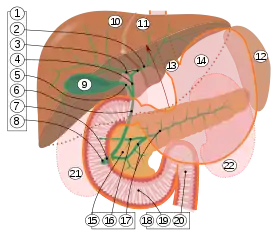
1. Bile ducts: 2. Intrahepatic bile ducts, 3. Left and right hepatic ducts, 4. Common hepatic duct, 5. Cystic duct, 6. Common bile duct, 7. Ampulla of Vater, 8. Major duodenal papilla
9. Gallbladder.
10–11. Right and left lobes of liver.
12. Spleen.
13. Esophagus.
14. Stomach.
15. Pancreas: 16. Accessory pancreatic duct, 17. Pancreatic duct.
18. Small intestine: 19. Duodenum, 20. Jejunum
21–22. Right and left kidneys.
The front border of the liver has been lifted up (brown arrow).[1]
9. Gallbladder.
10–11. Right and left lobes of liver.
12. Spleen.
13. Esophagus.
14. Stomach.
15. Pancreas: 16. Accessory pancreatic duct, 17. Pancreatic duct.
18. Small intestine: 19. Duodenum, 20. Jejunum
21–22. Right and left kidneys.
The front border of the liver has been lifted up (brown arrow).[1]
Intrahepatic bile ducts compose the outflow system of exocrine bile product from the liver.
They can be divided into:[2]
- Lobar ducts (right and left hepatic ducts) - stratified columnar epithelium.
- Interlobar ducts (between the main hepatic ducts and the interlobular ducts) - pseudostratified columnar epithelium.
- Interlobular bile ducts (between the interlobar ducts and the lobules) - simple columnar epithelium.
- Intralobular bile ducts (cholangioles or Canals of Hering) - simple cuboidal epithelium, then by hepatocytes
- Bile canaliculi - two half-canaliculi formed by the hepatocytes facing the perisinusoidal space
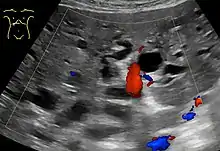
Abdominal ultrasonography (with Doppler) of dilated intrahepatic bile ducts, in this case because of pancreatic cancer. The bile ducts are colorless (black) in contrast to blood vessels (portal vein near center, and hepatic artery to the right of it) which have Doppler signal.
References
- ↑ Standring S, Borley NR, eds. (2008). Gray's anatomy : the anatomical basis of clinical practice. Brown JL, Moore LA (40th ed.). London: Churchill Livingstone. pp. 1163, 1177, 1185–6. ISBN 978-0-8089-2371-8.
- ↑ Roderick N. M. MacSween; Alastair D. Burt; Bernard Portmann; Linda D. Ferrell (2007). MacSween's pathology of the liver. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 518. ISBN 978-0-443-10012-3.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.