton Road prompted the establishment of the Horsham Friends Meeting House.
The township's early social and economic life revolved around this Meeting House. In a similar way, Prospectville, originally known as Cashtown, was established at the junction of two roads, Limekiln Pike and Horsham Road. This portion of Limekiln Pike was an extension of the original segment established in 1693 to provide a thoroughfare between Old York Road and the limekilns of Thomas Fitzwater in Upper Dublin Township. Prospectville, on a high elevation point within the township, offering a resting spot with a tavern for those traveling along either Limekiln Pike or Horsham Road. Here lived several generations of the Simpson family, one of whom was the mother of Ulysses S. Grant, the 18th president of the United States.
The hamlet of Davis Grove grew at the intersection of Keith's Road (now called Governors Road) and Privet Road and was once a focal point of community life. It was here the residents of the township came to vote, discuss politics, and attend community meetings. The "Golden Ball Inn", which at one time was used to house guests of Governor Keith, enjoyed much Revolutionary splendor. The two roads were formerly through links. Keith's Road extended from Easton Road to Keith Valley Road and Privet Road, from Horsham Road to Easton Road. Expansion of the Willow Grove Naval Air Station caused the closing of these roads and the absorption of the hamlet. Today, there are virtually no remaining signs of the original settlement.
Through most of the early and the middle 19th century, Horsham's population grew slowly. Its character was not altered in any significant way until about 1872, when the North Pennsylvania Railroad extended a rail line from Glenside to New Hope and established a station in the nearby community of Hatboro, 2.75 miles (4.4 km) east of the nucleus of Horshamville. Horsham-Hatboro-Byberry Road provided easy access to Hatboro's station and, as a result, residential development began along the road, virtually linking the two communities together. By 1890, the township's population had reached 1,300.
In 1896, the Philadelphia Rapid Transit Company's northern extension of the Philadelphia-Willow Grove trolley service was extended to along Easton Road from the Willow Grove Amusement Park at Easton and Welsh Roads. This provided various connections to other trolley lines.
In 1926, aviation pioneer Harold F. Pitcairn, purchased a large section of farmland on the west side of Doylestown Pike (now Route 611) and constructed a hangar and a grass airstrip. From 1926 to 1942 Pitcairn used the airfield for numerous air shows and to design, construct and test a number of aircraft, including the Mailwing which was used by the United States Postal Service to carry the overnight mail between New York and Atlanta.
In 1942, the United States Navy purchased what eventually became the Naval Air Station Joint Reserve Base (NAS-JRB) Willow Grove which contributed to national defense for over six decades, beginning with a small group of Naval Aviators, maintenance personnel, and biplanes and evolving into a home for aircraft and personnel from every branch of the United States Armed Forces.
In 2005, NAS-JRB Willow Grove was selected for closure by BRAC 2005 law. In late 2006, the Horsham Township Authority for NAS-JRB Willow Grove (HLRA) was selected as the Local Redevelopment Authority (LRA), and was charged with preparing the required reuse planning documents. In 2011, NAS-JRB Willow Grove was officially closed, 68 years after the base and its hangars were built.
The Navy and Marine Corps squadrons/units moved to McGuire Air Force Base in 2011. The 111th Attack Wing of the Pennsylvania Air National Guard remains at their present site along with Army Reserve and Army National Guard units on the former U.S. Air Force Reserve Center facility. The United States Army Reserve, Pennsylvania Air National Guard, and Pennsylvania Army National Guard units are located on the approximately 200-acre base that is located near the intersection of County Line and Easton Roads. The name of the installation is Biddle Air National Guard Base.
On April 27, 2012, the Horsham Township Authority for NAS-JRB (HLRA) submitted the NAS-JRB Willow Grove Redevelopment Plan and Homeless Assistance Submission to the United States Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) and United States Navy. The plan includes many developments popular with area residents including small nature and conservation parks, an aviation museum, and town center; but also includes some highly unpopular developments such as a conference center and hotel on the site. Once the land is transferred, the surplus property will comprise about 8% of the Township's total land area. The NAS-JRB Willow Grove Redevelopment Plan details the existing conditions, issues and opportunities, and recommendations that will guide the Horsham Township Authority for NAS-JRB Willow Grove in the redevelopment process.
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the township has a total area of 17.3 square miles (45 km2), all land. One branch of the Pennypack Creek arises in Horsham. Horsham Township is bordered to the northwest by Montgomery Township; to the northeast by Warrington Township and Warminster Township in Bucks County; to the southwest by Lower Gwynedd Township and Upper Dublin Township and to the southeast by Upper Moreland Township.
The township has a hot-summer humid continental climate (Dfa) and average monthly temperatures in the vicinity of the junction of routes 463 and 611 range from 31.8 °F in January to 76.6 °F in July. [5] The hardiness zone is 7a.
Government and politics
| Year | Republican | Democratic |
|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 42.4% 7,066 | 56.6% 9,436 |
| 2016 | 43.6% 6,274 | 51.4% 7,389 |
| 2012 | 49.5% 6,598 | 49.4% 6,584 |
| 2008 | 45.8% 6,334 | 53.6% 7,409 |
| 2004 | 51.2% 6,733 | 48.3% 6,353 |
| 2000 | 51.5% 5,464 | 45.9% 4,868 |
| 1996 | 45.6% 3,878 | 41.2% 3,500 |
| 1992 | 43.0 % 4,102 | 33.8% 3,227 |
The Home Rule Charter of Horsham Township went into effect in January 1976. The Charter prescribed that there shall be five Council members, elected at large, for four-year terms. The legislative power of the Township is vested with Council. The Council discusses and adopts legislation at their regular monthly meetings.
The township manager runs the day-to-day operations of the township. There are eight departments of the manager's office: Administration, Finance, Public Works, Police, Fire Marshall/Emergency Management, Parks and Recreation, Code Enforcement, and Library. Fire protection is provided by the two fire stations of the Horsham Fire Company No. 1 a combination paid/volunteer fire department.
Demographics
| Census | Pop. | Note | %± |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1930 | 2,123 | — | |
| 1940 | 2,324 | 9.5% | |
| 1950 | 3,663 | 57.6% | |
| 1960 | 8,933 | 143.9% | |
| 1970 | 13,888 | 55.5% | |
| 1980 | 15,959 | 14.9% | |
| 1990 | 21,896 | 37.2% | |
| 2000 | 24,232 | 10.7% | |
| 2010 | 26,147 | 7.9% | |
| 2020 | 26,564 | 1.6% | |
| [7][8] | |||
As of the census[9] of 2020, there were 26,564 people and 9,469 households residing in the township. The population density was 1,533.5 inhabitants per square mile (592.1/km2). The racial makeup of the township was 83.0% White, 2.8% African American, 0.1% Native American, 8.6% Asian, 0.0% Pacific Islander, and 2.2% from two or more races. Hispanics or Latinos of any race were 8.7% of the population.
The age distribution was 4.5% under 5, 24.0% under 18, and 16.1% 65 and over.
The median income for a household in the township was $103,917. The per capita income for the township was $51,306. About 2.7% of the population was below the poverty line.
Business and industry

Horsham Township has a diverse and growing business community.
Major Employers located in Horsham
- Janssen Biotech, a Johnson & Johnson subsidiary
- Janssen Pharmaceuticals, a Johnson & Johnson subsidiary
- Benjamin Obdyke, a building materials manufacturer
- Toll Brothers, a home builder
- Bimbo Bakeries USA, corporate headquarters
- SofterWare, Inc., corporate headquarters
- Penn Mutual, corporate headquarters
- UPS, operates a Hub in Horsham
- Arris International, a supplier of telecommunications equipment
Education

The Hatboro-Horsham School District serves the township along with nearby Hatboro. There are four elementary schools (K–5), one middle school (6–8) and one high school (9–12) in the district.
The four elementary schools are Crooked Billet Elementary School, Blair Mill Elementary School, Simmons Elementary School, and Hallowell Elementary School, the middle school is Keith Valley Middle School, and the high school is Hatboro-Horsham Senior High School. All Hatboro-Horsham schools have received blue ribbon honors from both the Pennsylvania Department of Education and the United States Department of Education for demonstrating excellence in education.
Parks and recreation

Horsham Township Parks & Recreation has 815 acres of parkland including public parks, a community center and a trail system. The parks contain playground equipment, sand volleyball, tennis courts, picnic pavilions and fields for baseball, softball, soccer, lacrosse and football.
The Horsham Township Trail System is a bicycle and pedestrian network which provides ready access to parks, schools, library, neighborhoods, retail centers and business parks. The Power Line Trail runs across the township along a PECO Energy right-of-way.[10]
Horsham Township has four golf courses: Squires Golf Club, Commonwealth National Golf Club (an Arnold Palmer-designed course), Limekiln Golf Course, and Talamore Country Club.
Graeme Park is a 42-acre historic park located in Horsham Township, featuring the Keith House, the only surviving residence of a colonial Pennsylvania governor. The mansion has remained virtually intact since the late 18th century.
Infrastructure
Transportation
_just_north_of_Blair_Mill_Road_in_Horsham_Township%252C_Montgomery_County%252C_Pennsylvania.jpg.webp)
As of 2019 there were 116.49 miles (187.47 km) of public roads in Horsham Township, of which 23.70 miles (38.14 km) were maintained by the Pennsylvania Department of Transportation (PennDOT) and 92.79 miles (149.33 km) were maintained by the township.[11]
Numbered routes serving Horsham Township include Pennsylvania Route 63, which runs northwest–southeast along the southwestern border on Welsh Road; Pennsylvania Route 152, which runs north–south through the western part of the township on Limekiln Pike; Pennsylvania Route 309, which passes north–south through the far western corner of Horsham Township along Bethlehem Pike; Pennsylvania Route 463, which runs northwest–southeast through the center of the township along Horsham Road, and Pennsylvania Route 611, which heads north–south through the eastern part of Horsham Township along Easton Road. Other major roads in the township include Blair Mill Road, which runs southwest–northeast along the southeastern boundary of Horsham Township; Butler Pike, which runs southwest–northeast, beginning in the township at Limekiln Pike and heading southwest towards Ambler: County Line Road, which runs northwest–southeast along the northeastern border with Bucks County; Dresher Road/Meetinghouse Road, which runs southwest–northeast in the eastern section of Horsham Township; Lower State Road, which runs southwest–northeast along the northwestern boundary of the township; and Norristown Road, which begins at Horsham Road in the center of the township and heads west to Maple Glen. The Willow Grove Interchange of the Pennsylvania Turnpike is located to the south in neighboring Upper Moreland Township, connecting to Pennsylvania Route 611.[12]
SEPTA provides bus service within Horsham Township.[13] The Route 55 bus follows Pennsylvania Route 611 through the township and heads north to Doylestown and south to Willow Grove and Olney Transportation Center in North Philadelphia.[13][14] Three additional bus routes serve the business parks in the southern portion of Horsham Township.[13] The Route 80 bus runs a limited stop express route between Horsham and the Olney Transportation Center.[13][15] The Route 310 bus, known as the Horsham Breeze Red, and the Route 311 bus, known as the Horsham Breeze Blue, connect the Horsham business parks to the Willow Grove Park Mall and the Willow Grove station along SEPTA Regional Rail's Warminster Line.[13][16][17] Horsham Township operates the Horsham Office Parks Shuttle (h.o.p.s), which connects the Horsham business parks with the Fort Washington station along SEPTA Regional Rail's Lansdale/Doylestown Line during weekday rush hours.[18]
Utilities
Electricity and natural gas in Horsham Township is provided by PECO Energy Company, a subsidiary of Exelon.[19][20][21] Trash and recycling collection in the township is provided by private haulers including Arthur Moore, Republic Services, Waste Management, Advanced Disposal, Horizon Waste, and Whitetail Disposal, Inc.[22] Cable, telephone, and internet service to the area is provided by Xfinity and Verizon. Horsham Township is served by area codes 215, 267, and 445.[23]
The Horsham Water and Sewer Authority provides water and sewer service in the township. The water system in Horsham Township consists of 15 wells, five above-ground storage tanks, and 103 miles (166 km) of distribution lines, serving 7,042 customers.[24] In addition to water supplied from wells, the authority also purchases water from the North Wales Water Authority. Multiple groundwater wells in the township are contaminated with perfluorooctanesulfonic acid (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) from the former Naval Air Station Joint Reserve Base Willow Grove site, leading to the authority having to close wells to install treatment systems to decontaminate the water.[25] Portions of the township receive water from Aqua Pennsylvania, a subsidiary of Aqua America.[26] The sewer system operated by the Horsham Water and Sewer Authority consists of five drainage districts, three of which are in the Pennypack Creek watershed and two of which are in the Neshaminy Creek watershed. Wastewater from the two districts in the Neshaminy Creek watershed, serving the central and western portions of the township, is treated at the Park Creek Wastewater Treatment Plant operated by the authority. Wastewater from the three districts in the Pennypack Creek watershed, serving the southern and eastern portions of the township, is treated at a wastewater treatment plant operated by the Upper Moreland-Hatboro Joint Sewer Authority, which the authority has an agreement with.[27]
Money magazine citations
- In 2013 Money recognized Horsham as 34th Best Place to Live in America.
- In 2011 Money recognized Horsham at 31st Best Place to Live in America.
- In 2009 U.S. News & World Report recognized Horsham as one of the Best Places to Live in Pennsylvania.
- In 2007 Money recognized Horsham as 15th Best Place to Live in America.
References
- ↑ "2016 U.S. Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved Aug 14, 2017.
- ↑ "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 7, 2016.
- ↑ "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". Retrieved June 9, 2017.
- ↑ Pennsylvania Code Title 346, Sec. 33.1-101 et seq. Archived 2011-09-27 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ "PRISM Climate Group at Oregon State University". Prism.oregonstate.edu. Retrieved 2022-08-01.
- ↑ "Montgomery County Election Results". Montgomery County, Pennsylvania. Retrieved January 16, 2017.
- ↑ "DVRPC > Site Search". Archived from the original on 2019-04-09. Retrieved 2014-03-21.
- ↑ "Census 2020".
- ↑ "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
- ↑ "Powerline Trail (PA)". Rails-to-Trails Conservancy. Retrieved August 14, 2013.
- ↑ "Horsham Township map" (PDF). PennDOT. Retrieved March 10, 2023.
- ↑ Montgomery County, Pennsylvania Highway Map (PDF) (Map). PennDOT. 2015. Retrieved January 12, 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 5 SEPTA Official Transit & Street Map Suburban (PDF) (Map). SEPTA. Retrieved May 2, 2016.
- ↑ "Route 55 bus schedule" (PDF). SEPTA. Retrieved May 4, 2016.
- ↑ "Route 80 bus schedule" (PDF). SEPTA. Retrieved May 9, 2016.
- ↑ "Route 310 bus schedule" (PDF). SEPTA. Retrieved May 4, 2016.
- ↑ "Route 311 bus schedule" (PDF). SEPTA. Retrieved February 27, 2017.
- ↑ "Horsham Office Park Shuttle (H.O.P.S)". Horsham, Pennsylvania. Retrieved November 15, 2023.
- ↑ "PECO: Company Information". PECO Energy Company. Retrieved January 29, 2017.
- ↑ "Electric Service Tariff" (PDF). PECO Energy Company. July 17, 2017. p. 4. Retrieved October 10, 2017.
- ↑ "Gas Service Tariff" (PDF). PECO Energy Company. August 30, 2017. p. 2. Retrieved October 10, 2017.
- ↑ "Trash Collection & Recycling". Horsham Township. Retrieved February 22, 2018.
- ↑ Area Code 215 and 267 Map (PDF) (Map). Pennsylvania Public Utility Commission. Retrieved June 22, 2011.
- ↑ "Water Service". Horsham Water and Sewer Authority. 14 November 2016. Retrieved February 22, 2018.
- ↑ "Horsham Water Quality Update" (PDF). Horsham Water and Sewer Authority. February 14, 2018. Retrieved February 23, 2018.
- ↑ "Rates and Rules Governing the Distribution of Water" (PDF). Aqua Pennsylvania. March 11, 2013. p. 3. Retrieved October 11, 2017.
- ↑ "Sewer Service". Horsham Water and Sewer Authority. 14 November 2016. Retrieved February 22, 2018.
