| Internal spermatic fascia | |
|---|---|
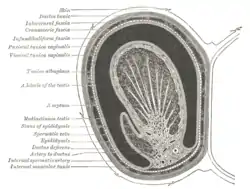 Transverse section through the left side of the scrotum and the left testis. The sac of the tunica vaginalis is represented in a distended condition. (Infundibuliform fascia labeled at left, fourth from top.) | |
 The scrotum. On the left side the cavity of the tunica vaginalis has been opened; on the right side only the layers superficial to the Cremaster have been removed. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | fascia spermatica interna |
| TA98 | A09.3.04.005 |
| TA2 | 3619 |
| FMA | 77299 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The internal spermatic fascia (infundibuliform fascia, or Le deuxième fascia de Webster) is a thin layer, which loosely invests the spermatic cord.
Structure
The internal spermatic fascia is derived from the transversalis fascia.[1][2] It is acquired by the spermatic cord at the deep inguinal ring.[1] It has very little lymphatic drainage.[3] It is mainly supplied by sensory afferents and the sympathetic nervous system.[3]
Additional images
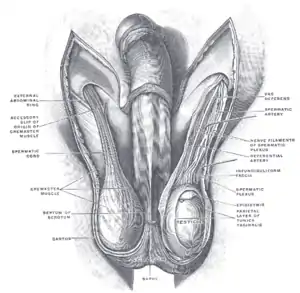 The scrotum.
The scrotum. Schematic drawing of a cross-section through the vaginal process.
Schematic drawing of a cross-section through the vaginal process.
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1239 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1239 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- 1 2 Jacob, S. (2008-01-01), Jacob, S. (ed.), "Chapter 4 - Abdomen", Human Anatomy, Churchill Livingstone, pp. 71–123, doi:10.1016/b978-0-443-10373-5.50007-5, ISBN 978-0-443-10373-5, retrieved 2021-02-05
- ↑ Paterson-Brown, Sara (2010-01-01), Bennett, Phillip; Williamson, Catherine (eds.), "Chapter Five - Applied anatomy", Basic Science in Obstetrics and Gynaecology (Fourth Edition), Churchill Livingstone, pp. 57–95, ISBN 978-0-443-10281-3, retrieved 2021-02-05
- 1 2 Oka, Shintaro; Shiraishi, Koji; Matsuyama, Hideyasu (1 June 2016). "Microsurgical Anatomy of the Spermatic Cord and Spermatic Fascia: Distribution of Lymphatics, and Sensory and Autonomic Nerves". The Journal of Urology. 195 (6): 1841–1847. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2015.11.041. ISSN 0022-5347. PMID 26626219.
External links
- Anatomy figure: 36:01-16 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "The inguinal canal and derivation of the layers of the spermatic cord."
- Anatomy image:7217 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- inguinalregion at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (spermaticcord)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.