 | |
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Iodine trichloride | |
| Other names
Diiodine hexachloride | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.011.582 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| Properties | |
| I2Cl6 | |
| Molar mass | 466.5281 g/mol |
| Appearance | yellow solid |
| Density | 3.11 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 63 °C (145 °F; 336 K) |
| −90.2×10−6 cm3/mol | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
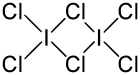
Iodine trichloride is an interhalogen compound of iodine and chlorine. It is bright yellow but upon time and exposure to light it turns red due to the presence of elemental iodine. In the solid state is present as a planar dimer I2Cl6, with two bridging Cl atoms.[1]
It can be prepared by reacting iodine with an excess of liquid chlorine at −70 °C. In the molten state it is conductive, which may indicate dissociation:[2]
- I2Cl6 ⇌ ICl+
2 + ICl−
4
Iodine trichloride can be created by heating a mixture of liquid iodine and chlorine gas to 105 °C.
It is an oxidizing agent, capable of causing fire on contact with organic materials.
References
- ↑ K. H. Boswijk; E. H. Wiebenga (1954). "The crystal structure of I2Cl6 (ICl3)". Acta Crystallographica. 7 (5): 417–423. doi:10.1107/S0365110X54001260.
- ↑ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.