Karditsa
Περιφερειακή ενότητα Καρδίτσας | |
|---|---|
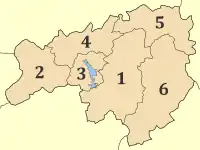 Municipalities of Karditsa | |
 Karditsa within Greece | |
| Coordinates: 39°20′N 22°00′E / 39.333°N 22.000°E | |
| Country | Greece |
| Region | Thessaly |
| Capital | Karditsa |
| Area | |
| • Total | 2,636 km2 (1,018 sq mi) |
| Population (2011) | |
| • Total | 113,544 |
| • Density | 43/km2 (110/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+3 (EEST) |
| Postal codes | 43x xx |
| Area codes | 244x0 |
| ISO 3166 code | GR-41 |
| Car plates | ΚΑ |
| Website | dimoskarditsas |
Karditsa (Greek: Περιφερειακή ενότητα Καρδίτσας, [karˈðit͡sa]) is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the region of Thessaly. Its name is derived from its capital Karditsa, a town of approximately 56,700 people.
Administration
The regional unit Karditsa is subdivided into 6 municipalities. These are (number as in the map in the infobox):[1]
Prefecture
Karditsa was created as a prefecture (Greek: Νομός Καρδίτσας) in 1899, and again in 1947. As a part of the 2011 Kallikratis government reform, the regional unit Karditsa was created out of the former prefecture Karditsa. The prefecture had the same territory as the present regional unit. At the same time, the municipalities were reorganised, according to the table below.[1]
| New municipality | Old municipalities | Seat |
|---|---|---|
| Argithea | Argithea | Anthiro |
| Anatoliki Argithea | ||
| Acheloos | ||
| Karditsa | Karditsa | Karditsa |
| Itamos | ||
| Kallifoni | ||
| Kampos | ||
| Mitropoli | ||
| Lake Plastiras (Limni Plastiras) | Plastiras | Morfovouni |
| Nevropoli Agrafon | ||
| Mouzaki | Mouzaki | Mouzaki |
| Ithomi | ||
| Pamisos | ||
| Palamas | Palamas | Palamas |
| Sellana | ||
| Fyllo | ||
| Sofades | Sofades | Sofades |
| Arni | ||
| Menelaida | ||
| Rentina | ||
| Tamasio |
History
Encompassing the ancient geographical region of Thessaliotis, one of the four ancient districts of Thessaly, the present day Karditsa regional unit was in the Kingdom of Macedonia and later the Roman Empire, the Byzantine Empire, the Ottoman Empire from the 15th century until 1881 and finally Greece after the liberation of Thessaly. Its economy and agriculture boomed during that period; Karditsa was administered as the Trikala–Karditsa prefecture until 1947. It was affected by World War II and the Greek Civil War which saw many buildings destroyed and inhabitants left homeless and in hiding. The prefecture was later rebuilt and received electricity, appliances and motorised transport, while emigration also began in the 1950s, when construction of Lake Plastiras was added. Television arrived in the 1970s and the 1980s for its villages, and its economy later declined, seeing high unemployment in the prefecture.
Population
The population was 121,775 in 2001.
The plains of central and southern Karditsa are inhabited by the Karagounides (Greek: Καραγκούνηδες), while the Agrafa mountains in the west of the prefecture are dominated by a strong Sarakatsani (Greek: Σαρακατσάνοι) and Aromanian, or Vlach (Greek: Βλάχοι - Vlahi), element.
Culture and education
The Public Market of Karditsa is one of UNESCO's protected cultural monuments.
The city is also an important knowledge centre, supporting the Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, the Public and Community Health, Forestry and Wood Sciences, and Science of Foods and Nutrition, departments of the University of Thessaly. There is also a Police Academy.
Sporting teams
- Anagennisi Karditsa (football) - Karditsa (city) - fourth division
- A.O. Karditsa - Karditsa - local division
- Iraklis Sofades - Sofades
- Tavropos - Karditsa - fourth division
Notable residents
Archbishops:
- Damaskinos of Athens
- Seraphim of Athens Archbishop of Athens and all Greece
Athletes:
- Ioannis Bourousis
- Ekaterini Koffa
- Labros Papakostas
- Dimosthenis Tampakos
- Konstantinos Thanos
- Dimitrios Tsiamis
Military:
Politicians:
Singers:
Others:
- George Mitsikostas - Comedian
- Vassilis Papazachos - Seismologist
Transport
There are a number of highways E75 and the main railway from Volos to Meteora crosses Thessaly. The region is directly linked to the rest of Europe through International Airport of Central Greece located in Nea Anchialos in a small distance from Karditsa.
See also
References
- 1 2 "ΦΕΚ A 87/2010, Kallikratis reform law text" (in Greek). Government Gazette.
External links
- Karditsa (regional unit) at Curlie (in English)
- Municipality of Karditsa (in Greek)
- http://www.karditsa-net.gr/ (in Greek)
- Karditsa Wireless Metropolitan Network, Karditsas Wifi Community Network (in Greek)
- http://www.e-karditsa.gr/ (in Greek)
