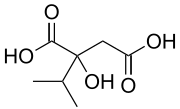
 2-Isopropylmalic acid | |
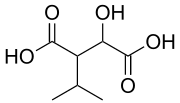 3-Isopropylmalic acid | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC names
3-Isopropylmalic acid 2-Hydroxy-3-isopropylsuccinic acid | |
| Other names
Isopropylmalate | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.159.209 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H12O5 | |
| Molar mass | 176.168 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 | |
| Warning | |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Isopropylmalic acid (isopropylmalate) is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of leucine,[1] synthesized from oxoisovalerate by 2-isopropylmalate synthase and converted into isopropyl-3-oxosuccinate by 3-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase. Two isomers are important, the 2- and 3-isopropyl derivatives, and these are interconverted by isopropylmalate dehydratase.
References
- ↑ Strassman, Murray; Ceci, Louis N. (1963). "Enzymatic Formation of α-Isopropylmalic Acid, an Intermediate in Leucine Biosynthesis". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 238 (7): 2445–2452. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)67991-3. PMID 13978769.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.