 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Iridium dioxide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.031.572 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| IrO2 | |
| Molar mass | 224.22 g/mol |
| Appearance | blue-black solid |
| Density | 11.66 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 1,100 °C (2,010 °F; 1,370 K) decomposes |
| insoluble | |
| +224.0·10−6 cm3/mol | |
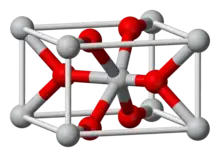
| Structure | |
| Rutile (tetragonal) | |
| Octahedral (Ir); Trigonal (O) | |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions |
iridium(IV) fluoride, iridium disulfide |
Other cations |
rhodium dioxide, osmium dioxide, platinum dioxide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Iridium(IV) oxide, IrO2, is the only well-characterised oxide of iridium. It is a blue-black solid. The compound adopts the TiO2 rutile structure, featuring six coordinate iridium and three coordinate oxygen.[1]
It is used with other rare oxides in the coating of anode-electrodes for industrial electrolysis and in microelectrodes for electrophysiology research.[2]
As described by its discoverers, it can be formed by treating the green form of iridium trichloride with oxygen at high temperatures:
- 2 IrCl3 + 2 O2 → 2 IrO2 + 3 Cl2
A hydrated form is also known.[3]
Application
Iridium dioxide can be used as an anode electrode for industrial electrolysis and as a microelectrode for electrophysiological studies.[4]
Iridium dioxide can be used to make coated electrodes.[5]
References
- ↑ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ↑ Cogan, Stuart F. (August 2008). "Neural Stimulation and Recording Electrodes". Annual Review of Biomedical Engineering. 10 (1): 275–309. doi:10.1146/annurev.bioeng.10.061807.160518. PMID 18429704.
- ↑ H. L. Grube (1963). "The Platinum Metals". In G. Brauer (ed.). Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry, 2nd Ed. NY: Academic Press. p. 1590.
- ↑ Cogan, Stuart F. (August 2008). "Neural Stimulation and Recording Electrodes". Annual Review of Biomedical Engineering. 10 (1): 275–309. doi:10.1146/annurev.bioeng.10.061807.160518. ISSN 1523-9829. PMID 18429704.
- ↑ "改性二氧化铱电极研制--《无机盐工业》1998年03期". www.cnki.com.cn. Retrieved 2021-05-21.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.