
The Isenheim Altarpiece is an altarpiece sculpted and painted by, respectively, the Germans Nikolaus of Haguenau and Matthias Grünewald in 1512–1516.[1] It is on display at the Unterlinden Museum at Colmar, Alsace, in France. It is Grünewald's largest work and is regarded as his masterpiece. It was painted for the Monastery of St. Anthony in Issenheim near Colmar, which specialized in hospital work. The Antonine monks of the monastery were noted for their care of plague sufferers as well as for their treatment of skin diseases, such as ergotism. The image of the crucified Christ is pitted with plague-type sores, showing patients that Jesus understood and shared their afflictions. The veracity of the work's depictions of medical conditions was unusual in the history of European art.[2]
Composition
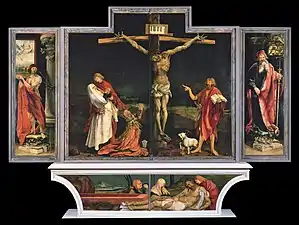

_-_WGA10758.jpg.webp)
(the wings in this picture are actually the back of those in the second one, so that they can be seen when the altar is closed, with the saints Anthony and Paul at the right side and the demons at the left)
The altarpiece has two sets of wings, displaying three configurations:
Wings closed:
With the exception of certain holy days, the wings of the altarpiece were kept closed, displaying The Crucifixion framed on the left by the martyrdom of Saint Sebastian pierced by arrows and on the right by Saint Anthony the Great, who remains placid even while being taunted by a frightening monster. The two saints protect and heal the sick, Saint Anthony as the patron saint of the victims of Saint Anthony's fire, and Saint Sebastian, whose aid was invoked to ward off the plague. Grünewald's Crucifixion stands as one of the most poignant representations of this scene in Western art, due to the artist's masterful depiction of horrific agony, with Christ's emaciated body writhing under the pain of the nails driven through his hands and feet. This body covered with sores and riddled with thorns must have terrified the sick, but it also left no doubt about Christ's suffering, thus comforting them in their communion with the Saviour, whose pain they shared. "Grünewald depicts Jesus' body ravaged by crucifixion yet evokes pointedly the Christian message of Jesus' horrible suffering; originally intended for a hospital, the altar painting may have been designed to provide comfort and solace to the sick."[3] Mary, the mother of Jesus, is shown at Christ's right, collapsing in anguish in the arms of John, the beloved disciple of Christ, and shrouded in a large piece of white cloth. Also at Christ's right is Mary Magdalene, kneeling with hands clasped in prayer.
At Christ's left, John the Baptist is accompanied by a lamb, symbolising the sacrifice of Jesus. The presence of John the Baptist is anachronistic. Beheaded by order of Herod in 29 AD, he could not possibly have witnessed the death of Christ. This last figure announces the New Testament by crying out in Latin, illum oportet crescere me autem minui (Vulgate, John 3:30), "He must increase, but I must decrease."[4] The inclusion of John the Baptist in this scene is symbolic, since he is considered as the last of the prophets to announce the coming of the Messiah.
Outer wings opened:
The outer wings of the Isenheim Altarpiece were opened for important festivals of the liturgical year, particularly those in honour of the Virgin Mary. Thus are revealed four scenes: the left wing represents the Annunciation during which the archangel Gabriel comes to announce to Mary that she will give birth to Jesus, the son of God. The Virgin Mary is depicted in a chapel to indicate the sacred character of the event. In the central corpus, the Concert of Angels and the Nativity are not independent scenes but instead fit within a unified concept: the viewer witnesses Christ's coming to earth as a newborn baby, who will be led to combat the forces of evil personified by certain of the angels, disturbing in their physical appearance.

A number of symbols provide keys to aid in interpretation: the enclosed garden represents Mary's womb and is a sign of her perpetual virginity, the rose bush without thorns refers to her as free of original sin, the fig tree symbolises mother's milk. The bed, the bucket and the chamber pot underscore the human nature of Christ. Lastly, the right wing shows the Resurrection, in which Christ emerges from the tomb and ascends into Heaven bathed in light transfiguring the countenance of the Crucified into the face of God. The Resurrection and the Ascension are therefore encapsulated in a single image.
Inner wings opened:
– The sculptures of Saint Augustine and Guy Guers, Saint Anthony, Two Bearers of Offerings, Saint Jerome, Christ and the Twelve Apostles are by Niclaus of Haguenau. With its inner wings open, the altarpiece allowed pilgrims and the afflicted to venerate Saint Anthony, protector and healer of Saint Anthony's fire. Saint Anthony occupies the place of honour at the centre of the corpus and at his side a pig is depicted, the emblem of the Antonite order. On his left and right, two bearers of offerings illustrate these contributions in kind, an important source of income for the Antonites. This central section is framed by Saint Augustine and Saint Jerome, two of the four great fathers of the Latin Church. Guy Guyers, who had commissioned the Altarpiece, is depicted kneeling at the feet of Saint Augustine.
– Visit of Saint Anthony to Saint Paul the Hermit. The two hermits meet in a stunning landscape, intended to represent the Theban Desert. Grünewald created a fantastic universe, surrounding the date palm with a strange mixture of vegetation, in marked contrast with the calmness and tranquillity of the encounter, in which the animals in attendance take part, with the crow bringing two morsels of bread to the two recluses. In this dreamlike scene, medicinal plants, painted in naturalistic fashion, sprout at the feet of the two main figures.
– Saint Anthony Tormented by Demons. This panel depicts Saint Anthony being tormented by monstrous creatures sent by Satan. Trampled to the ground, beaten with sticks, torn by claws and bitten, Saint Anthony appeals to God for help who sends angels to combat these evil demons. In the lower left corner, the being with webbed feet and a distended belly seems to personify the disease caused by ergot poisoning, resulting in swelling and ulcerous growths.
Iconography
The iconography of the altarpiece has several unusual elements derived from closely following the accounts left by Saint Bridget of Sweden of her mystical visions. These had long had a significant influence on art, especially on depictions of the Nativity of Christ, a scene not included here.
Recent history
The altarpiece's location in Alsace has meant that, in recent times, control of the work has alternated between Germany and France according to the fortunes of war.[5] Following the Franco-Prussian war of 1870-71 and the passing of control to Germany, German writers developed the concept that the altarpiece somehow represented the essential character of the German nation. The work subsequently became an object of extraordinary scenes of veneration in Munich during its temporary relocation there during the First World War, and again when Alsace passed back into French hands at the end of the War.[5]
In the immediate postwar period the altarpiece, with its strong overtones of violent sensation and emotion, became a natural source of inspiration for many painters in the influential Expressionist school, such as George Grosz and Otto Dix.[6][7] It also provided the basis for Paul Hindemith's modernist opera Mathis der Maler. In the later 1930s, it appears to have suffered a temporary decline in official esteem in Germany as a result of the National Socialists’ branding of both Expressionism and of Hindemith's work as "degenerate".[8]
Due to renovation work in the former convent and until April 2015, the Isenheim Altarpiece was on view in the local Dominican Church, located about 200 metres from the Unterlinden Museum. This temporary transfer offered an exceptional and unprecedented opportunity to present, alongside Grünewald and Haguenau's monumental masterwork, all three painted works by the Colmar native Martin Schongauer held in Colmar: the Orlier Altarpiece (1470–1475), the Altarpiece of the Dominicans (c. 1480) and the Virgin of the Rose Bush (1473). The altarpiece depicting Saint Catherine and Saint Lawrence (c. 1510) and sculptures from the Late Middle Ages rounded out the presentation.[9]
Recent restoration
In mid-2022, the altarpiece was re-shown at the Unterlinden Museum after it underwent cleaning and restoration by a team of restorers led by Anthony Pontabry. Haguenau's sculptures were restored in the polychrome wood restoration workshop in Paris of the Center for Research and Restoration of Museums of France by a team of sculpture restorers led by Juliette Levy. A study had been conducted by the Research Centre of the Musées de France in 2014 when they determined the state of the altarpiece and established the protocol for its restoration.[10]
Gallery

 Isenheim Altarpiece: The Resurrection
Isenheim Altarpiece: The Resurrection
References
- ↑ "The Isenheim altarpiece". Musée Unterlinden. Archived from the original on 27 July 2015. Retrieved 4 November 2015.
- ↑ Cabello, Felipe (2018). "El retablo de Isenheim: religión, arte y medicina". Revista Médica de Chile. 146 (9): 1050–1058. doi:10.4067/s0034-98872018000901050. ISSN 0034-9887. PMID 30725027.
- ↑ Hillerbrand, Hans J.; Stefon, Matt (August 26, 2016). "Christology. Jesus in the visual arts. Painting and sculpture. The Middle Ages through the 19th century". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved February 25, 2018.
- ↑ John 3:30
- 1 2 Stieglitz, Ann (1989). "The Reproduction of Agony: Toward a Reception-History of Grünewald's Isenheim Altar after the First World War". Oxford Art Journal. Oxford University Press. 12 (2): 87–103. doi:10.1093/oxartj/12.2.87. JSTOR 1360358.
- ↑ Flavell, M. Kay (1988). George Grosz. A Biography. New Haven: Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-04145-3.
- ↑ McCouat, Philip. "The Isenheim Altarpiece Pt 2: Nationalism, Nazism and Degeneracy".
- ↑ Stephanie Barron, "1937: Modern Art and Politics in Prewar Germany", in Degenerate Art: The Fate of the Avant-Garde in Nazi Germany, Harry A Abrams/Los Angeles County Museum of Art, New York, 1991
- ↑ "Musée Unterlinden | the Isenheim altarpiece". Archived from the original on 2014-11-10. Retrieved 2012-09-26.
- ↑ Restoration of the Isenheim Altarpiece, Whitehot Magazine of Contemporary Art, July 2022. Retrieved 15 July 2023
Further reading
- Bryda, Gregory (June 2018). "The Exuding Wood of the Cross at Isenheim." The Art Bulletin 100.2: 6–36. DOI https://doi.org/10.1080/00043079.2018.1393323
- Snyder, James (1985). Northern Renaissance Art. Painting, Sculpture, and the Graphic Arts from 1350 to 1575. New York City: Abrams. ISBN 0-8109-1081-0.
- Ruck, Carl A.P.; Staples, Blaise Daniel; Heinrich, Clark (2001). The Apples of Apollo, Pagan and Christian Mysteries of the Eucharist. Durham, N.C: Carolina Academic Press. ISBN 0-89089-924-X.
- Hayum, Andrée (December 1977). "The Meaning and Function of the Isenheim Altarpiece: The Hospital Context Revisited". The Art Bulletin. Routledge. 59 (4): 501–517. doi:10.1080/00043079.1977.10787476. JSTOR 3049705.
External links
- Article in the Smithsonian Magazine
- Two appreciations by Joris Carl Huysmans
- "Encounter with Grunewald," in Currents in Theology and Mission, Feb, 2004, by Roy A. Harrisville – Useful summary of the history of the reception of the painting