Jean-Baptiste Donatien de Vimeur de Rochambeau | |
|---|---|
 Portrait by Charles Wilson Peale, 1782 | |
| Born | 1 July 1725 Vendôme, Orléanais, France |
| Died | 30 May 1807 (aged 81) Thoré, Loir-et-Cher, France |
| Allegiance | Kingdom of France |
| Service/ | French Army |
| Years of service | 1742–1792 |
| Rank | Marshal of France |
| Battles/wars | War of the Austrian Succession |
| Awards | Society of the Cincinnati |
| Signature | |
Marshal Jean-Baptiste Donatien de Vimeur, comte de Rochambeau (1 July 1725 – 10 May 1807) was a French nobleman and general whose army played a critical role in helping the United States defeat the British Army at Yorktown in 1781 during the American Revolutionary War. He was commander-in-chief of the French expeditionary force sent by France to help the American Continental Army fight against British forces.
Military life
Jean-Baptiste Donatien de Vimeur was born in Vendôme, in the province of Orléanais, and he was educated at the Jesuit college in Blois. After the death of his elder brother, he entered a cavalry regiment and served in Bohemia, Bavaria, and on the Rhine during the War of the Austrian Succession. By 1747, he had attained the rank of colonel. He took part in the siege of Maastricht and became governor of Vendôme in 1749. He distinguished himself in the Battle of Minorca on the Seven Years' War outbreak and was promoted to Brigadier General of infantry. In 1758, he fought in Germany, notably in the Battle of Krefeld and the Battle of Clostercamp, receiving several wounds at Clostercamp.[1]
American Revolution

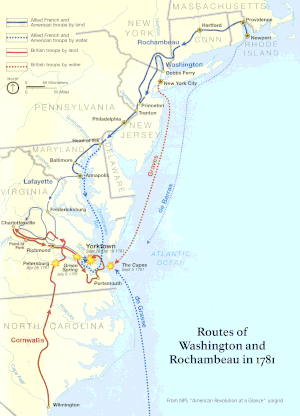
In 1780, Rochambeau was appointed commander of land forces as part of the project code-named Expédition Particulière.[2] He was given the rank of Lieutenant General in command of 7,000 French troops and sent to join the Continental Army under George Washington during the American Revolutionary War. Axel von Fersen the Younger served as his aide-de-camp and interpreter. The small size of the force at his disposal made him initially reluctant to lead the expedition.[3]

He landed at Newport, Rhode Island on 10 July but was held there inactive for a year due to his reluctance to abandon the French fleet blockaded by the British in Narragansett Bay.[1] The College in the Colony of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations (now Brown University) served as an encampment site for some of Rochambeau's troops. The College Edifice was converted into a military hospital, now known as University Hall.[4] In July 1781, the force left Rhode Island and marched across Connecticut to join Washington on the Hudson River in Mount Kisco, New York. The Odell farm served as Rochambeau's headquarters from 6 July to 18 August 1781.[5]
Washington and Rochambeau then marched their combined forces to the siege of Yorktown and the Battle of the Chesapeake. On 22 September, they combined with the Marquis de Lafayette's troops and forced Cornwallis to surrender on 19 October. The Congress of the Confederation presented Rochambeau with two cannons taken from the British in recognition of his service. He returned them to Vendôme, and they were requisitioned in 1792.
Return to France
Upon his return to France, Rochambeau was honored by King Louis XVI and was made governor of the province of Picardy.[1] He supported the French Revolution of 1789, and on 28 December 1791 he and Nicolas Luckner became the last two generals created Marshal of France by Louis XVI.
When the French Revolutionary Wars broke out, he commanded the Armée du Nord for a time in 1792 but resigned after several reversals to the Austrians. He was arrested during the Reign of Terror in 1793–94 and narrowly escaped the guillotine. He was subsequently pensioned by Napoleon.
Death
Rochambeau died at Thoré-la-Rochette during the First Empire.[1]
Legacy
Honors

President Theodore Roosevelt unveiled a statue of Rochambeau by Ferdinand Hamar as a gift from France to the United States on 24 May 1902, standing in Lafayette Square, Washington, D.C. The ceremony was made the occasion of a great demonstration of friendship between the two nations. France was represented by ambassador Jules Cambon, Admiral Fournier, General Henri Brugère, and a detachment of sailors and marines from the battleship Gaulois. Representatives of the Lafayette and Rochambeau families also attended. A Rochambeau fête was held simultaneously in Paris.[1] In 1934, A. Kingsley Macomber donated a statue of General Rochambeau to Newport, Rhode Island. The sculpture is a replica of a statue in Paris.[6]
The French Navy gave his name to the ironclad frigate Rochambeau. USS Rochambeau was a transport ship that saw service in the United States Navy during World War II. President Obama signed the Omnibus Public Land Management Act on 30 March 2009 with a provision to designate the Washington-Rochambeau Revolutionary Route as a National Historic Trail. A bridge was named for Rochambeau in the complex of bridges known as the 14th Street Bridge (Potomac River) connecting Washington, D.C., with Virginia. A mansion on the campus of Brown University is named Rochambeau House and houses the French Department.
Memoirs

Rochambeau's Mémoires militaires, historiques et politiques, de Rochambeau was published by Jean-Charles-Julien Luce de Lancival in 1809. Part of the first volume was translated into English and published in 1838 under the title Memoirs of the Marshal Count de R. relative to the War of Independence in the United States. His correspondence during the American campaign was published in 1892 in H. Doniol's History of French Participation in the Establishment of the United States.[7][1]
Monuments

- There is a statue of Rochambeau in Newport, Rhode Island, and another in Washington, D.C., on Pennsylvania Avenue across from the White House in Lafayette Park that was sculpted by Fernand Hamar and cast by the Pal d'Osne foundry in France and dedicated 24 May 1904
- There is a Rochambeau monument at French Hill in Marion, Connecticut, close to the Asa Barnes Tavern, the eighth campsite of his troops through Connecticut in 1781.
Motto and coat of arms
| Coat of arms | Motto |
.svg.png.webp) |
|
Notes
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 One or more of the preceding sentences incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Rochambeau, Jean Baptiste Donatien de Vimeur". Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 23 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 425–426.
- ↑ Kennett, Lee (1977). The French Forces in America, 1780–1783. Greenwood Press, Inc. Page 10
- ↑ Herbermann, Charles, ed. (1913). . Catholic Encyclopedia. New York: Robert Appleton Company.
- ↑ "05-137 (March to Yorktown)".
- ↑ Lenore M. Rennenkampf (February 1973). "National Register of Historic Places Registration:Odell House". New York State Office of Parks, Recreation and Historic Preservation. Retrieved 24 December 2010.
- ↑ "Rochambeau, (sculpture)". Smithsonian.
- ↑ Doniol, H. Histoire de la participation de la France en l'établissement des Etats Unis d'Amérique, Vol. V. [publisher unknown] Paris: 1892
- ↑ Johannes Baptist Rietstap, Armorial général : contenant la description des armoiries des familles nobles et patriciennes de l'Europe : précédé d'un dictionnaire des termes du blason, G.B. van Goor, 1861, 1171 p
References
- "Jean Baptiste Donatien De Vimeur Rochambeau." in Dictionary of American Biography (1936). online
- Kennett, Lee. The French Forces in America, 1780–1783 (Greenwood, 1977),
- Nager, Cody E. "The Fading Mirage Of Revolution: The French Expeditionary Force's Disillusionment With America, 1780–1782." The Historian 81#3 (2019), p. 426+. online
- Whitridge, Arnold. "Rochambeau And The American Revolution" History Today (May 1962), Vol. 12 Issue 5, pp 312–320.
- Tugdual de Langlais, L'armateur préféré de Beaumarchais Jean Peltier Dudoyer, de Nantes à l'Isle de France, Éd. Coiffard, 2015, 340 p. (ISBN 9782919339280).
- Jean-Baptiste-Donatien de Vimeur, comte de Rochambeau, Memoirs of the Marshal Count de Rochambeau, Relative to the War of Independence of the United States, ed. and trans, by M. W. E. Wright (New York: The New York Times and Arno Press, 1971),
External links
| Library resources about Rochambeau |
