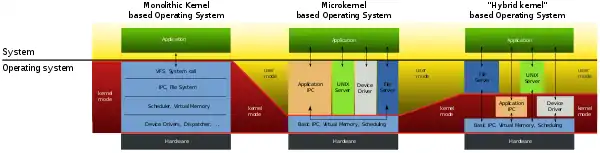
A hybrid kernel is an operating system kernel architecture that attempts to combine aspects and benefits of microkernel and monolithic kernel architectures used in operating systems.[1][2]
Overview
The traditional kernel categories are monolithic kernels and microkernels (with nanokernels and exokernels seen as more extreme versions of microkernels). The "hybrid" category is controversial, due to the similarity of hybrid kernels and ordinary monolithic kernels; the term has been dismissed by Linus Torvalds as simple marketing.[3]
The idea behind a hybrid kernel is to have a kernel structure similar to that of a microkernel, but to implement that structure in the manner of a monolithic kernel. In contrast to a microkernel, all (or nearly all) operating system services in a hybrid kernel are still in kernel space. There are none of the reliability benefits of having services in user space, as with a microkernel. However, just as with an ordinary monolithic kernel, there is none of the performance overhead for message passing and context switching between kernel and user mode that normally comes with a microkernel.
Examples
NT kernel
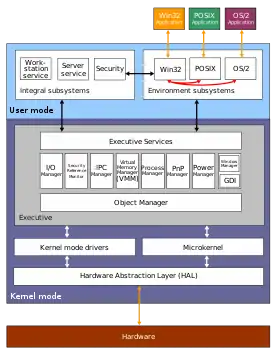
One prominent example of a hybrid kernel is the Microsoft Windows NT kernel that powers all operating systems in the Windows NT family, up to and including Windows 11 and Windows Server 2022, and powers Windows Phone 8, Windows Phone 8.1, and Xbox One.
Windows NT was the first Windows operating system based on a hybrid kernel. The hybrid kernel was designed as a modified microkernel, influenced by the Mach microkernel developed by Richard Rashid at Carnegie Mellon University, but without meeting all of the criteria of a pure microkernel. NT-based Windows is classified as a hybrid kernel (or a macrokernel[4]) rather than a monolithic kernel because the emulation subsystems run in user-mode server processes, rather than in kernel mode as on a monolithic kernel, and further because of the large number of design goals which resemble design goals of Mach (in particular the separation of OS personalities from a general kernel design). Conversely, the reason NT is not a microkernel system is because most of the system components run in the same address space as the kernel, as would be the case with a monolithic design (in a traditional monolithic design, there would not be a microkernel per se, but the kernel would implement broadly similar functionality to NT's microkernel and kernel-mode subsystems).
The primary operating system personality on Windows is the Windows API, which is always present. The emulation subsystem which implements the Windows personality is called the Client/Server Runtime Subsystem (csrss.exe). On versions of NT prior to 4.0, this subsystem process also contained the window manager, graphics device interface and graphics device drivers. For performance reasons, however, in version 4.0 and later, these modules (which are often implemented in user mode even on monolithic systems, especially those designed without internal graphics support) run as a kernel-mode subsystem.[4]
Applications that run on NT are written to one of the OS personalities (usually the Windows API), and not to the native NT API for which documentation is not publicly available (with the exception of routines used in device driver development). An OS personality is implemented via a set of user-mode DLLs (see Dynamic-link library), which are mapped into application processes' address spaces as required, together with an emulation subsystem server process (as described previously). Applications access system services by calling into the OS personality DLLs mapped into their address spaces, which in turn call into the NT run-time library (ntdll.dll), also mapped into the process address space. The NT run-time library services these requests by trapping into kernel mode to either call kernel-mode Executive routines or make Local Procedure Calls (LPCs) to the appropriate user-mode subsystem server processes, which in turn use the NT API to communicate with application processes, the kernel-mode subsystems and each other.[5]

XNU kernel
XNU is the kernel that Apple Inc. acquired and developed for use in the macOS, iOS, watchOS, and tvOS operating systems and released as free and open source software as part of the Darwin operating system. XNU is an acronym for X is Not Unix.[6]
Originally developed by NeXT for the NeXTSTEP operating system, XNU was a hybrid kernel combining version 2.5 of the Mach kernel with components from 4.3BSD and an object-oriented API for writing drivers called Driver Kit.
After Apple acquired NeXT, the Mach component was upgraded to OSFMK 7.3,[7] which is a microkernel.[8] Apple uses a heavily modified OSFMK 7.3 functioning as a hybrid kernel with parts of FreeBSD included.[7] (OSFMK 7.3 includes applicable code from the University of Utah Mach 4 kernel and applicable code from the many Mach 3.0 variants that forked off from the original Carnegie Mellon University Mach 3.0 kernel.) The BSD components were upgraded with code from the FreeBSD project and the Driver Kit was replaced with a C++ API for writing drivers called I/O Kit.
Description
Like some other modern kernels, XNU is a hybrid, containing features of both monolithic and microkernels, attempting to make the best use of both technologies, such as the message passing capability of microkernels enabling greater modularity and larger portions of the OS to benefit from protected memory, as well as retaining the speed of monolithic kernels for certain critical tasks.
Others
- BeOS
- Syllable
- BSD-based
- DragonFly BSD (first non-Mach BSD OS to use a hybrid kernel)
- NetWare[9]
- Plan 9 from Bell Labs
- OS/2[10]
- eComStation
- ArcaOS
- OS/4
- ReactOS
See also
Notes
- ↑ "Hybrid Kernel - OSDev Wiki". wiki.osdev.org. Retrieved 2021-01-11.
- ↑ "What is Hybrid Kernel? - Definition from Techopedia". Techopedia.com. 22 August 2011. Retrieved 2021-01-11.
- ↑ "Linus Torvalds".
As to the whole "hybrid kernel" thing - it's just marketing. It's "Oh, those microkernels had good PR, how can we try to get good PR for our working kernel? Oh, I know, let's use a cool name and try to imply that it has all the PR advantages that that other system has.
- 1 2 "MS Windows NT Kernel-mode User and GDI White Paper". Microsoft Corporation. 2007. Retrieved 2022-08-24.
- ↑ Probert, Dave (2005). "Overview of Windows Architecture". Using Projects Based on Internal NT APIs to Teach OS Principles. Microsoft Research/Asia - Beijing. Archived from the original on 2007-11-28. Retrieved 2007-03-01.
- ↑ "Porting UNIX/Linux Applications to OS X: Glossary". Apple Computer. 2005. Retrieved 2017-06-16.
- 1 2 Jim Magee. WWDC 2000 Session 106 - Mac OS X: Kernel. 14 minutes in.
- ↑ Douglas M. Wells (1994). A Trusted, Scalable, Real-Time Operating System Environment (PDF). 1994 IEEE Dual-Use Technologies and Applications Conference. S2CID 5205380. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-08-22.
- ↑ Drew Major; Greg Minshall; Kyle Powell. "An Overview of the NetWare Operating System".
- ↑ "OS/2 Kernel". Retrieved 2020-09-04.
References
- Mark Russinovich (November 23, 2004). "Inside the Native API". Sysinternals. Archived from the original on March 15, 2006. Retrieved July 24, 2006.