
X-ray scattering techniques are a family of non-destructive analytical techniques which reveal information about the crystal structure, chemical composition, and physical properties of materials and thin films. These techniques are based on observing the scattered intensity of an X-ray beam hitting a sample as a function of incident and scattered angle, polarization, and wavelength or energy.
Note that X-ray diffraction is now often considered a sub-set of X-ray scattering, where the scattering is elastic and the scattering object is crystalline, so that the resulting pattern contains sharp spots analyzed by X-ray crystallography (as in the Figure). However, both scattering and diffraction are related general phenomena and the distinction has not always existed. Thus Guinier's classic text[1] from 1963 is titled "X-ray diffraction in Crystals, Imperfect Crystals and Amorphous Bodies" so 'diffraction' was clearly not restricted to crystals at that time.
Scattering techniques
Elastic scattering
- X-ray diffraction or more specifically Wide-angle X-ray diffraction (WAXD)
- Small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) probes structure in the nanometer to micrometer range by measuring scattering intensity at scattering angles 2θ close to 0°.
- X-ray reflectivity is an analytical technique for determining thickness, roughness, and density of single layer and multilayer thin films.
- Wide-angle X-ray scattering (WAXS), a technique concentrating on scattering angles 2θ larger than 5°.
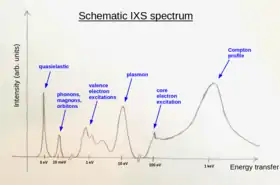
Inelastic X-ray scattering (IXS)
In IXS the energy and angle of inelastically scattered X-rays are monitored, giving the dynamic structure factor . From this many properties of materials can be obtained, the specific property depending on the scale of the energy transfer. The table below, listing techniques, is adapted from.[2] Inelastically scattered X-rays have intermediate phases and so in principle are not useful for X-ray crystallography. In practice X-rays with small energy transfers are included with the diffraction spots due to elastic scattering, and X-rays with large energy transfers contribute to the background noise in the diffraction pattern.
| Technique | Typical Incident Energy, keV | Energy transfer range, eV | Information on: |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compton scattering | 100 | 1,000 | Fermi Surface Shape |
| Resonant IXS (RIXS) | 4-20 | 0.1 - 50 | Electronic Structure & Excitations |
| Non-Resonant IXS (NRIXS) | 10 | 0.1 - 10 | Electronic Structure & Excitations |
| X-ray Raman scattering | 10 | 50 - 1000 | Absorption Edge Structure, Bonding, Valence |
| High resolution IXS | 10 | 0.001 - 0.1 | Atomic Dynamics,Phonon Dispersion |
See also
References
- ↑ Guinier, A. (1963). X-ray diffraction in Crystals, Imperfect Crystals and Amorphous Bodies. San Francisco: W.H. Freeman & Co.
- ↑ Baron, Alfred Q. R (2015). "Introduction to High-Resolution Inelastic X-Ray Scattering". arXiv:1504.01098 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci].