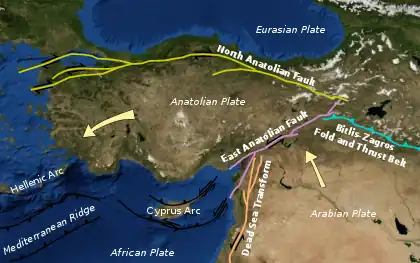
The Karlıova Triple Junction is a geologic triple junction of three tectonic plates: the Anatolian Plate, the Eurasian Plate and the Arabian Plate.
Location
The Karlıova Triple Junction is found where the east–west trending North Anatolian Fault intersects the East Anatolian Fault coming up from the southwest, and is ~700 km distant from the Maras Triple Junction. Because each arm of the junction is a transform fault (F), the Karlıova Triple Junction is an F-F-F type junction.
Geometry
The Karliova triple junction is a geological intersection point located in eastern Turkey, where the boundaries of the Arabian Plate, the Eurasian Plate, and the African Plate meet. It is a complex structure with multiple faults and fractures, resulting from the collision and convergence of these tectonic plates.
The geometry of the Karliova triple junction is characterized by three intersecting arms, each representing the boundary of one of the plates. The arms meet at an angle of approximately 120 degrees, forming a Y-shaped configuration. The Arabian Plate boundary extends to the southeast, the African Plate boundary extends to the southwest, and the Eurasian Plate boundary extends to the north.[1][2]
References
- ↑ Bird, Peter. "Bird, P. (2003). An updated digital model of plate boundaries". AGU.org. AGU Publications. Retrieved 26 October 2023.
- ↑ Karaoğlu, Özgür; Sağlam Selçuk, Azad; Gudmundsson, Agust. "Tectonic controls on the Karlıova triple junction (Turkey): Implications for tectonic inversion and the initiation of volcanism". Science Direct. Science Direct. Retrieved 26 October 2023.
- "New constraints on the Karliova Triple Junction between Arabia, Eurasia and Anatolia", A. Hubert-Ferrari, Geophysical Research Abstracts, Vol. 9, 06822, 2007.
- MAY 1, 2003 BİNGÖL (TURKEY) EARTHQUAKE, Preliminary Report (Updated on May 13, 2003)